Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
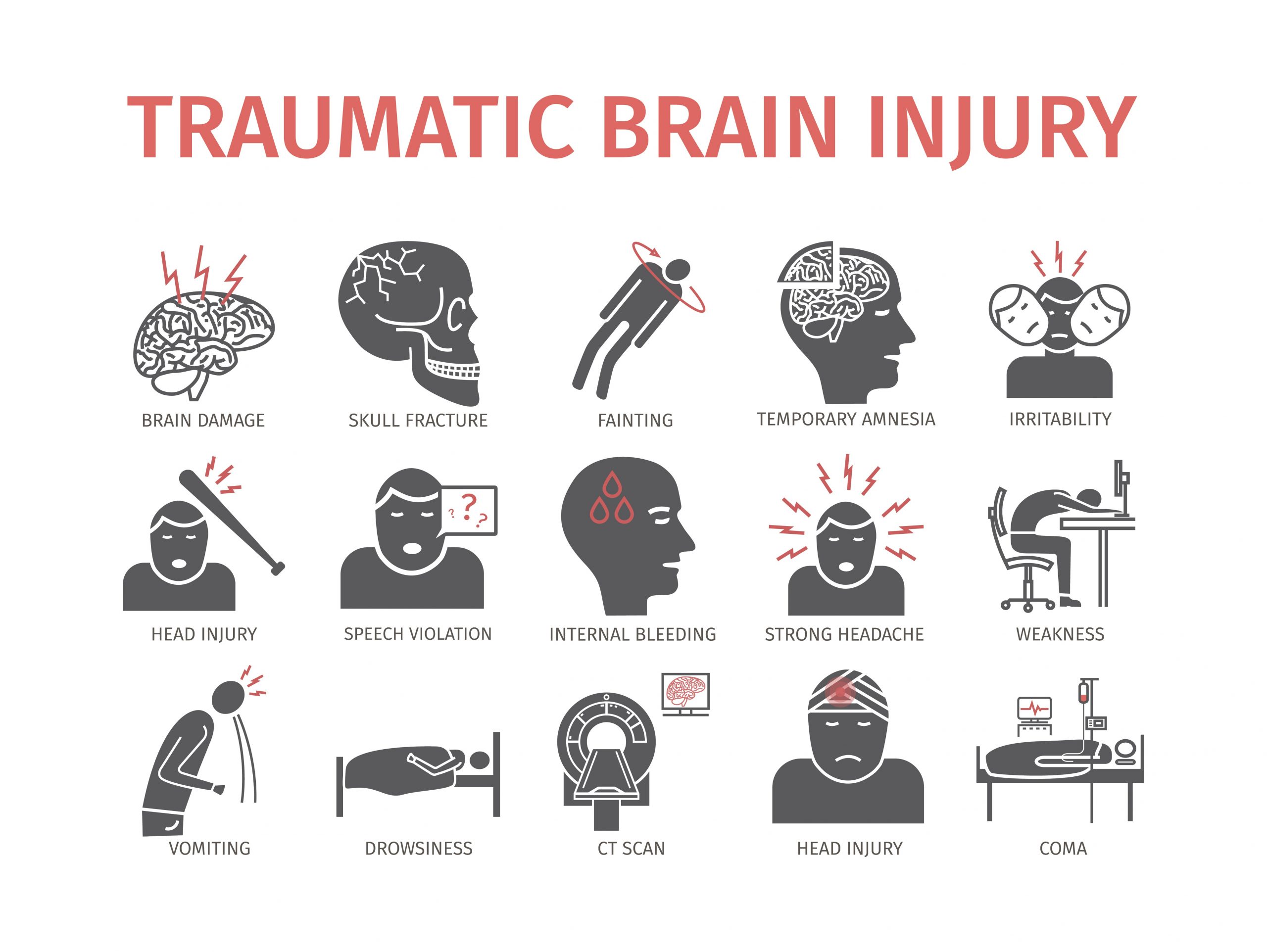
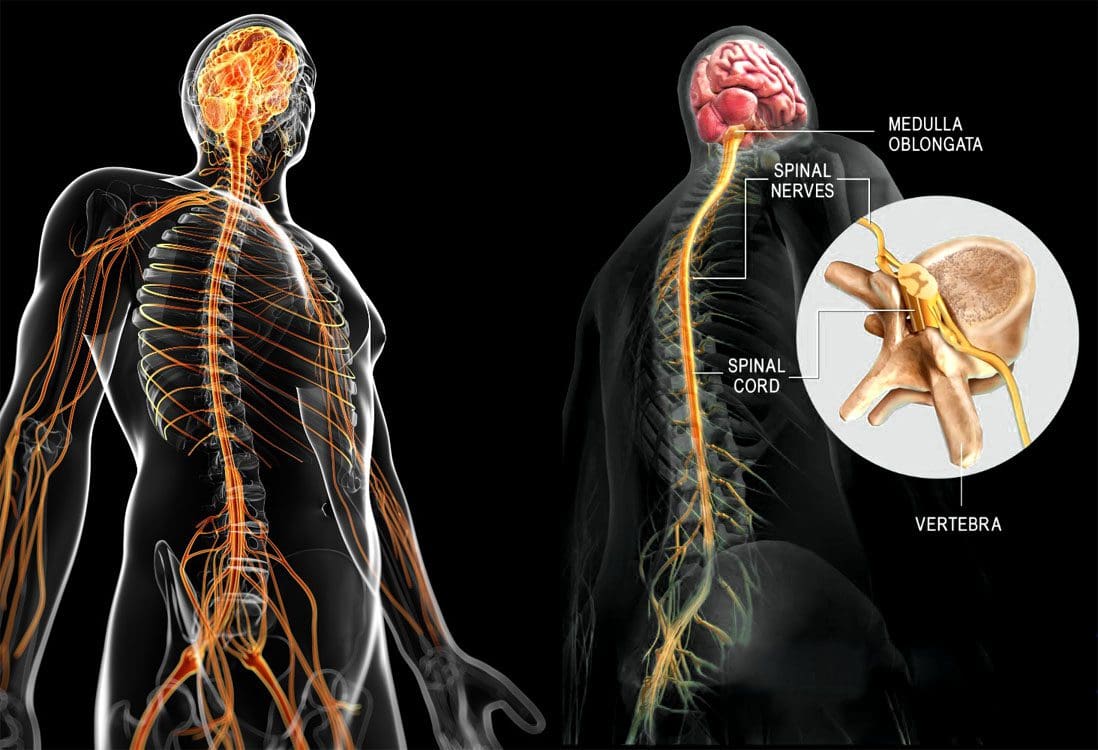
Permanent brain damage. Coma. Death. Gabapentin Overdose: Precautions & Interactions. Gabapentin is one of those drugs that is rarely misused and can therefore easily be overlooked as a cause for concern. Nevertheless, if not careful, it can be used as an opportunity to enhance the effects of other drugs. This comprehensive review highlights the diverse range of atypical side effects associated with gabapentin use, expanding beyond conventional knowledge. Healthcare practitioners must be cognizant of these manifestations, recognizing their potential impact on patient well-being. As clinical decision- Overall, the risk of being hospitalized with altered mental status after initiating gabapentin remains low, but may be reduced through the judicious use of gabapentin, use of the lowest dose to control pain, and vigilance for early signs of altered mental status. The new work also pinpoints, for the first time, the biochemical mechanism by which the widely prescribed drug gabapentin (also marketed under the trade name Neurontin) works. "We have solved the longstanding mystery of how this blockbuster drug acts," said Ben Barres, MD, PhD, professor and chair of neurobiology. The study shows that 2025 著作権. 不許複製 プライバシーポリシー Not a doctor but yes lol. Every drug can damage your brain, but cns depressants are the worst. Go spend some time in r/benzorecovery. Benzos are worse than gabapentin obviously so that's more of a worst case scenario. But yeah taking any cns depressants for a long period of time will fuck your brain. Although studies have revealed the administration of some drugs involved in GABA mechanisms of function, can damage memory by harming the neural pathways responsible for controlling cognition [27, 28, 29], some preclinical studies of the effect of PGB on memory, have proven otherwise [22, 27, 30, 31, 32, 33, 34, 35]. Gabapentin initiation was significantly associated with cognitive/functional status decline: worsening CDRGLOB at index+1 visit (odds ratio [95% confidence interval]: 1.55 [1.07, 2.25]); CDR-SB at index+1 visit (1.94 [1.22, 3.09]); and mean of FAQ at index+2 visit (1.78 [1.12, 2.83]). Gabapentin and Permanent Brain Damage. Gabapentin is a commonly prescribed drug that has proven to be effective in treating several conditions, including nerve pain, seizures, and anxiety disorders. However, the drug’s withdrawal symptoms have been at the center of controversy, with some patients expressing concerns about permanent brain damage. Some individuals report experiencing cognitive issues with long-term gabapentin use, such as difficulty concentrating, memory loss, or mental fog. These effects can be particularly concerning for individuals who rely on clear thinking for their work or daily tasks. Gabapentin works its magic by calming overactive nerves in the brain. It’s like a gentle hand soothing a frazzled mind, bringing relief to those who’ve long suffered. But here’s the rub: our brains are intricate machines, and tinkering with one part can have unexpected effects on others. There's no conclusive evidence to suggest that Gabapentin causes permanent brain damage. However, some studies suggest that prolonged and high-dose use of Gabapentin may lead to cognitive impairments in some individuals. Taking the gabapentin away without proper care can lead to the development of distressing and potentially dangerous withdrawal systems, as the brain and body struggle to adapt to the sudden lack of gabapentin. For those with epilepsy, this is of special concern; without gabapentin, they are at risk for experiencing seizures, which can be very Gabapentin can be an effective treatment for brain damage symptoms such as neuropathy, seizures, and autonomic dysfunction. However, it is not without side effects or risks. Therefore, consult with your doctor carefully before trying it, and alert your doctor immediately if any side effects appear. Avoid taking gabapentin with other medications and substances that slow down the brain. Examples include opioids, benzodiazepines, and alcohol. These combinations can lead to dangerously slowed breathing. GoodRx Health. Gabapentin (Neurontin) is FDA approved to treat certain types of seizures. In people with partial seizures, gabapentin works by decreasing abnormal activity in the brain. Experts believe gabapentin may cause brain cells to produce more of a chemical called GABA, which reduces abnormal electrical activity of brain cells. Complex pathophysiological mechanisms lead to secondary brain injury, and these include excitotoxicity, oxidative stresses, peri-infarct depolarization, inflammation; all these mechanisms take hours or days to take effect. 3,4 Among many syndromes associated with secondary brain injury, PSH is a syndrome where episodes of increased sympathetic My doctor said gabapentin needs to be taken every 8 hours to maintain a steady blood concentration. So taking it once a day at bedtime would cause a spike and then a withdrawal every morning. Called inter dose withdrawal. I doubt you caused any brain damage from 600 mg. There are many ppl taking 2400 mg - 3600 mg a day for years. Chronic administration of gabapentin and carbamazepine may cause increase in neurodegenerative changes in the adult brain. Keywords: Epilepsy, Antiepileptic drugs, Histology, Brain, Rats. Epilepsy is a chronic neurological disorder characterized by intermittent unprovoked seizures. It affects about 65 million people globally. Gabapentin new users with normal cognition at the visit of gabapentin initiation (i.e., index visit) were included. New-users were matched on year of first enrollment and time of gabapentin initiation since enrollment to randomly select nonusers with replacement.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |