Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
/male-kidney-anatomy--illustration-758313113-5aa15ae80e23d90037526254.jpg) | 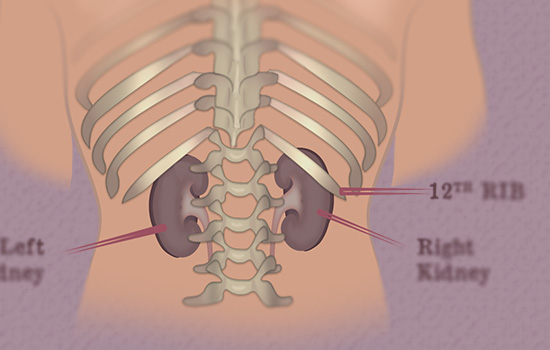 |
 |  |
Higher-dose gabapentinoids (gabapentin >300 mg/d or pregabalin >75 mg/d) versus lower-dose gabapentinoids (gabapentin ≤300 mg/d or pregabalin ≤75 mg/d). Outcomes The primary composite outcome was the 30-day risk of a hospital visit with encephalopathy, a fall, or a fracture or a hospitalization with respiratory depression. In most cases, gabapentin doesn’t hurt the liver or kidneys, though proper dosing is important to prevent side effects. Learn how gabapentin affects the liver and kidneys here. Given that gabapentin relies heavily on the kidneys for elimination, careful dose adjustments are crucial for those with pre-existing kidney problems. Healthcare providers typically start individuals with renal impairment on a lower dose and closely monitor their response to the medication. Background: Gabapentinoids (GPs) are frequently prescribed in individuals with chronic kidney disease (CKD); however, their exclusive renal elimination warrants dose adjustments to decrease risk of toxicity. This study evaluated GP prescribing patterns and whether excessive dosing was associated with increased incidence of gabapentinoid-related Learn about the potential effects of Gabapentin on your liver and kidneys. Find out if it is safe to use and how to protect your organs while taking this medication. We can help! Here are some of the most common questions about gabapentin and kidney disease: 1. Is it safe to take gabapentin if I have stage 3 kidney disease? Taking gabapentin with stage 3 kidney disease requires significant dose adjustments and close monitoring due to the risk of drug accumulation. Here’s a scenario of using gabapentin in chronic kidney disease. A 42 year old African American man with a history of coronary artery disease and decompensated heart failure s/p heart transplant and chronic kidney disease presented to a hospital on 9/29/16 complaining of shortness of breath, dyspnea upon exertion and LE edema. ABSTRACT. Objective. This case report outlines a significant type of morbidity due to continued use of gabapentin during an episode of acute renal failure. Gabapentin’s apparent total clearance is 100 mL/min in adults with normal renal function, which is essentially equivalent to CrCl and does not suggest the involvement of tubular reabsorption. 1 Some evidence suggest that active tubular secretion mediated by organic cation transporter-1 (OCT-1) may play a role in gabapentin’s renal clearance. NSAIDs have the most potential for risk when it comes to your kidneys. The best pain med for you depends on a variety of factors, including kidney health. Let's discuss: Close monitoring of renal function, dosage adjustment based on kidney function, and avoidance of nephrotoxic medications are crucial in managing and preventing gabapentin-related kidney problems. Gabapentin, an anticonvulsant medication, can potentially cause kidney problems. The short answer is: yes, gabapentin can be problematic for individuals with kidney failure and chronic kidney disease (CKD). While gabapentin is often prescribed for pain management, particularly nerve pain, and sometimes for seizures, its primary elimination pathway is through the kidneys. Gabapentin is not absolutely contraindicated in kidney disease, but it demands meticulous management. The key to its safe use is careful dose adjustments, rigorous monitoring for toxicity, and an open dialogue with your healthcare provider. Patients with chronic kidney disease often receive inappropriately high gabapentin dosage for their kidney function, occasioning overt toxicity; advanced age and comorbidity predispose these patients for toxicity. Gabapentin is actually toxic to the kidneys. Gabapentin is frequently used as an analgesic in patients with chronic kidney disease. Although gabapentin is well known for its well recieved pharmacokinetics, it is exclusively eliminated renally, and patients with chronic kidney disease are at risk for toxicity. People with chronic kidney disease Some of its most common side effects include the following: ataxia, nystagmus, drowsiness, headaches, diplopia, fatigue and myoclonic twitches. 1 All of these effects appear quite often in patients with chronic kidney disease, especially if they are undergoing dialysis and their doses are not adjusted to their glomerular filtration rates. 2 We Gabapentinoids are opioid substitutes whose elimination by the kidneys is reduced as kidney function declines. To inform their safe prescribing in older adults with chronic kidney disease (CKD), we examined the 30-day risk of serious adverse events according to the prescribed starting dose. Taking gabapentin can make you sleepy. According to studies, about 20% of people taking gabapentin experience drowsiness or fatigue. It may be even more likely, affecting 20% to 30% of people, with Horizant. Gabapentin is frequently used as an analgesic in patients with chronic kidney disease. Although gabapentin is well known for its favorable pharmacokinetics, it is exclusively eliminated renally, and patients with chronic kidney disease are at risk for toxicity. Existing literature on such risk is lacking. Challenges in pain management in patients with kidney disease. Pain assessment. This should start with assessment of a) pain severity using various standardized tools, most common of which is the numerical rating scale []; b) pathophysiologic evaluatio n into mechanism of injury and type of pain; c) psychosocial evaluation of co-occurring factors that contribute to pain or make treatment of
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
/male-kidney-anatomy--illustration-758313113-5aa15ae80e23d90037526254.jpg) |  |
 |  |