Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
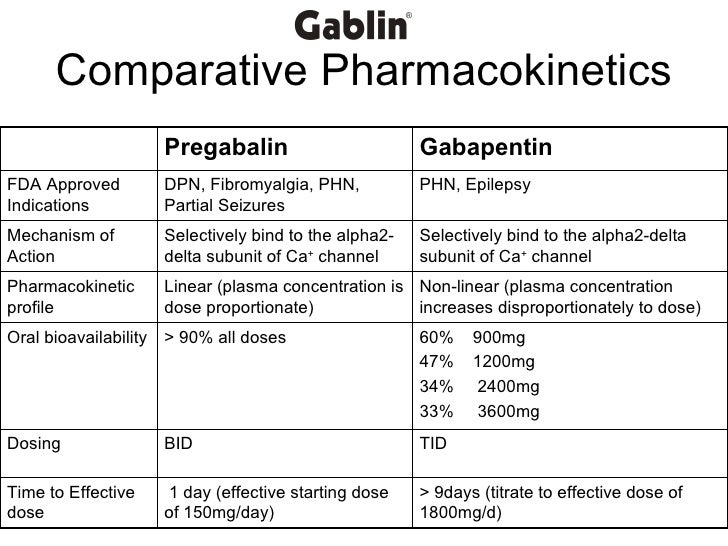
Continue reading for an in-depth comparison of pregabalin versus gabapentin, including an analysis of their respective uses, proven efficacy, dosing regimens, side effects, and more. Most side effects of Lyrica and gabapentin are mild and go away after using either medication for a few weeks. If the side effects bother or concern you or don’t go away, talk with your doctor Pregabalin (Lyrica) and gabapentin (Neurontin and others) are drugs used to prevent seizures and to treat nerve pain associated with various conditions (shingles, diabetic neuropathy). Lyrica and gabapentin both cause similar side effects, including tremors, blurred or double vision, memory or concentration problems, dizziness, and drowsiness. Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant with pain-relieving effects that may be used to treat certain seizure disorders or relieve nerve pain. Common side effects include dizziness or drowsiness and it may Using gabapentin together with pregabalin may increase side effects such as dizziness, drowsiness, confusion, and difficulty concentrating. Some people, especially the elderly, may also experience impairment in thinking, judgment, and motor coordination. You should avoid or limit the use of alcohol while being treated with these medications. Because these drugs have few side effects and are usually well tolerated, they are often the first medications to try for neuropathic pain. Most doctors will prescribe gabapentin first; if that doesn't work, they will try pregabalin. You may experience side effects, such as drowsiness, dizziness, confusion, or swelling in the feet and legs. Pregabalin starts working faster because it is absorbed more quickly than gabapentin. The common side effects of Pregabalin include dry mouth, blurred vision, headache, weight gain, indigestion, and constipation. At the same time, the common side effects of Gabapentin include – shaking, diarrhea, dizziness, drowsiness, and weakness. Gabapentin Vs Pregabalin Side Effects. The side effects of both Gabapentin and Pregabalin are similar; however, some studies indicate that Pregabalin may have a lower risk of adverse effects. Two of the most common side effects of Gabapentin and Pregabalin include sleepiness and dizziness. That said, differences in the occurrence rates of side effects for pregabalin and gabapentin may be less significant than available medical literature suggests. As of current, there are no convincing data to substantiate the idea that pregabalin is significantly more tolerable (i.e. causes fewer side effects) than gabapentin – or vice-versa. Yes, Lyrica (pregabalin) can cause extreme drowsiness (somnolence) and may affect your ability to drive, operate machinery, or do other dangerous activities. This may lead to an injury or fall. In studies, up to 20% of children and 35% of adults experienced drowsiness as a side effect. Gabapentin is more likely to cause different side effects from pregabalin, including: Fever; Increased risk of infection; Difficulty speaking; Jerky movements; Unusual eye movements Pregabalin and gabapentin are often considered first-line treatments for various neuropathic pain syndromes, generally irrespective of cause. Editor's note: This article has been updated. For an update to this article, read Appropriate Gabapentin Dosing for Neuropathic Pain here. Neuropathic pain causes significant morbidity in the United States. Gabapentin: Blurred vision, weight gain, peripheral edema, dizziness, and drowsiness. Pregabalin: Similar effects but may cause mild pain, shallow breathing, and potential for abuse. Pregabalin resulted in lower opioid consumption (OR 0.50, 95% CI 0.33–0.76). Gabapentin had a higher incidence of nausea and vomiting. Sensitivity analysis supported the efficacy of pregabalin. In conclusion, pregabalin demonstrated superior and faster efficacy in alleviating neuropathic pain than gabapentin did. Nevertheless, preliminary studies show that their combined use may potentially provide synergistic pain-relieving effects and a decreased incidence of side effects. More data is needed, however. Lyrica ( pregabalin ) and gabapentin generally aren't used together due to the similarity in how they work. Both medications have common side effects, such as drowsiness, dizziness, and edema. But pregabalin is more likely to cause weight gain. More serious side effects, such as suicidal thoughts and behaviors, heart problems, or misuse, are more rare. Side Effects: Both gabapentin and pregabalin cause similar adverse effects, such as dizziness, drowsiness, somnolence, blurred vision, dry mouth, nausea, and vomiting. Rarely, these two medications can cause serious adverse events, including allergic reactions with skin rash, hives, itching, swelling of the face, tongue, and lips, respiratory Using pregabalin with other drugs that slow your breathing can cause dangerous side effects or death. Ask your doctor before using opioid medication, a sleeping pill, cold or allergy medicine, a muscle relaxer, or medicine for anxiety or seizures. The main adverse effects (in >10% of consumers) for both gabapentin and pregabalin are ataxia, drowsiness, dizziness, and fatigue [5, 6]. Around one-third of the patients taking these would experience dizziness and somnolence [ 7 , 8 ]. Taking gabapentin or pregabalin with opioids, anxiety meds or antidepressants, or if you have lung issues or are elderly, can lead to serious breathing problems. Watch for breathing issues
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |