Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
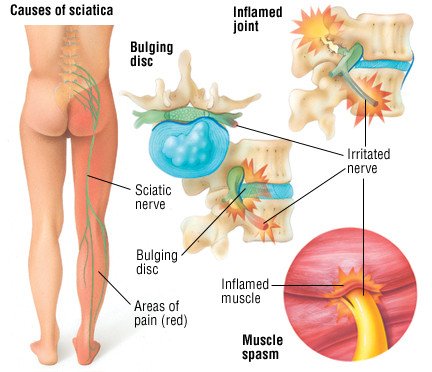
For those at their wits end with endless sciatica flare ups, gabapentin could provide much needed respite. In this article, we’ll explore the growing body of research on gabapentin for sciatica and how this medication is giving new hope to sciatica sufferers. Drugs like gabapentin, duloxetine, nortriptyline and pregabalin can be useful for managing severe pain or pain that makes it hard to sleep. Corticosteroids are another treatment option. These potent anti-inflammatory drugs are delivered via an injection that places the medication just where it is needed. Sciatica is commonly seen in primary care. Its prevalence in the general population varies between 3% and 14%, depending on the definition used. 1 The prognosis of acute sciatica is generally favourable: data from a prospective study of 183 patients with a median disease duration of 16 days show that in approximately one third of patients, symptoms improve greatly (ie, measured on a 4 point We describe two patients with sciatica who were successfully treated with gabapentin. The first was a 32-year-old man with severe shooting pain in his left leg that was later diagnosed as sciatica secondary to a fifth lumbar-first sacral intervertebral disk herniation. Gabapentin changes the way the brain and body exchange messages. It calms the nerves by blocking pain-causing neurotransmitters, making gabapentin an effective treatment for sciatica and Gabapentin for sciatica is considered alongside NSAIDs including naproxen or ibuprofen, corticosteroids and physical therapy to help in the pain management caused by this condition. To address the following questions keep reading this article: Does Gabapentin help with sciatica nerve pain? What is the Gabapentin dosage for sciatica nerve pain? One study assessed the effect of gabapentin vs pregabalin in a crossover head-to-head trial. A statistically significant improvement on leg pain at 2 weeks and leg pain with movement at 3 and 4 months was found in a RCT comparing gabapentin with placebo. This randomized clinical trial of pregabalin vs gabapentin in 18 patients with chronic sciatica found that gabapentin was superior to pregabalin with greater reduction of leg pain intensity and fewer adverse events. Meaning. Gabapentin was superior to pregabalin and should be commenced before pregabalin to permit optimal crossover of medicines. Gabapentin can help relieve sciatica, intense pain that runs along the sciatic nerve from the lower back through the hips and buttocks (12). Sciatica affects one side of the body and is usually caused by disk herniation or spinal stenosis (12). Gabapentin for sciatica pain can take 1-2 weeks to start showing any noticeable effects. Although, depending on the patient’s condition, dosage and response to the treatment, it may take longer to register relief. Gabapentin is commonly prescribed for sciatica. But the evidence supporting its use for sciatic nerve pain is weak. Sciatica is a very common condition that’s also known as lumbosacral radiculopathy. Up to 40% of people will have sciatica within their lifetime. While gabapentin is not a cure for sciatica, it can provide a 1-2 point average reduction in pain scores, allowing better mobility and function. Its favorable side effect profile, lack of drug interactions, and reduced risks of dependency make gabapentin a potentially useful part of a comprehensive sciatica treatment plan. Gabapentin is a remedy for nerve pain that’s also prescribed for back pain. See how it works and if it can help back pain from sciatica, shingles, and more. Previous trials of pregabalin and gabapentin in patients with chronic low back pain or sciatica did not show a beneficial effect over placebo. 10,11 Our trial extends this finding by the inclusion Because gabapentin has the potential to prevent central sensitization, consideration should be given to prescribing this therapy early in the course of sciatica. Further research using randomized, placebo-controlled trials are needed to validate the benefit of gabapentin in the treatment of sciatica. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and systemic steroids should not be used in patients with sciatica. (SOR: A, based on a meta-analyses of RCTs.) Topiramate (Topamax) and pregabalin Nerve pain medication: Gabapentin (Neurontin) and pregabalin (Lyrica) may help reduce neck and back nerve pain, especially sciatica. Begin with low doses to avoid daytime drowsiness and fall risk. Muscle relaxants. Tizanidine (Zanaflex) and baclofen (Lioresal) may reduce pain from muscle spasms. Chronic sciatica (CS), like most neuropathic pain states, is often resistant to simple treatment regimens. 1,2 Chronic sciatica is sciatica lasting longer than 3 months. 3 Neuropathic pain states are typically managed by super-adding anticonvulsant drugs onto simple drug regimens. The drugs most commonly used are gabapentin (GBP) or pregabalin NICE has published an update to NG59 Low Back Pain and Sciatica. The updated guideline advises healthcare professionals NOT to offer benzodiazepines, gabapentinoids or opioids for sciatica. This extends advice in the original 2016 guideline to avoid gabapentinoids and routine use of opioids for low back pain.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |