Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
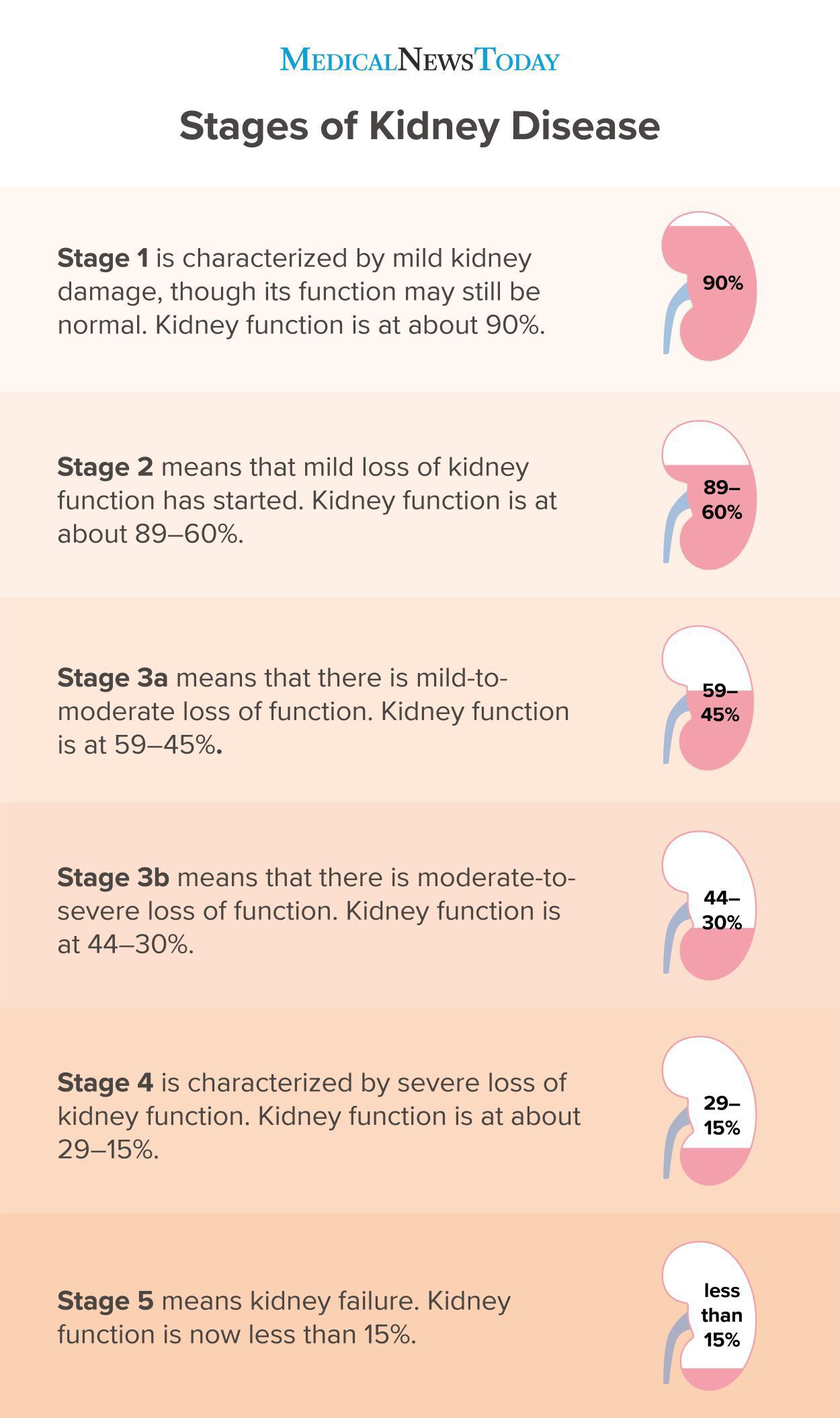
Pain is one of the most common and distressing symptoms among patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD) . The prevalence of pain has been associated with substantially lower health-related quality of life and greater psychosocial distress, insomnia, and depressive symptoms [ 2-9 ]. If you have diabetes and chronic kidney disease, check with your physician to see if any dosing changes need to be made based on your level of kidney function. Upset stomach/antacid medications. This group of over-the-counter medications can disrupt the body's electrolyte balance if you have chronic kidney disease. Patients with chronic kidney disease often receive dangerously high gabapentin dosage for their kidney function, which can lead to all sorts of problems. An alternative we recommend instead of Gabapentin is Alpha Lipoic Acid. I currently take gabapentin for trigeminal neuralgia and have CKD stage 3. Take 900-1200 gabapentin daily over past 20 years. Experiencing severe side effects of gabapentin that Im beginning to think correlate with decreased kidney function. It’s becoming cyclic. Take normal dose of gabapentin until start to become confused and lethargic. function into account and both dose and choice of agent should be checked. Specialist advice should be sought where appropriate. < 15 5 On dialysis 5D Acute kidney injury (AKI) refers to a sudden deterioration in renal function and is common in hospital inpatients. The presence and severity of acute kidney The combination can lead to dangerous interactions and health concerns. These include liver damage (especially with acetaminophen), acute kidney injury (especially with NSAIDs), and dizziness, tiredness, and falls (especially with antidepressants, anti-seizure medicines, and opioids). Aspirin and kidney disease Here are some of the most common questions about gabapentin and kidney disease: 1. Is it safe to take gabapentin if I have stage 3 kidney disease? Taking gabapentin with stage 3 kidney disease requires significant dose adjustments and close monitoring due to the risk of drug accumulation. Gabapentinoids are opioid substitutes whose elimination by the kidneys is reduced as kidney function declines. To inform their safe prescribing in older adults with chronic kidney disease (CKD), we examined the 30-day risk of serious adverse events according to the prescribed starting dose. Rationale & Objective: Gabapentinoids are opioid substitutes whose elimination by the kid-neys is reduced as kidney function declines. To inform their safe prescribing in older adults with chronic kidney disease (CKD), we examined the 30-day risk of serious adverse events according to the prescribed starting dose. Patients with chronic kidney disease often receive inappropriately high gabapentin dosage for their kidney function, occasioning overt toxicity; advanced age and comorbidity predispose these patients for toxicity. .table_layout tbody td{ font-size:0.95em;} Usual Gabapentin Dosing (Adults) Usual initial gabapentin dose: 300mg q8h. Usual maintenance dose: 300-600mg q8h. Maximum dosage/day: 3600 mg Gabapentin Renal Dosing [>60 ml/min]: Give usual dosage : Dosage range: 400-1400mg/day (divided doses - Usually bid) : Dosage range: 200-700mg/day. : 100-300 mg/day. Use lower end of this range for CRCL Gabapentin is widely used in the management of pain. It is entirely excreted through the renal system so this needs to be considered in any patient becoming acutely ill and developing renal failure. We describe a patient who developed significant deterioration in her conscious level due to iatrogenic gabapentin overdose. Gabapentin impacts kidney function by reducing its ability to clear the drug, leading to its accumulation and potential damage. Clinical manifestations include increased creatinine levels, swelling, and decreased urine output. This study addresses specified outcomes in patients taking gabapentinoids with impaired kidney function compared to patients with normal kidney function. Minimal exclusion criteria allowed for the inclusion of patients with a wide range of CrCl and gabapentinoid dosing. Drug dosing requirements for antihypertensives in patients with chronic kidney disease are listed in Table 4. 4, 5 Thiazide diuretics are first-line agents for treating uncomplicated hypertension The short answer is: yes, gabapentin can be problematic for individuals with kidney failure and chronic kidney disease (CKD). While gabapentin is often prescribed for pain management, particularly nerve pain, and sometimes for seizures, its primary elimination pathway is through the kidneys. Gabapentin’s apparent total clearance is 100 mL/min in adults with normal renal function, which is essentially equivalent to CrCl and does not suggest the involvement of tubular reabsorption. 1 Some evidence suggest that active tubular secretion mediated by organic cation transporter-1 (OCT-1) may play a role in gabapentin’s renal clearance. In most cases, gabapentin doesn’t hurt the liver or kidneys, though proper dosing is important to prevent side effects. Learn how gabapentin affects the liver and kidneys here. Challenges in pain management in patients with kidney disease. Pain assessment. This should start with assessment of a) pain severity using various standardized tools, most common of which is the numerical rating scale []; b) pathophysiologic evaluatio n into mechanism of injury and type of pain; c) psychosocial evaluation of co-occurring factors that contribute to pain or make treatment of Gabapentinoids are opioid substitutes whose elimination by the kidneys is reduced as kidney function declines. To inform their safe prescribing in older adults with chronic kidney disease (CKD), we examined the 30-day risk of serious adverse events according to the prescribed starting dose.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |