Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
+Symptoms-+Causes-+Risk+factors-+Complications-+Prevention+-+Treatment.jpg) |  |
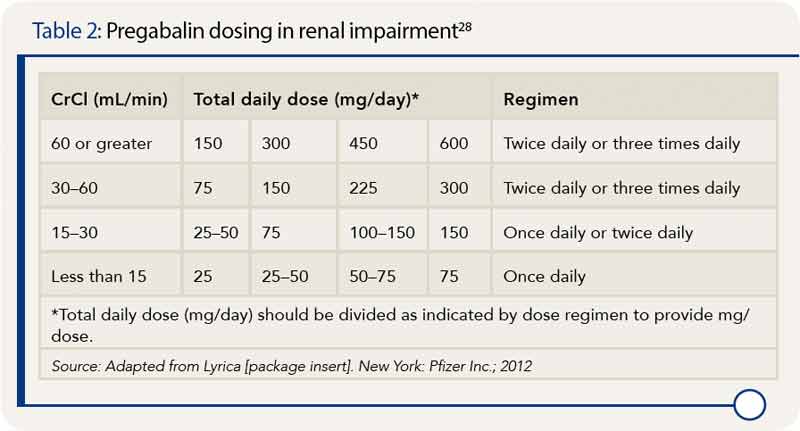
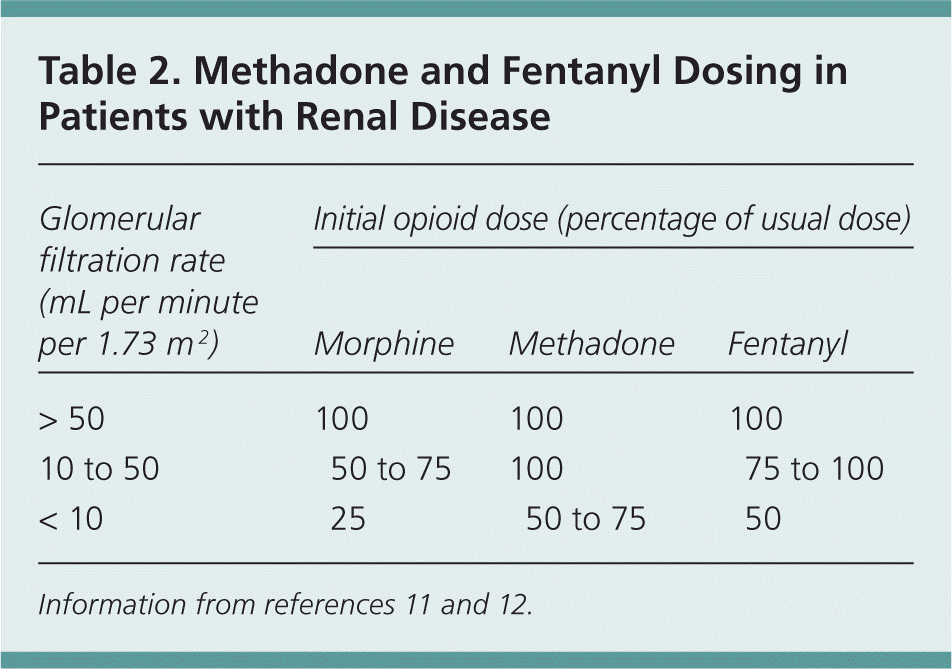
As in the other 2 cases of gabapentin-induced acute renal failure and rhabdomyolysis, the patients involved had multiple illnesses and were affected by multiple medications or other factors that might lead to rhabdomyolysis and renal failure. Therefore, it is crucial to adjust the dosage in patients with renal insufficiency to avoid severe adverse effects. In this case report, we present a patient with chronic renal impairment who experienced devastating myoclonic jerky movements shortly after increasing his gabapentin dose. Notwithstanding, most reports of toxicities were associated with concentrations higher than 15 mg/L for gabapentin and concentrations higher than 13 mg/L for pregabalin, whereas individuals with normal renal function on maximum recommended dosing yielded concentrations of ~5–8 mg/L for gabapentin and 2.8–8.2 mg/L for pregabalin. 22–25 The In patients with normal renal function, the maximum dose of gabapentin is 3600mg daily in divided doses. However, gabapentin is renally cleared and so the dose needs to be adjusted according to the GFR. For patients on dialysis, the recommended dose is 100-300mg post dialysis on dialysis days only. Dosing recommendations for individual drugs can be found in Drug Prescribing in Renal Failure: Dosing Guidelines for Adults. 4 The guidelines are divided into three broad GFR categories (less than The short answer is: yes, gabapentin can be problematic for individuals with kidney failure and chronic kidney disease (CKD). While gabapentin is often prescribed for pain management, particularly nerve pain, and sometimes for seizures, its primary elimination pathway is through the kidneys. When it comes to gabapentin and kidney disease, kidney disease sufferers should be aware of the risks that are involved in taking gabapentin with kidney disease. Gabapentin is actually toxic to the kidneys. Gabapentin is frequently used as an analgesic in patients with chronic kidney disease. The short answer is: yes, gabapentin can be problematic for individuals with kidney failure and chronic kidney disease (CKD). While gabapentin is often prescribed for pain management, particularly nerve pain, and sometimes for seizures, its primary elimination pathway is through the kidneys. In patients with normal renal function, the maximum dose of gabapentin is 3600mg daily in divided doses. However, gabapentin is renally cleared and so the dose needs to be adjusted according to the GFR. For patients on dialysis, the recommended dose is 100-300mg post dialysis on dialysis days only. People with chronic kidney disease who take gabapentin should be very aware of this as to not cause further damage to their kidneys. Gabapentin toxicity in patients with chronic kidney disease is underrecognized. Patients with chronic kidney disease often receive dangerously high gabapentin dosage for their kidney function, which can lead to Gabapentin and pregabalin are commonly used for neuropathic pain in CKD patients but are not fully understood as this population remains excluded from efficacy and safety trials. Renal adjustments for the gabapentinoids are prodigiously recommended in the literature. Gabapentin toxicity in renal failure: the importance of dose adjustment. Pain Med, 10 (2009), pp. 190-192. Epub 2008 Aug 18. Crossref View in Scopus Google Scholar. 14. Gabapentin is frequently used as an analgesic in patients with chronic kidney disease. Although gabapentin is well known for its favorable pharmacokinetics, it is exclusively eliminated renally, and patients with chronic kidney disease are at risk for toxicity. Existing literature on such risk is lacking. Rationale & Objective: Gabapentinoids are opioid substitutes whose elimination by the kid-neys is reduced as kidney function declines. To inform their safe prescribing in older adults with chronic kidney disease (CKD), we examined the 30-day risk of serious adverse events according to the prescribed starting dose. Patients with chronic kidney disease often receive inappropriately high gabapentin dosage for their kidney function, occasioning overt toxicity; advanced age and comorbidity predispose these patients for toxicity. The range of Gabapentin toxicity across the spectrum of renal insufficiency is underrecognized. In this case report, the patient with AKI only was confused and the patient with ESRD had myoclonus and seizure in addition to confusion. There seems to be a graded increase in toxicity with the corresponding deterioration of renal function. It is entirely excreted through the renal system so this needs to be considered in any patient becoming acutely ill and developing renal failure. We describe a patient who developed significant deterioration in her conscious level due to iatrogenic gabapentin overdose. Usual initial gabapentin dose: 300mg q8h. Usual maintenance dose: 300-600mg q8h. Maximum dosage/day: 3600 mg. [15-29]: Dosage range: 200-700mg/day. [<15]: 100-300 mg/day. Use lower end of this range for CRCL <7.5 ml/min. TABLE 1. Gabapentin Dosage Based on Renal Function. TID = Three times a day; BID = Two times a day; QD = Single daily dose. a. Gabapentinoids are opioid substitutes whose elimination by the kidneys is reduced as kidney function declines. To inform their safe prescribing in older adults with chronic kidney disease (CKD), we examined the 30-day risk of serious adverse events according to the prescribed starting dose. Myoclonus in renal failure: two cases of gabapentin toxicity. Kaufman KR, Parikh A, Chan L, Bridgeman M, Shah M. Epilepsy Behav Case Rep. 2014;2:8–10. doi: 10.1016/j.ebcr.2013.12.002. [PMC free article] [Google Scholar] 2. Rational dosing of gabapentin and pregabalin in chronic kidney disease.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
+Symptoms-+Causes-+Risk+factors-+Complications-+Prevention+-+Treatment.jpg) |  |