Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
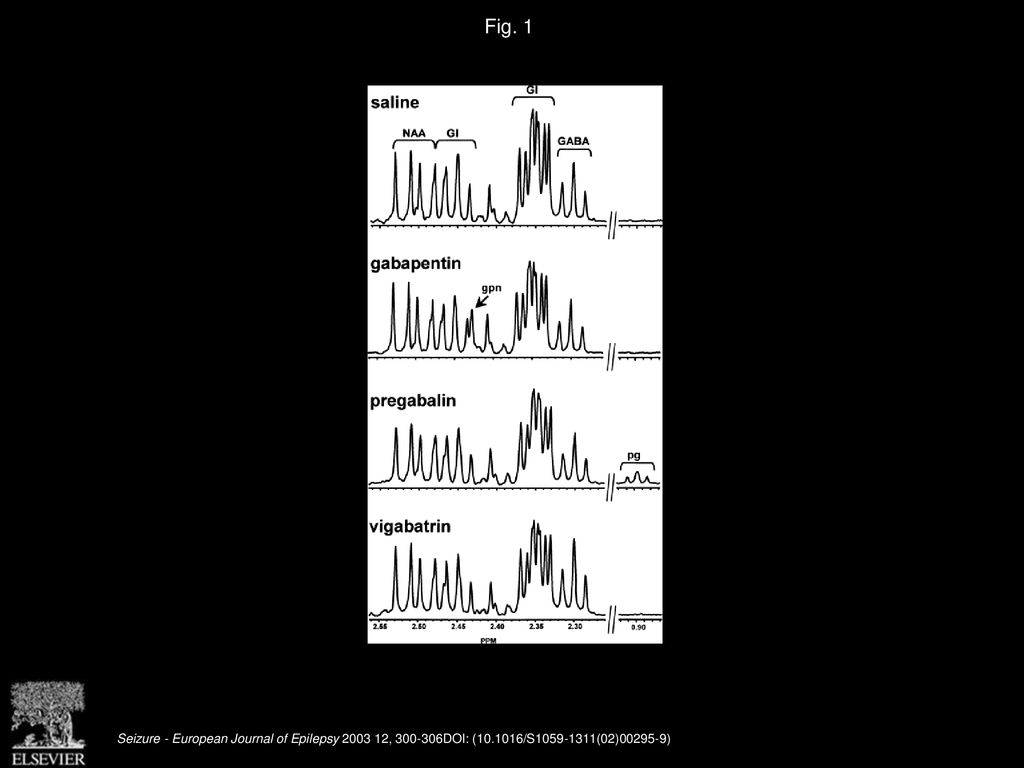
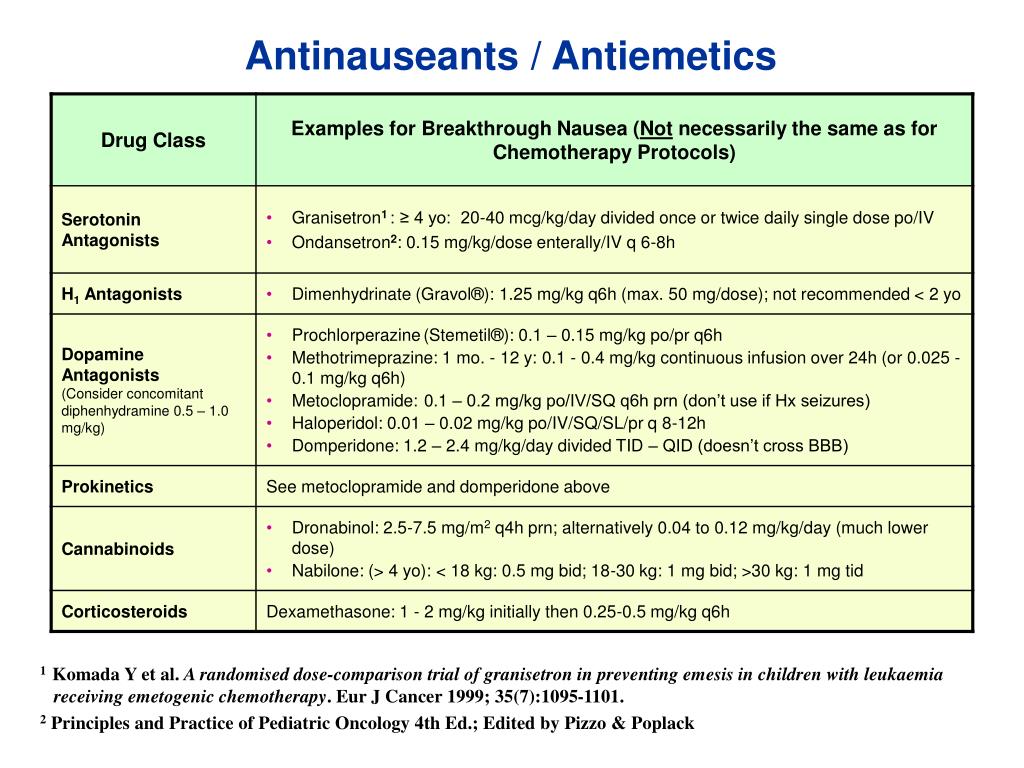
Regular Monitoring: Check your blood sugar levels more frequently, especially when you first start taking gabapentin or when your dosage is adjusted. Communicate with Your Doctor: Inform your doctor about any changes in your blood sugar readings, particularly if you notice consistent or significant increases or decreases. Pharmacokinetics of gabapentin vary widely among patients, particularly those with compromised renal function. Adverse effects may include somnolence, dizziness, ataxia, and fatigue. Gabapentin is used to control seizures, to treat nerve pain that can happen after having had shingles, and to treat a condition called restless legs syndrome. In addition to these FDA-approved uses, doctors sometimes prescribe gabapentin off-label. From a search of the medical literature, 2 articles speak to the effect of gabapentin on blood glucose levels. Backonja and colleagues 5 conducted a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel arm, multicenter study to determine the efficacy and safety of gabapentin as monotherapy for diabetes neuropathy. Yes, Neurontin – Gabapentin is known to cause high WBC (white blood cell) count. How many years can you take gabapentin? According to the World Health Organization (WHO), “the efficacy and safety of gabapentin have not been examined in clinical studies for treatment periods longer than five months.” If you have diabetes or high blood sugar, you probably know some of the things that cause your glucose (another name for blood sugar) to go up. Like a meal with too many carbohydrates, or not Gabapentin (Neurontin®) is an oral antiepileptic agent that is structurally related to the neurotransmitter γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) but it does not interact with GABA receptors in the brain. Its mechanism of action is unknown but it has properties in common with other anticonvulsant medications. Gabapentin - Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant drug commonly used as adjunctive therapy to treat partial seizures. Therapeutic drug monitoring is useful to optimize dose and to avoid toxicity. Draw sample 2 hours after last dose. Chromatography/Mass Spectrometry. Drug (and Some common Detectable duration Urine cut–off points Toxic Blood reference trade name) street names in urine after for reporting positive blood level (therapeutic) range last dose or limit of quantitation* Pentobarbital Goof balls, 2 days 425 ng/mL (S)(1) >11 µg/mL <10 µg/mL (Nembutal) Downers, 200 ng/mL (C)(3) Collect the specimen before the next dose (trough). Unacceptable conditions: Whole blood, gel separator tubes. Clinical Info. Monitoring concentrations in serum or plasma to assess drug therapy and patient compliance. Blood glucose (blood sugar) testing: There are a handful of tests that can help you understand your blood glucose levels. Check out the most common tests for diabetes. Early signs of diabetes: Learn how to recognize the signs and symptoms of diabetes. Early management and treatment can help prevent long-term health problems. Gabapentin: Gabapentin is indicated for postherpetic neuralgia and serves as adjunctive therapy for managing partial seizures (with or without secondary generalization) in adults and pediatric patients aged 3 or older. Experience to date indicated that gabapentin is safe and relatively nontoxic. Therapeutic ranges are based on specimens collected immediately before the next dose (ie, trough). Most epileptic patients show a response to the drug when the trough concentration is in the range of 2 to 20 mcg/mL. In cases in which gabapentin was determined to be a cause of death, the blood concentrations ranged from 1.1 to 134.0 mg/L. Persons who died of a gabapentin-related drug death were prescribed the drug legitimately 91.4% of the time, with 84.2% of those also having a known prior history of abuse or misuse of prescription medications. Gabapentin is an antiepileptic drug that is effective in treating seizures, neuropathies, and a variety of neurological and psychological maladies. Although designed as a gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) analogue, gabapentin does not bind to GABA receptors, nor does it affect the neuronal uptake or degradation of GABA. Gabapentin is an antiepileptic drug effective as add-on therapy in treating complex partial seizures and partial seizures with secondary generalization. Gabapentin does not bind to serum proteins and does not exhibit pharmacokinetic interactions with other antiepileptic drugs. Test sent to Mayo Clinic Laboratories. Gabapentin concentrations determined in the detailed case study described herein were: 20 mg/L (antemortem blood); 20 mg/L (postmortem peripheral blood); and 18 mg/L (central blood). A liver specimen was not available for analysis. A blood ethanol level of 0.05% (w/v), and a therapeutic concentration of quetiapine were also detected. Learn the differences and similarities between gabapentin and an opioid medication. 1. Dizziness is the No. 1 side effect of gabapentin. In studies, almost 30% of people taking gabapentin for postherpetic neuralgia, and over 15% of people taking it for seizures, experienced dizziness. Dizziness is similarly common with Horizant. Gabapentin is most often dosed based on the patients renal (kidney) function. The prescribing information for the medication does not even mention therapeutic blood levels to watch for. Over time however, certain blood levels have been determined. Although blood glucose fluctuations are a possible adverse drug reaction (ADR) of gabapentin 1, hypoglycaemia in relation to this drug was found in just one publication 3. We received six cases of (severe) hypoglycaemia in both diabetic and non-diabetic patients exposed to gabapentin, which occurred between July 2002 and July 2012.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |