Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
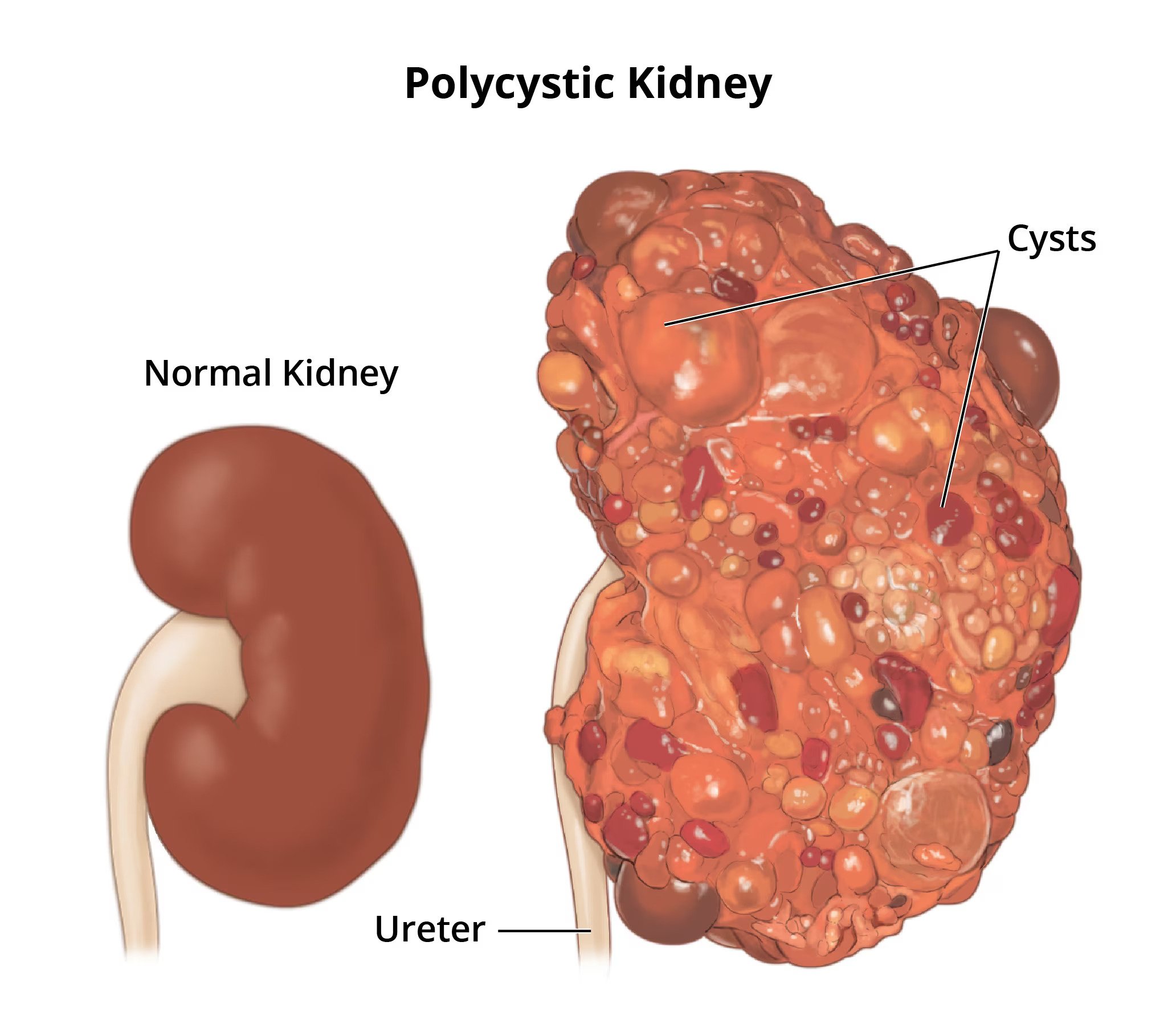 |  |
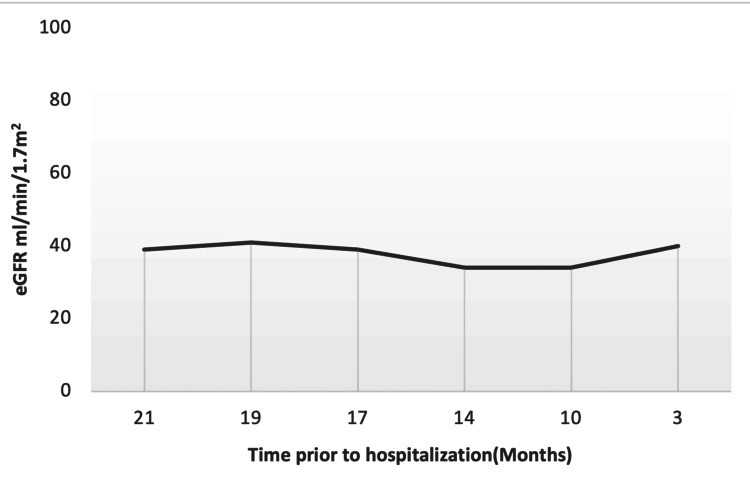
Gabapentin and pregabalin are commonly used for neuropathic pain in CKD patients but are not fully understood as this population remains excluded from efficacy and safety trials. Renal adjustments for the gabapentinoids are prodigiously recommended in the literature. Medications can impact your kidneys, especially with chronic kidney disease. Learn which drugs may need adjustments to protect your kidney health. Aspirin and kidney disease. Your healthcare professional may recommend low-dose aspirin (81-100 mg per day) if you have a history of heart disease or a very high risk of heart disease. This helps prevent future heart attacks without worsening kidney disease. Patients with chronic kidney disease often receive inappropriately high gabapentin dosage for their kidney function, occasioning overt toxicity; advanced age and comorbidity predispose these patients for toxicity. Higher-dose gabapentinoids (gabapentin >300 mg/d or pregabalin >75 mg/d) versus lower-dose gabapentinoids (gabapentin ≤300 mg/d or pregabalin ≤75 mg/d). Outcomes The primary composite outcome was the 30-day risk of a hospital visit with encephalopathy, a fall, or a fracture or a hospitalization with respiratory depression. Patients with chronic kidney disease often receive dangerously high gabapentin dosage for their kidney function, which can lead to all sorts of problems. An alternative we recommend instead of Gabapentin is Alpha Lipoic Acid. We found that patients with chronic kidney disease had elevated serum gabapentin concentrations, in some cases leading to gabapentin toxicity; those with advanced age and multiple comorbidities were more prone to the toxicity, and the toxicity tended to be underrecognized. Background: Gabapentinoids (GPs) are frequently prescribed in individuals with chronic kidney disease (CKD); however, their exclusive renal elimination warrants dose adjustments to decrease risk of toxicity. This study evaluated GP prescribing patterns and whether excessive dosing was associated with increased incidence of gabapentinoid-related Gabapentin is widely used in the management of pain. It is entirely excreted through the renal system so this needs to be considered in any patient becoming acutely ill and developing renal failure. We describe a patient who developed significant deterioration in her conscious level due to iatrogenic gabapentin overdose. If you have diabetes and are diagnosed with kidney disease, your doctor may need to adjust your medication dosage. Antacids Over-the-counter medications for heartburn and upset stomach can interfere with your body’s electrolyte balance, which can be problematic for people with chronic kidney disease. Dr. Chebib is a nephrologist and associate professor of medicine at Mayo Clinic Florida, where he leads both the Polycystic Kidney Disease Center of Excellence and the Discovery and Translational PKD Research Laboratory. Dr. Chebib's clinical and research efforts are focused on advancing the treatment of Polycystic Kidney Disease (PKD). Pruritus is very itchy skin that is most common in patients with advanced CKD and end-stage kidney disease (ESKD), but which can also happen in the early stages of CKD.. Pruritus is also known as uremic pruritus because the build-up of toxins and wastes in damaged kidneys, known as uremia, has been associated with itch Pierelli F et al. Gabapentin treatment for muscle cramps: an open-label trial. Clin Neuropharmacol 2000; 23:45. • In one small open-label trial (n=30), gabapentin was effective in reducing muscle cramps by 50% or more in 100% patients with eGFR > 60 mL/min and this effect lasted at 6 months. Mean gabapentin daily Exposure: Higher-dose gabapentinoids (gabapentin >300 mg/d or pregabalin >75 mg/d) versus lower-dose gabapentinoids (gabapentin ≤300 mg/d or pregabalin ≤75 mg/d). Outcomes: The primary composite outcome was the 30-day risk of a hospital visit with encephalopathy, a fall, or a fracture or a hospitalization with respiratory depression. Gabapentinoids are opioid substitutes whose elimination by the kidneys is reduced as kidney function declines. To inform their safe prescribing in older adults with chronic kidney disease (CKD), we examined the 30-day risk of serious adverse events according to the prescribed starting dose. Majority drugs, including Gabapentin, are eliminated by the kidneys and will accumulate to a toxic level in renally compromised patients as in this case. Per Lexicomp, Gabapentin’s recommended dose in patients with renal impairment is as follows: CrCl >15 to 29 mL/minute: 200 to 700 mg once daily. CrCl 15 mL/minute: 100 to 300 mg once daily Treatments for autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD) improve quality of life. Some may slow disease progression. Learn which ADPKD treatments may be right for you. Autosomal-dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD) Chronic renal pain is the most common presenting symptom of ADPKD. A defect of the PKD1 gene on chromosome 16 or the PKD2 gene on chromosome 4 results in the development of multiple renal cysts that begins in childhood and continues progressively throughout life. Aside from common causes of pain in the general population, patients with CKD have multifactorial (ischemic, neuropathic, bone, and musculoskeletal) pain conditions associated with their disease.⁸ They may experience pain caused by primary disease (polycystic kidney disease), bone disease (osteitis fibrosa cystica, osteomalacia, and 2 We would like to show you a description here but the site won’t allow us.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |