Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
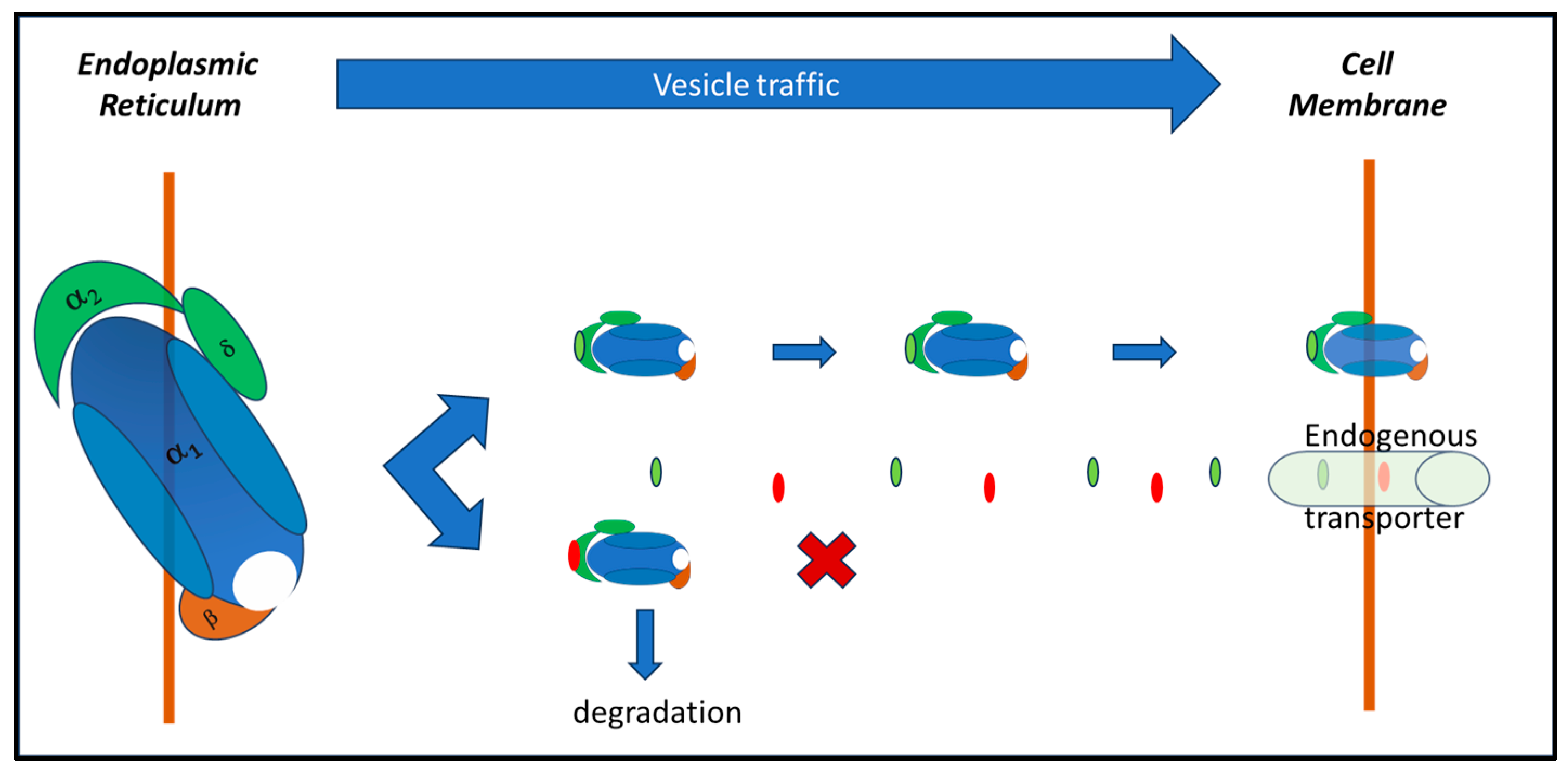
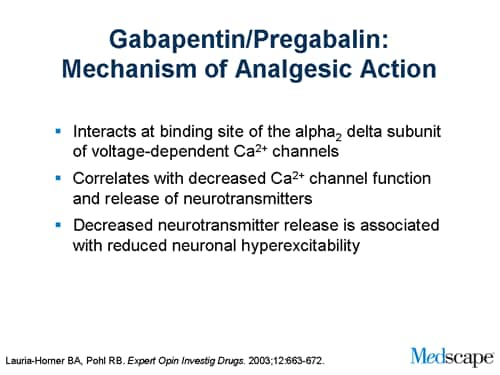
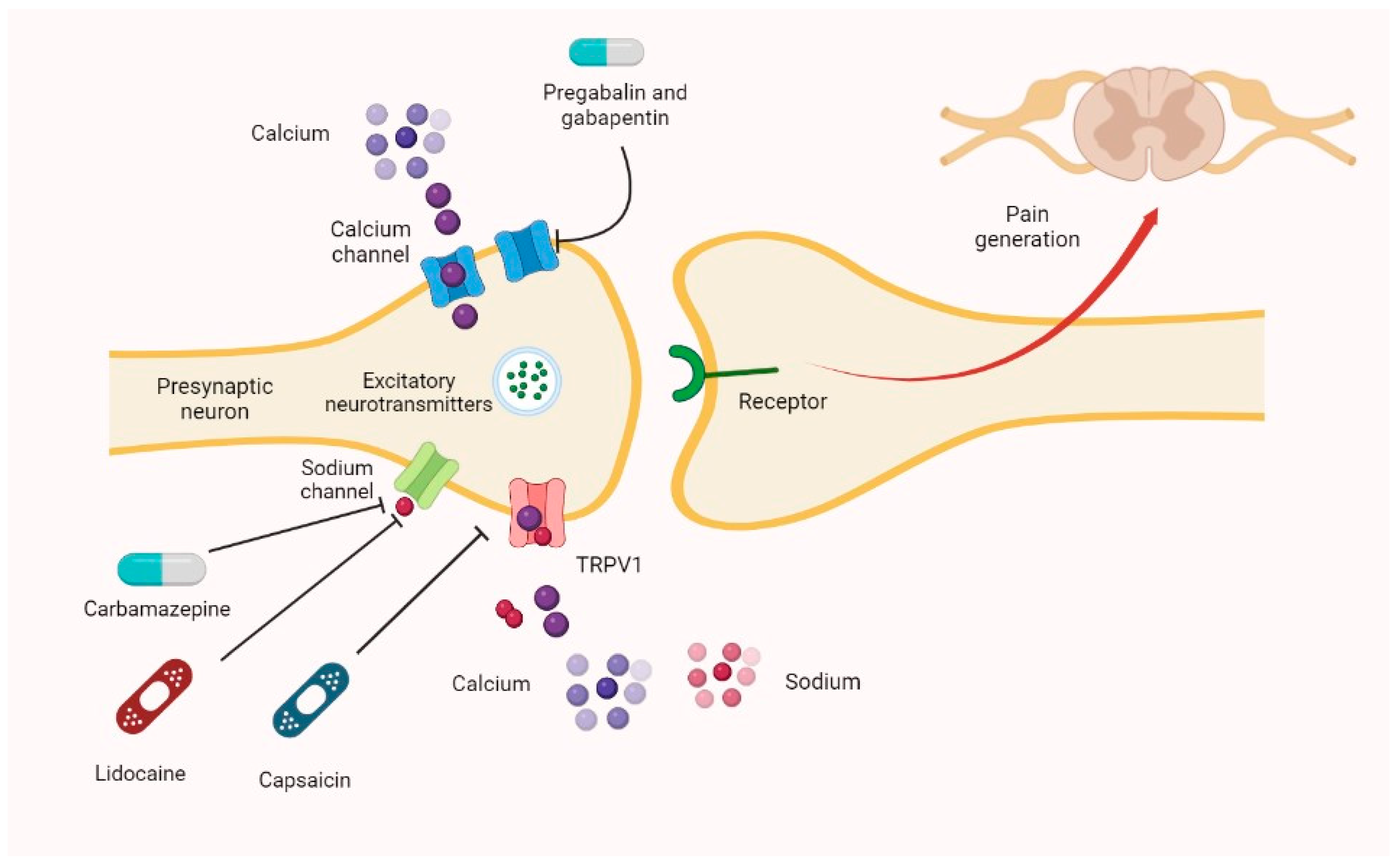
Gabapentin: Modulates the activity of calcium channels and reduces the release of neurotransmitters, thereby reducing pain signals. Nortriptyline: Increases the levels of certain chemicals in the brain that help elevate mood and reduce pain perception. GABAPIN NT is a fixed-dose combination product containing gabapentin and nortriptyline. It is intended for oral use in neuropathic pain. Gabapentin is basically an anticonvulsant. It also alleviates neuropathic pain. Although the general mechanisms of action of pregabalin and gabapentin are similar, important differences exist in terms of pharmacodynamics . Pregabalin has greater binding affinity for the alpha-2/delta-1 subunit, and therefore its analgesic potency in neuropathic pain is higher compared with gabapentin, thus justifying the utility of Oxonortriptyline; Route of elimination. Nortriptyline and its metabolites are mainly excreted in the urine, where only small amounts (2%) of the total drug is recovered as unchanged parent compound. 21 Approximately one-third of a single orally administered dose is excreted in urine within 24 hours. 20 Small amounts are excreted in feces via biliary elimination. 21 the following nonprescription product may interact with nortriptyline: cimetidine (Tagamet). Be sure to let your doctor and pharmacist know that you are taking this medication before you start taking nortriptyline. Do not start this medication while taking nortriptyline without discussing with your healthcare provider. The mechanism of action of nortriptyline in the treatment of neuropathic pain remains uncertain, although it is known to inhibit both serotonin and noradrenaline reuptake. Nortriptyline Hydrochloride 25 mg (TEVA 25 mg 0811) View larger images Drugs.com Mobile App Access drug & treatment information, identify pills, check interactions and set up personal medication records. Patients with neuropathic pain and an inadequate response to nortriptyline alone may benefit from a combination with gabapentin (Gilron 2009). Diabetic neuropathy (off-label use): Oral: Initial: 10 to 25 mg/day; may gradually increase based on response and tolerability to a target dose of 25 to 100 mg/day. Additional data may be necessary to Interpretation: Combined gabapentin and nortriptyline seems to be more efficacious than either drug given alone for neuropathic pain, therefore we recommend use of this combination in patients who show a partial response to either drug given alone and seek additional pain relief. Future trials should compare other combinations to their Gabapentin enhances the GABA derivative across the brain, enhances GABA action, and modulates the ca+ channel; both are involved in controlling neuronal excitability in the brain. Thereby, it helps to treat neuropathic pain. Antidepressants and gabapentinoids are first line treatments for neuropathic pain. Chronic treatment in models of neuropathic pain provided mechanistic insights. Gabapentinoids target the α2δ-1 subunit of voltage-dependent calcium channels. Neuropathic pain arises as a consequence of a lesion or disease affecting the somatosensory system. Nortriptyline (Pamelor) is a tricyclic antidepressant medication. It’s FDA-approved for depression, but it’s also used off-label for pain-related conditions. Common nortriptyline side effects include dry mouth, drowsiness, and constipation. Weight gain and trouble peeing are also possible. Gabapentin vs Nortriptyline for nerve pain involves two different approaches: gabapentin, an anticonvulsant, stabilizes nerve activity, while nortriptyline, a tricyclic antidepressant, helps by increasing certain neurotransmitters to reduce pain. Gabapentin is a GABA derivative and it bounds to lipophilic molecule. The mechanism of action of Gabapentin is not exactly known. It crosses blood brain barrier and enhances release of GABA. Absorption: It is not well absorbed after oral administration. The bioavailability is not dose dependent. Manufacturer advises plasma-nortriptyline concentration monitoring if dose above 100 mg daily, but evidence of practical value uncertain. Treatment cessation Withdrawal effects may occur within 5 days of stopping treatment with antidepressant drugs; they are usually mild and self-limiting, but in some cases may be severe. Mechanism of action. The precise mechanism through which gabapentin exerts its therapeutic effects is unclear. 16,17 The primary mode of action appears to be at the auxillary α2δ-1 subunit of voltage-gated calcium channels (though a low affinity for the α2δ-2 subunit has also been reported). 10,8,14 The major function of these subunits is The development of newer classes of antidepressants and second-generation antiepileptic drugs has created unprecedented opportunities for the treatment of chronic pain. These drugs modulate pain Mechanism of Action. Nortriptyline is an antidepressant that falls under the pharmacological category of tricyclics (secondary amine), more commonly known as TCAs.The consensus is that nortriptyline inhibits the reuptake of serotonin and norepinephrine by the presynaptic neuronal membrane, thereby increasing the concentration of those neurotransmitters in the synapse. Treatment guidelines list nortriptyline (Pamelor) as an option for nerve pain. But a large review of studies suggested that there isn't enough strong evidence to know for sure whether nortriptyline (Pamelor) works well to treat nerve pain. Note that nortriptyline (Pamelor) isn't FDA approved for treating nerve pain. This randomised trial of three treatments—gabapentin, nortriptyline, and combined gabapentin and nor trip tyl-ine—had a three-period (A, B, and C) crossover design with 6 weeks per treatment period. As per a balanced Latin square crossover design, patients were randomised (double-blind) in a 1:1:1 ratio and allocated to one of three
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |