Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
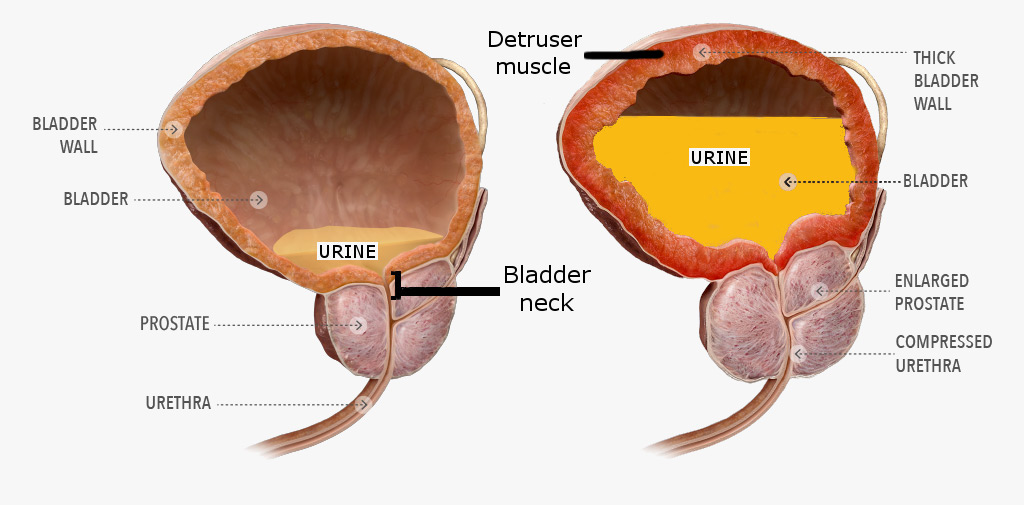
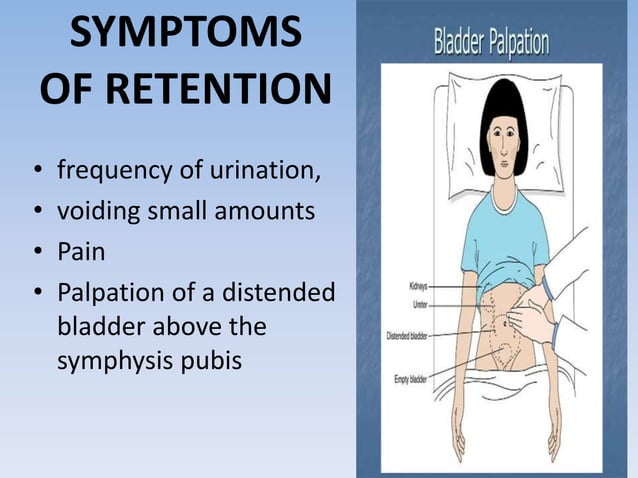
Urinary retention is a condition in which impaired emptying of the bladder results in postvoidal residual urine. It is generally classified into 'acute' or 'chronic' urinary retention. Because of the complex mechanism of micturition, many drugs can interact with the micturition pathway, all via diff Assuming that the urinary symptom was an adverse drug reaction, the GBP was withdrawn and the patient's incontinence completely resolved within 2 days. Several weeks later, a rechallenge with GBP was tried. In the day 1 of GBP use, the subject reported intermittent urinary incontinence. Medication was discontinued and her continence returned. Urinary retention is reported as a side effect among people who take Gabapentin (gabapentin), especially for people who are female, 60+ old, have been taking the drug for < 1 month also take Aspirin, and have Multiple sclerosis. Gabapentin is a first-line agent for neuropathic pain management and has a favorable safety profile. The literature includes a few cases of gabapentin-induced incontinence, and most of them involved patients with epilepsy who were between the ages of 12 and 43 years. Urinary retention is the acute or chronic inability to voluntarily pass an adequate amount of urine. The condition predominantly affects men. The most common causes are obstructive in nature, with Urinary retention (UR) is a urological syndrome characterized by the patient’s inability to empty all the urine from the bladder. It is usually caused by obstructive diseases of the lower urinary tract (eg, benign prostatic hyperplasia [BPH] and urethral stricture), urinary tract infections and/or inflammatory diseases, and neurological disorders (eg, diabetic neuropathy, multiple sclerosis Urinary retention (UR) is a urological syndrome characterized by the patient’s inability to empty all the urine from the bladder. It is usually caused by obstructive diseases of the lower urinary tract (eg, benign prostatic hyperplasia [BPH] and urethral stricture), urinary tract infections and/or inflammatory diseases, and neurological disorders (eg, diabetic neuropathy, multiple sclerosis Gabapentin (GBP) is a structural analog of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) that is commonly used in palliative care for symptom management indications including neuropathic pain syndromes, hiccups, Gabapentin helps with pain and overactive bladder (OAB), but it can cause urinary problems too. Studies show a big drop in OAB symptoms after taking 1200 mg of gabapentin daily for six weeks. This makes gabapentin a good option, but we must watch how patients do. The literature includes a few cases suggesting an association between gabapentin use and urinary incontinence. This case focuses on a previously unrecorded association between gabapentin and increased urinary frequency, which was dose dependent. Gabapentin side effects are usually mild, and they may be less common with gabapentin ER forms. Examples of mild side effects that can happen include: Though rare, serious gabapentin side effects can also happen. Examples include: Gabapentin drug interactions: Along with side effects, gabapentin has possible interactions to know about. Physicians who administer gabapentin should inform their patients about the potential risk of gabapentin-induced incontinence and its negative impact on quality of life. Gabapentin is a first-line agent for neuropathic pain management and has a favorable safety profile. Clinically, even one episode may result in permanent damage to the bladder with longstanding pathologic effects and symptoms . This topic will review issues related to evaluation and management of AUR. The diagnosis and treatment of BPH and chronic urinary retention in females are discussed separately. Gabapentin has been linked to increased urinary retention, meaning that the body is having difficulty emptying the bladder. It can also cause a decrease in urine output, which can be dangerous in people with certain medical conditions. It can also lead to other urinary symptoms, such as frequent urination and burning or pain when urinating. In this analysis of the Italian spontaneous reporting system database, we found new urinary retention signals, requiring further evaluation, for dapagliflozin, gabapentin, lithium, celecoxib, and piroxicam. Some researchers found out that gabapentin can directly affect the functions of your bladder and make it overactive. A 2004 study has revealed that gabapentin has helped relieve the symptoms of overactive bladder in some patients. Urinary retention (UR) is a urological syndrome characterized by the patient’s inability to empty all the urine from the bladder. It is usually caused by obstructive diseases of the lower urinary tract (eg, benign prostatic hyperplasia [BPH] and urethral stricture), urinary tract infections and/or inflammatory diseases, and neurological disorders (eg, diabetic neuropathy, multiple sclerosis Bladder pain syndrome is a chronic disease that manifests as bladder pain, frequency, nocturia, and urgency. Gabapentin, amitriptyline, and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are efficacious treatments for bladder pain syndrome. Gabapentin, is now being prescribed for over active bladder, I sends messages from the brain to the bladder to slow down the muscles, so yes it can reduce how often you go to the toilet, cause fluid retention, and make it difficult to start a flow. Check with your doctor immediately if any of the following side effects occur while taking gabapentin: More common in children. Some side effects of gabapentin may occur that usually do not need medical attention. These side effects may go away during treatment as your body adjusts to the medicine.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |