Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | 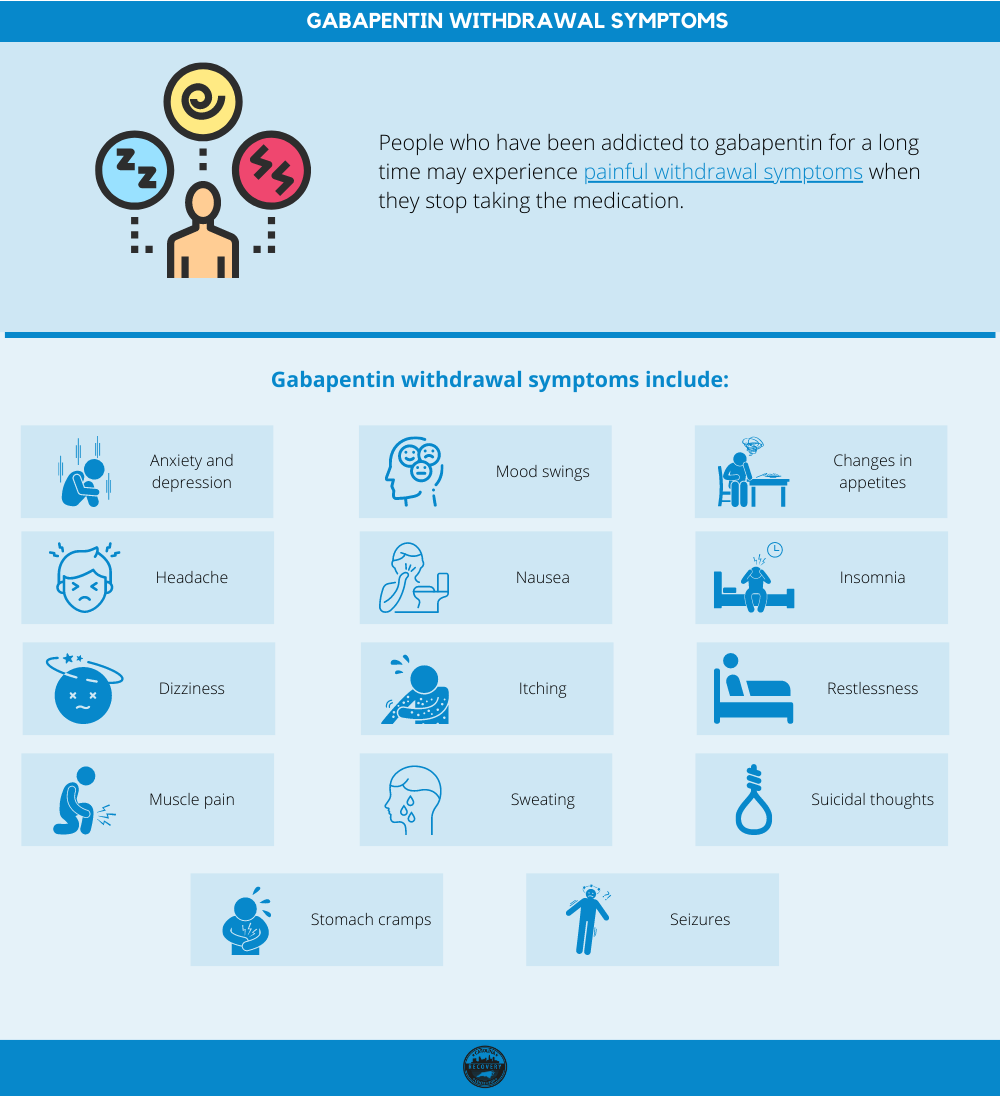 |
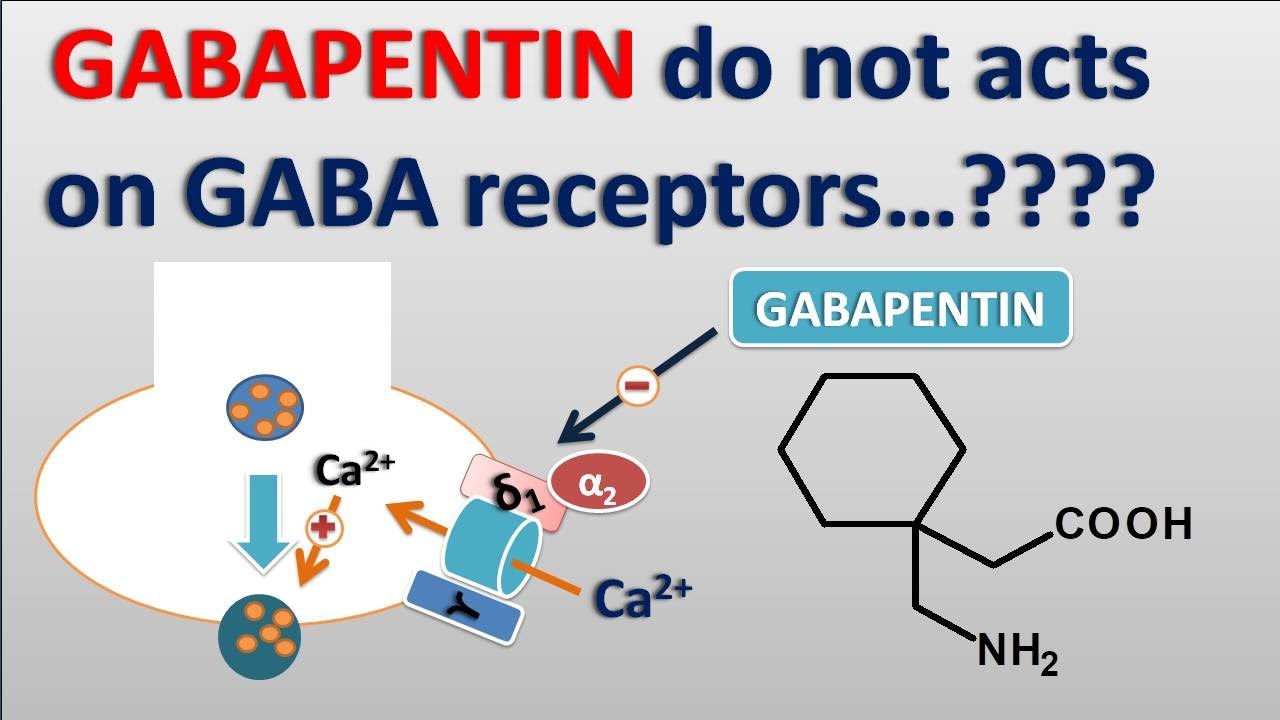
GABA is the primary inhibitory neurotransmitter in the brain, and imbalances in GABA signaling have been implicated in various neurological and psychiatric disorders, including ADHD. By modulating GABA activity, Gabapentin may help regulate neural circuits involved in attention and impulse control. Gabapentin (3-cyclohexyl-GABA) is designed as a lipophilic analogue of GABA for blood-brain barrier penetration and closely resembles pregabalin. Although gabapentin does not directly modify GABA-A receptor function, it may indirectly increase tonic inhibition via enhanced expression of extrasynaptic receptors in specific brain regions GABA is a naturally occurring neurotransmitter in the brain, primarily responsible for inhibiting nerve transmission, which helps to reduce neuronal excitability. In contrast, gabapentin is a medication designed to mimic the effects of GABA, used primarily to treat conditions like epilepsy and neuropathic pain. Gabapentin (Neurontin) Carisoprodol (Soma) Diazepam (Valium) Alprazolam (Xanax) Lorazepam (Ativan) There are also herbs and amino acids available without a prescription that can be used as GABA surrogates: Valerian root. Ashwagandha. Taurine. Brahmi. Bacopa. Glutamine: GABA’s Precursor GABA acts as a neurotransmitter and interacts with GABA receptors in the central nervous system, while gabapentin interacts with the α2δ subunit of the voltage-sensitive calcium channel. Both help reduce neuronal excitability, but the mechanisms are not fully understood. Gabapentin is a GABA analog, meaning that it looks very similar structurally but it is not completely the same. GABA is an inhibitory neurotransmitter found in the central nervous system (CNS) that regulates its excitability. Gabapentin is a structural analog of the inhibitory neurotransmitter γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA). Its anticonvulsant, analgesic and anxiolytic properties suggest that it increases GABAergic inhibition; however, the molecular basis for these effects is unknown as gabapentin does not directly modify GABA type A (GABA A) receptor function, nor does it modify synaptic inhibition. Gabapentin stimulates GAD at drug concentrations of 1.0 to 2.5 mM (Silverman et al, 1991; Taylor et al, 1992) and inhibits the GABA-catabolizing enzyme, GABA-transaminase (GABA-T) at high Recommended doses range from 20 mg to 40 mg daily, preferably dissolved under the tongue. However, it's crucial to emphasize that GABA supplementation should not be viewed as a substitute for professional medical advice in addressing prostate problems. GABA's therapeutic potential has been harnessed in the treatment of various medical conditions. Gabapentin is a prescription medication known as a gamma aminobutyric acid (GABA) analogue. GABA reduces the excitability of nerve cells (neurons) in the brain, which play a role in seizures and the transmission of pain signals. Gabapentin mirrors the effects of GABA calming excited neurons. Gabapentin, marketed for the treatment of seizures and neuropathic pain, has been shown to increase in vivo GABA concentration in the brain of both rodents and humans. Gabapentin effects on glutamate are not known. Drug interactions are reported among people who take Gaba (gaba (gamma - aminobutyric acid)) and Gabapentin (gabapentin). Common drug interactions include constipation among females and acne among males. Gabapentin, originally developed as an anticonvulsant medication, has found its way into the arsenal of treatments for various conditions beyond epilepsy. This versatile drug works by modulating the activity of certain neurotransmitters in the brain, particularly gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), which plays a crucial role in calming neural activity. Gabapentin (Neurontin, Gralise, Horizant) is a medicine used to treat partial seizures, nerve pain from shingles and restless leg syndrome. It works on the chemical messengers in your brain and nerves. Gabapentin is from a group of medicines called anticonvulsants. GABA is a naturally occurring neurotransmitter in the brain that inhibits or slows down nerve activity, helping to reduce anxiety and promote relaxation. On the other hand, Gabapentin is a medication that is structurally similar to GABA but does not directly bind to GABA receptors. The differences between GABA and gabapentin lie in their mechanisms of action in the brain – GABA targets GABA receptors whereas gabapentin interacts with voltage-gated calcium channels. Research about the effects of gabapentin on gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) neurotransmitter levels has reported inconsistent results, i.e., increase in GABA levels based on human studies, 10 but no effects have been reported in in vitro studies. 11 Moreover, gabapentin affects GABA(A), but not GABA(B) receptor responses, based on in vitro Chemical structures of GABA and gabapentin, with commonalities highlighted. Gabapentin is a 3,3-disubstituted derivative of GABA. Therefore, it is a GABA analogue, as well as a γ-amino acid. [102] [103] It is similar to several other compounds that collectively are called gabapentinoids. Some people may also experience impairment in thinking and judgment. You should avoid or limit the use of alcohol while being treated with gabapentin. Do not use more than the recommended dose of gabapentin, and avoid activities requiring mental alertness such as driving or operating hazardous machinery until you know how the medication affects We would like to show you a description here but the site won’t allow us.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |