Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
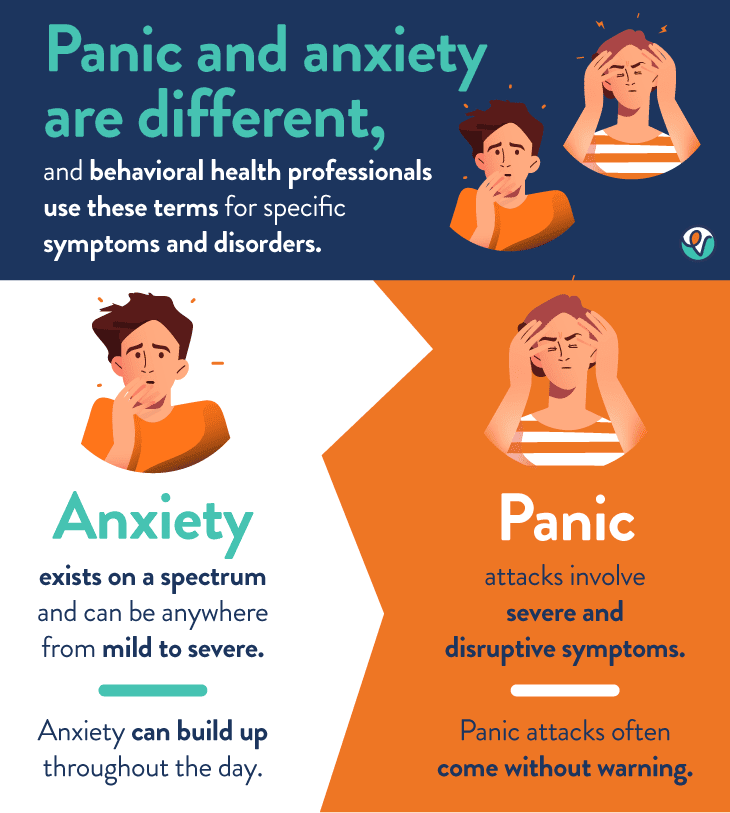
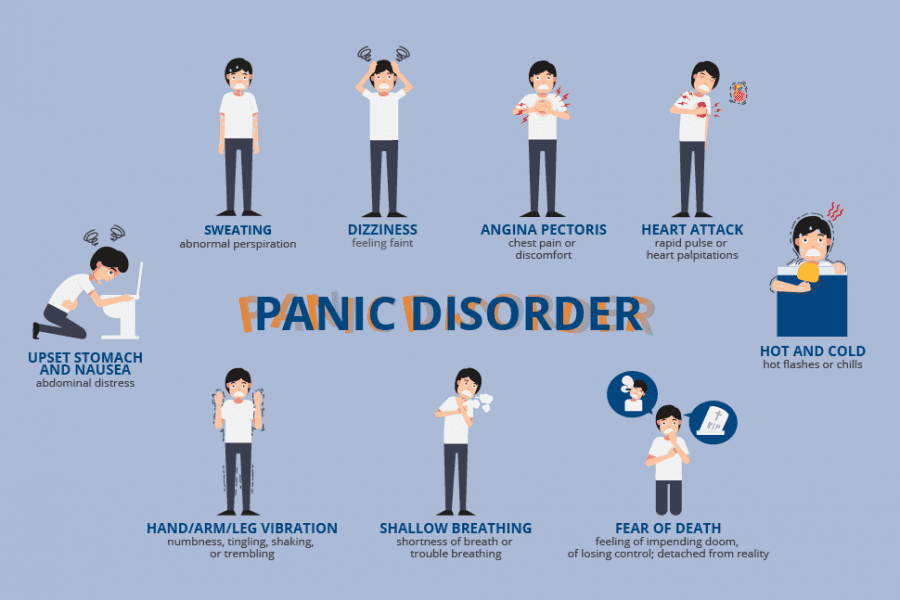
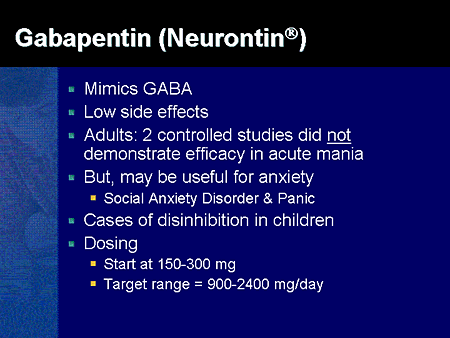
Abstract. Anxiety disorders are the most prevalent psychiatric disorders and a leading cause of disability. While there continues to be expansive research in posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD), depression and schizophrenia, there is a relative dearth of novel medications under investigation for anxiety disorders. Uncover essential facts about Gabapentin's potential to ease anxiety symptoms. Explore how this medication offers relief, its mechanisms, and the latest research. Discover the benefits, side effects, and expert insights for a comprehensive understanding of this promising treatment option. Gabapentin (Neurontin) is FDA approved to treat seizure disorder and nerve pain from shingles. But it’s also used off-label to treat many other conditions, including anxiety, nerve pain from diabetes, and hot flashes. Previously presumed to have a low abuse and misuse potential, gabapentin has been commonly prescribed for the treatment of anxiety disorders. 10, 11 While pregabalin has shown efficacy for generalized anxiety disorder (GAD) in two RCTs, 12, 13 the authors could find no such RCTs done for gabapentin. 9 One randomized, double-blind, placebo While it's true that GABA plays a role in anxiety, anxiety is complex, and researchers are still trying to figure out how and if gabapentin might work to ease symptoms of moderate or severe anxiety. GABA helps regulate anxiety and stress responses in the brain, so increasing levels can cause a calming effect, reducing feelings of anxiety and promoting relaxation. While more research is warranted, some studies show certain types of anxiety and depression can be helped with Gabapentin, including: In this review, the author examines the evidence for psychopharmacologic treatments among adults for generalized anxiety disorder, panic disorder, and social anxiety disorder derived from clinical trials. For each disorder, major categories of drugs are reviewed, and then the evidence-based medications in each category are discussed. The author reviews key safety and tolerability Gabapentin can help control seizures as well as nerve pain from shingles. It may sometimes cause side effects, especially if you misuse it. Learn more. Some patients report feeling like they’re on an emotional rollercoaster, complete with unexpected loops and sudden drops. Next up on our tour of gabapentin’s mental funhouse is anxiety and restlessness. It’s like your brain decided to drink a triple espresso and then immediately regretted it. Gabapentin users with GAD have been demonstrated to have fewer irritable episodes, cut back on alcohol use as a self-medication, also experience fewer symptoms of depression, feel less anxious when thinking about the future, and improve their phobic avoidance (going out in public more often). Gabapentin, a medication commonly prescribed for various conditions including anxiety, can sometimes lead to an unexpected and challenging experience known as rebound anxiety when discontinued. This phenomenon underscores the complex relationship between anxiety disorders, medication, and the body’s response to treatment changes. Although evidence is limited, some studies show gabapentin can help with anxiety symptoms. One 2020 review suggests gabapentin may help with different types of situational anxiety, including: For Anxiety "I took 300 mg of gabapentin one time for panic attacks and anxiety. My psychiatrist prescribes this to use when anxious symptoms become severe. After several hours, I do feel that it helped my anxiety briefly, however, I became very drowsy. If you struggle with anxiety, you may be prescribed gabapentin to help to control your symptoms. Here’s what you need to know about anxiety, how gabapentin might help, how long it might take to start working, and what side effects or special precautions you need to be aware of while under medication. Have you considered clinical trials for Anxiety? Gabapentin is a good anti-anxiety medication but it can cause day time sedation (which you had). The way you have tapered off Gabapentin suggests that the current symptoms you are experiencing cannot be a withdrawal state. Rather it is anxiety which is manifesting in such a manner. The normal stress you have mentioned may not be normal for you. Gabapentin may take longer to produce noticeable effects, and its benefits for anxiety may emerge more gradually as the dose is titrated. Both medications share similarities in that they help modulate excitatory neurotransmitters, leading to a calming effect that can alleviate anxiety symptoms. Gabapentin isn't generally associated with causing anxiety in adults, but similar adverse reactions have been reported with the drug, such as: Feeling 'abnormal.' More commonly, gabapentin is associated with sedative and CNS (central nervous system) depressant effects. 11. Anxiety and Panic Attacks. While gabapentin is frequently prescribed by doctors as a treatment for anxiety, it has been reported that it might actually cause further anxiety or panic attacks, especially if the person has a preexisting psychiatric disorder. 12. Violent behavior. Violent behavior is a dangerous side effect of taking gabapentin. The potential benefits of gabapentin for various sleep issues are wide-ranging. It has shown promise in addressing insomnia, particularly in individuals with chronic pain conditions or anxiety disorders. Gabapentin may also be helpful for those experiencing restless leg syndrome (RLS), a condition that can significantly disrupt sleep.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |