Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
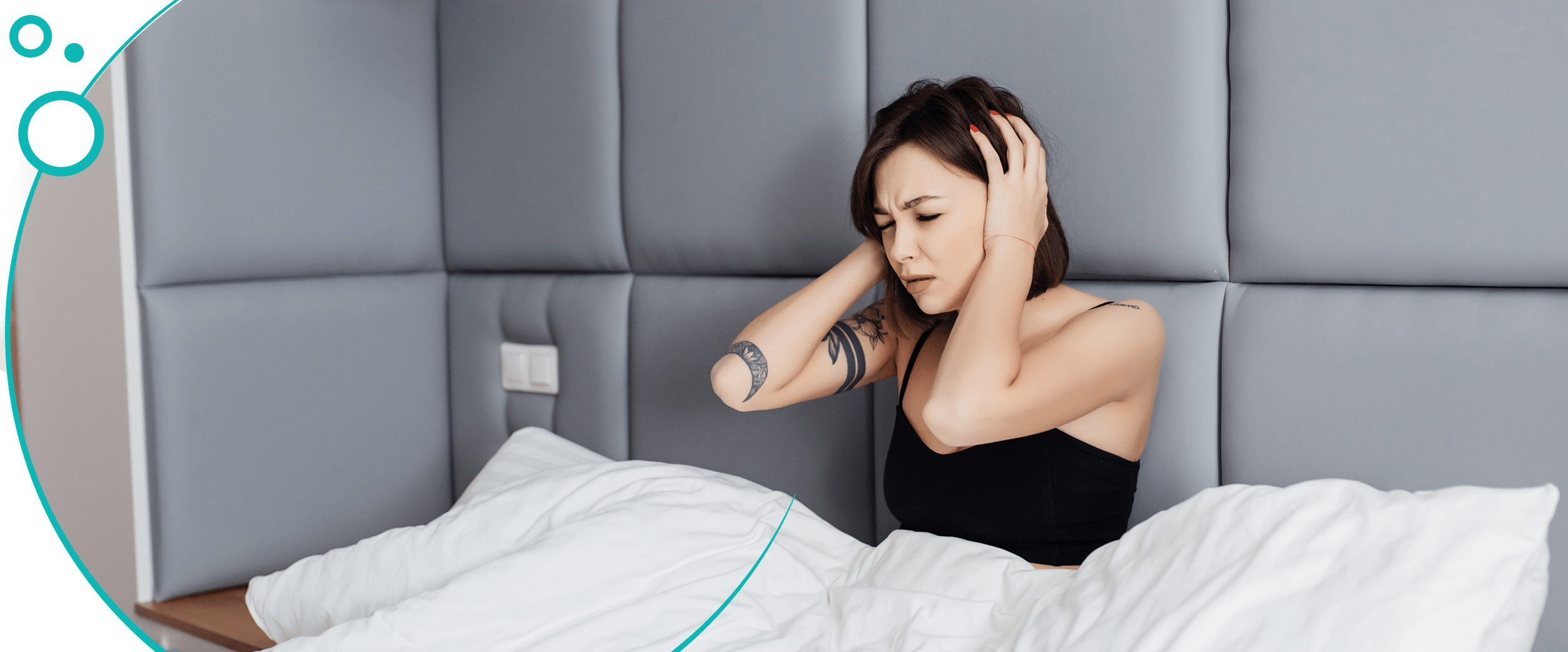
Clinical studies have revealed that gabapentin could improve the objective and subjective outcomes of sleep disturbance in patient with medical illness (13 – 37). Gabapentin Enacarbil (GEn) or XP13512 is a prodrug of gabapentin, used as an anticonvulsant and for pain relief in postherpetic neuralgia. Studies show 250 mg or 400 mg doses taken 30 minutes to two hours before bed can extend sleep duration effectively. Gabapentin works by affecting neurotransmitters in the brain, which helps to calm neural activity. For individuals struggling with insomnia or disruptive sleep patterns, this calming effect can be particularly beneficial. Gabapentin enhances slow-wave sleep in patients with primary insomnia. It also improves sleep quality by elevating sleep efficiency and decreasing spontaneous arousal. The results suggest that gabapentin may be beneficial in the treatment of primary insomnia. The Mechanism Behind Gabapentin’s Sleep-Inducing Effects. To comprehend how gabapentin works for sleep, it’s essential to delve into its mechanism of action in the brain. Gabapentin for Sleep: Effectiveness, Dosage, and Considerations explores this topic in depth, but let’s break it down further. Gabapentin primarily affects the Preliminary evidence indicates that gabapentin can attenuate insomnia, bolster sleep quality, and increase total sleep duration. Moreover, gabapentin has been shown to increase slow-wave sleep (SWS), promote sleep maintenance, and decrease unwanted awakenings throughout the night. Most studies show that gabapentin improves slow wave sleep (“deep sleep”) and total sleep time. Two small studies showed that gabapentin may help people with primary insomnia and occasional sleep disturbance improve total sleep time and wakefulness in the morning. Some studies have found that gabapentin may increase slow-wave sleep, also known as deep sleep, which is crucial for physical restoration and cognitive function. Additionally, it may reduce sleep fragmentation, leading to fewer nighttime awakenings and improved sleep continuity. The dosage of Gabapentin prescribed by doctors to treat the sleep disorder insomnia and improve overall sleep quality is generally between 100-400 mg. Some research shows gabapentin may be effective for sleep. But it comes with risks, including dizziness, falls, and fluid buildup. Gabapentin is a controlled substance in some states. It can lead to dependence and misuse. It’s best to avoid taking gabapentin with other medications that cause drowsiness, like opioids and benzodiazepines. Research suggests that gabapentin may increase slow-wave sleep, also known as deep sleep, which is crucial for physical recovery and memory consolidation. This effect could be particularly beneficial for individuals who struggle to achieve restorative sleep due to pain or anxiety. Most doctors will prescribe between 100mg and 400mg of gabapentin for insomnia. Typically, a doctor will start you off with the lowest possible dose and then gradually increase it, as needed. When used for insomnia, gabapentin should be taken once a day shortly before bed. Always take it as directed by your doctor. Also, experiencing multiple wakeups, especially during the night is a sure hallmark of insomnia. To overcome this problem, you need to visit a doctor for a diagnosis. Most likely, your doctor will prescribe you gabapentin for sleep. Gabapentin for primary insomnia will help you fall asleep quickly and even enjoy deep sleep for long hours. Gabapentin For Sleep. Gabapentin, also referred to as Neurontin, is a medication that’s often prescribed by doctors for quite a few different purposes. Primarily, it’s known as an anticonvulsant, a medication that helps prevent or stop seizures resulting from epilepsy. The Role of Gabapentin in Sleep Regulation. Sleep disturbance can significantly impact our overall health and well-being. Gabapentin has been studied for its potential in regulating sleep patterns and improving sleep quality. Research suggests that gabapentin may increase slow-wave sleep, which is the deep restorative sleep that we need for Gabapentin: a study has been done in 2010 regarding the effect of Gabapentin on insomnia, the results were promising, the treatment was used in the study for 4 wks every night so I believe you will see better result for your insomnia if you take it regularly. While these findings suggest that Gabapentin may help with sleep, more robust studies are needed to confirm its safety and effectiveness for primary insomnia. Is Gabapentin the best option for sleep? While Gabapentin can help with sleep, especially for those with co-existing conditions, it’s typically not the first choice for treating insomnia. Anyone in this group taking Gabapentin for insomnia? I've attached a study from PubMed and the NIH regarding how Gabapentin can help with this. "Gabapentin enhances slow-wave sleep in patients with primary insomnia. It also improves sleep quality by elevating sleep efficiency and decreasing spontaneous According to a study, gabapentin not only helps to treat insomnia symptoms [1*] by decreasing spontaneous arousal — like waking up in the middle of the night. It also helps improve sleep quality by enhancing slow-wave sleep. Slow-wave sleep also referred to as deep sleep, is the type of sleep that makes individuals feel rested. "Taking gabapentin to ease withdrawal from the last of a clonazepam withdrawal, 5 weeks ago. Worked so great for sleep! Deep sleep, REM, rested in the morning, no wake-ups at night. Suddenly stopped working for sleep 2 nights ago. Severe insomnia, so I upped from 300 to 600 mg at night. Still no sleep until 4 am. Then only 4.5 hours.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |