Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/If-your-dog-has-a-seizure-1117423_final-de77450b4b8845349ac555e2e28df723.png) | 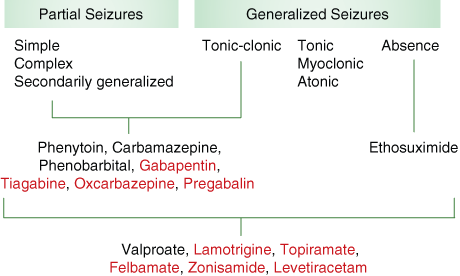 |
 |  |
 | :max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/nonconvulsive-status-epilepticus-2488649_v2-a14455e62a4a467da617ca5ca299429f.png) |
Gabapentin: Gabapentin is indicated for postherpetic neuralgia and serves as adjunctive therapy for managing partial seizures (with or without secondary generalization) in adults and pediatric patients aged 3 or older. Types of studies. We will search for and include randomised controlled trials comparing the following: gabapentin with placebo or any other antiepileptic drug; and. differing dose of gabapentin as monotherapy for partial seizures with and without secondary generalisation. Gabapentin capsules, tablets, and oral solution are used along with other medications to help control certain types of seizures in people who have epilepsy. Gabapentin capsules, tablets, and oral solution are also used to relieve the pain of postherpetic neuralgia (PHN; the burning, stabbing pain or aches that may last for months or years after In a randomized, double blind, placebo controlled trial conducted by Chadwick, et al., gabapentin demonstrated a significant reduction in seizure frequency compared to placebo in patients with refractory complex partial seizures. The most common side effects that were reported in studies of gabapentin are drowsiness (somnolence), dizziness, problems with movement and balance (ataxia), fatigue, and rapid and uncontrolled eye movement (nystagmus) in patients with epilepsy >12 years of age and viral infection, fever, nausea and/or vomiting, somnolence, and hostility in Anti-seizure drugs designed to treat epilepsy often are used to control nerve pain associated with diabetes, shingles, and other types of nerve damage. This content does not have an English version. This content does not have an Arabic version. Doctors prescribe gabapentin to treat epilepsy, restless legs syndrome, and some types of nerve pain. Learn more the drug's uses, risks, and safety here. Gabapentin capsules, tablets, and oral solution are used along with other medications to help control certain types of seizures in people who have epilepsy. Gabapentin capsules, tablets, and oral solution are also used to relieve the pain of postherpetic neuralgia (PHN; the burning, stabbing pain or aches that may last for months or years after Gabapentin is FDA-approved as Neurontin to treat partial seizures in adults and children with epilepsy. Partial seizures are convulsions that originate from a single location in the brain. Neurontin is also approved to treat a type of nerve pain called postherpetic neuralgia, or PHN. Several ASDs are effective as first‐line monotherapy in focal seizures, including lamotrigine, carbamazepine, phenytoin, levetiracetam, and zonisamide. Valproate remains the first‐line drug for many patients with generalized and unclassified epilepsies. Gabapentin is a Pfizer-made medication for focal aware and impaired seizures. For more information, visit the Epilepsy Foundation online. Gabapentin is 1 of many antiseizure medications available for the treatment of epilepsy in adults; however, there are potential risks associated with its use. Therefore, it is important to determine the place of therapy of gabapentin in the treatment of epilepsy. Gabapentin (Neurontin, Gralise, Horizant) is a medicine used to treat partial seizures, nerve pain from shingles and restless leg syndrome. It works on the chemical messengers in your brain and nerves. Gabapentin is from a group of medicines called anticonvulsants. Lennox-Gastaut syndrome (LGS) Difficult to treat seizures of mixed types – Atonic – Tonic – Atypical absence – Can also have myoclonic, GTC or focal EEG findings: generalized slow spike and wave (<3 Hz) Gabapentin requires three times daily administration because of its short duration of effect. Gabapentin enacarbil (brand name Horizant) only requires once-daily dosing. Only effective for partial-onset seizures, not other types of seizure disorders. Some branded and generic forms of gabapentin are not interchangeable. Children may be treated with gabapentin 23 to 78 mg/kg per day. Based on controlled and open trials, the majority of patients will tolerate gabapentin well enough for an adequate therapeutic assessment. Titration to effect can be accomplished rapidly, if necessary; however, as with other AEDs, optimal seizure control may take months to achieve. One guideline recommends against the use of gabapentin in people with myoclonic seizures or people with epilepsy with myoclonic-atonic seizures. One guideline states that there is insufficient evidence to consider gabapentin instead of carbamazepine in patients with new-onset focal epilepsy or unclassified generalized tonic-clonic seizures. Seizure types are limited to myoclonic seizures, generalized tonic-clonic convulsions (GTCs), and absence (petit mal). In contrast, symptomatic epilepsy, as well called 2° generalized, is a destructive type of epilepsy in which developmental anomaly exists, and a structural defect is recognized. There is a risk of increased seizures or different types of seizures when taking gabapentin. It is important to monitor any changes in seizure patterns or the emergence of new symptoms and report them to the doctor. Gabapentin also carries a risk of suicidal thoughts and behavior. During the controlled epilepsy trials in patients older than 12 years of age receiving doses of gabapentin up to 1800 mg daily, somnolence, dizziness, and ataxia were reported at a greater rate in patients receiving gabapentin compared to placebo: i.e., 19% in drug versus 9% in placebo for somnolence, 17% in drug versus 7% in placebo for
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/If-your-dog-has-a-seizure-1117423_final-de77450b4b8845349ac555e2e28df723.png) |  |
 |  |
 | :max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/nonconvulsive-status-epilepticus-2488649_v2-a14455e62a4a467da617ca5ca299429f.png) |