Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 | |
 | |
 | %3B+open+bars%2C+placebo%3B+colored+bars%2C+therapies%3B+length+of+bars%2C+ranges+in+studies%3B+horizontal+bar%2C+means.+All+of+these+agents+are+generally+well+tolerated+(226).+Hypersensitivity+or+prior+adverse+drug+reactions+to+each+of+these+agents+represent+contraindications.+For+the+SSRI/SNRIs%2C+prior+neuroleptic+syndrome%2C+serotonin+syndrome%2C+and+concurrent+use+of+monoamine+oxidase+inhibitors+are+also+contraindications.+SSRI/SNRIs+should+be+used+with+caution+in+patients+with+bipolar+disease%2C+uncontrolled+seizures%2C+hepatic+or+renal+insufficiency%2C+uncontrolled+hyponatremia%2C+concurrent+use+of+other+SSRI/SNRIs%2C+or+poorly+controlled+hypertension.+These+agents+uncommonly+induce+suicidal+thoughts+within+the+first+few+months+of+treatment.+Preliminary+evidence+suggests+a+possible+increase+in+risk+of+bone+fracture.+Gabapentin+and+pregabalin+may+increase+suicidal+thoughts+and+behaviors%2C+cause+drowsiness+or+dizziness%2C+and+impair+balance+and+coordination.+Pregabalin+may+impair+memory+and+concentration.+Clonidine+is+contraindicated+in+patients+with+low+blood+pressure+and+may+cause+lightheadedness%2C+hypotension%2C+headache%2C+and+constipation%3B+sudden+cessation+of+treatment+can+be+associated+with+significant+increments+in+blood+pressure+(63)..jpg) |
 |  |
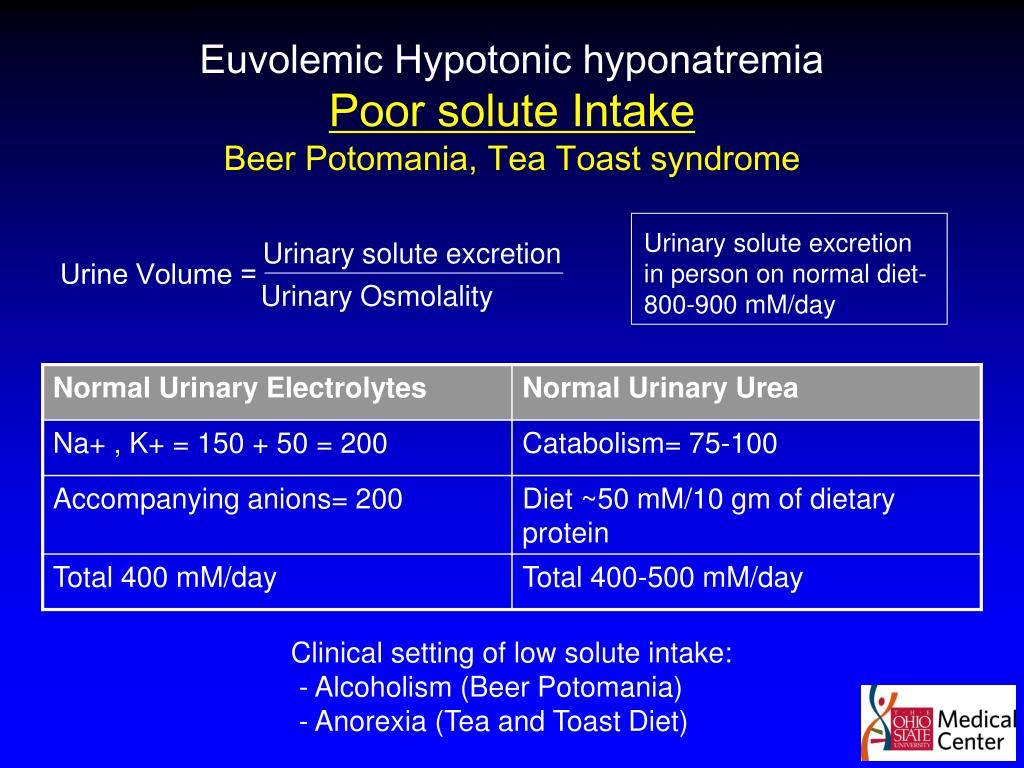 | 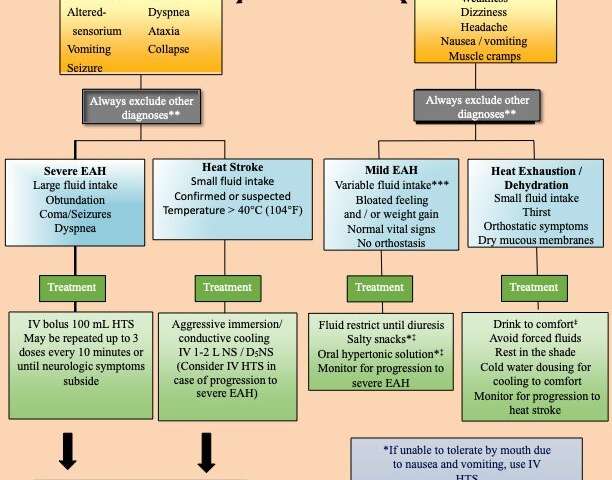 |
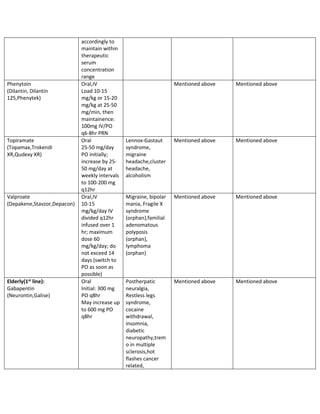
A Review of Drug-Induced Hyponatremia George Liamis, MD, Haralampos Milionis, MD, and Moses Elisaf, MD Hyponatremia (defined as a serum sodium level 134 mmol/L) is the most common electrolyte Carbamazepine and oxcarbazepine are the most common antiepileptic drugs (AEDs) associated with hyponatremia. 1,21 Recently, other AEDs, such as eslicarbazepine, sodium valproate, lamotrigine, levetiracetam and gabapentin, have also been reported to induce hyponatremia. 43 In fact, older adults on valproic acid, phenytoin or topiramate have a hig ASMs such as carbamazepine (CBZ), oxcarbazepine (OXC), and valproic acid have a higher risk of hyponatremia. Hyponatremia induced by an antiseizure medication can occur through various mechanisms depending on the drug's specific mechanism of action. Hyponatremia can be a potentially fatal side effect. Hyponatremia (defined as a serum sodium level < 134 mmol/L) is the most common electrolyte abnormality in hospitalized patients. Certain drugs (eg, diuretics, antidepressants, and antiepileptics) have been implicated as established causes of either asymptomatic or symptomatic hyponatremia. Hyponatremia is reported as a side effect among people who take Gabapentin (gabapentin), especially for people who are male, 60+ old, have been taking the drug for < 1 month also take Ondansetron, and have Stress and anxiety. Chronic hyponatremia is associated with fractures [2], which impair the quality of life and the vital prognosis, and severe hyponatremia can occasionally lead to permanent neurological sequelae and death. Carbamazepine and oxcarbazepine are the anticonvulsants most commonly reported to be associated with hyponatremia in patients with epilepsy, although other anticonvulsants, such as eslicarbazepine, sodium valproate, lamotrigine, levetiracetam, and gabapentin, have also been reported to cause hyponatremia . Expert opinion: Carbamazepine and oxcarbazepine are the most common AEDs which induce hyponatremia in patients with epilepsy. Recently, other AEDs, such as eslicarbazepine, sodium valproate, lamotrigine, levetiracetam and gabapentin have also been reported to cause hyponatremia. Do you take Gabapentin and have Hyponatremia? Check whether Hyponatremia is associated with a drug or a condition The risk for hyponatremia was lower during ongoing treatment. Lamotrigine and gabapentin had the lowest risk both during initiation and ongoing treatment and may be advantageous in patients at risk of developing hyponatremia. A study reported that ~14% of thiazide-treated outpatients had hyponatremia (serum sodium concentration <135 mmol/L), whereas age >70 years was associated with a fourfold increase in the risk of hyponatremia. 40 Thiazide-associated hyponatremia is more frequent in patients with heart failure, liver disease or malignancy, and in those taking Carbamazepine and oxcarbazepine are the anticonvulsants most commonly reported to be associated with hyponatremia in patients with epilepsy, although other anticonvulsants, such as eslicarbazepine, sodium valproate, lamotrigine, levetiracetam, and gabapentin, have also been reported to cause hyponatremia . Recently, other AEDs, such as eslicarbazepine, sodium valproate, lamotrigine, levetiracetam and gabapentin have also been reported to cause hyponatremia. Understanding the risk associated with AED-induced hyponatremia and taking effective measures to combat serum sodium imbalance induced by AED therapy are necessary. The most frequent electrolyte disorder in hospitalized patients is hyponatremia [1]. The clinical spectrum in hyponatremia ranges from mild, non-specific symptoms such as fatigue, headache, and gait instability to life-threatening symptoms such as seizures, coma and ultimately death, secondary to brain oedema [2,3]. Pharmaceutical drugs, e.g., thiazide diuretics, antidepressants and The incidence of hyponatremia induced by ESL was not statistically different from that induced by OXC (43% of patients with OXC and 33% with ESL, p > 0.05). Both were associated with hyponatremia more often than CBZ (16%). OXC-induced hyponatremia was dose-related, ESL-induced hyponatremia was not. When taking gabapentin, there are steps you can take to lower the risk of hyponatremia. Eating a balanced diet with enough sodium is key. Eating foods high in sodium is important for keeping electrolytes balanced. When we evaluated the risk of hospitalization with hyponatremia in unmatched users, carbamazepine use and phenytoin use were associated with higher 30-day adjusted RRs of hospitalization with hyponatremia compared to valproic acid use (carbamazepine, RR 4.22 95% CI [2.33–7.64] and phenytoin, RR 2.59 [95% CI 1.36–4.91]) (Table S11). Gandhi et al. found an increased risk associated with newly initiated phenytoin (adjusted RR 4) and also reported it to be increased compared to valproate [6]. In contrast, we found valproate to be associated with a slightly higher OR for hyponatremia. Moreover, ongoing use of valproate, but not of phenytoin, was associated with hyponatremia. In humans, hyponatremia has been associated with dopaminergic agents. 4 An 85-year-old woman with Parkinson disease developed hyponatremia and SIADH after treatment with pramipexole, a dopamine agonist used as anti-Parkinson therapy. 5 Hyponatremia has been noted with the use of levodopa-carbidopa. 4 In another report, hyponatremia also has Hyponatremia (defined as a serum sodium level < 134 mmol/L) is the most common electrolyte abnormality in hospitalized patients. Certain drugs (eg, diuretics, antidepressants, and antiepileptics) have been implicated as established causes of either asymptomatic or symptomatic hyponatremia.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 | |
 | |
 | %3B+open+bars%2C+placebo%3B+colored+bars%2C+therapies%3B+length+of+bars%2C+ranges+in+studies%3B+horizontal+bar%2C+means.+All+of+these+agents+are+generally+well+tolerated+(226).+Hypersensitivity+or+prior+adverse+drug+reactions+to+each+of+these+agents+represent+contraindications.+For+the+SSRI/SNRIs%2C+prior+neuroleptic+syndrome%2C+serotonin+syndrome%2C+and+concurrent+use+of+monoamine+oxidase+inhibitors+are+also+contraindications.+SSRI/SNRIs+should+be+used+with+caution+in+patients+with+bipolar+disease%2C+uncontrolled+seizures%2C+hepatic+or+renal+insufficiency%2C+uncontrolled+hyponatremia%2C+concurrent+use+of+other+SSRI/SNRIs%2C+or+poorly+controlled+hypertension.+These+agents+uncommonly+induce+suicidal+thoughts+within+the+first+few+months+of+treatment.+Preliminary+evidence+suggests+a+possible+increase+in+risk+of+bone+fracture.+Gabapentin+and+pregabalin+may+increase+suicidal+thoughts+and+behaviors%2C+cause+drowsiness+or+dizziness%2C+and+impair+balance+and+coordination.+Pregabalin+may+impair+memory+and+concentration.+Clonidine+is+contraindicated+in+patients+with+low+blood+pressure+and+may+cause+lightheadedness%2C+hypotension%2C+headache%2C+and+constipation%3B+sudden+cessation+of+treatment+can+be+associated+with+significant+increments+in+blood+pressure+(63)..jpg) |
 |  |
 |  |