Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
%2C+Newcastle+upon+Tyne%2C+UK+2+Medical+Toxicology+Centre%2C+Newcastle+University%2C+Newcastle+upon+Tyne%2C+UK..jpg) |  |
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Health-How-To-Check-Your-Heart-Rate-67f1e3c1f4a9494d9b165b8d34d0144e.jpg) | :max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/symptoms-of-iron-deficiency-5188449-V1-8373d720093241b993bc13816e3fb63c.png) |
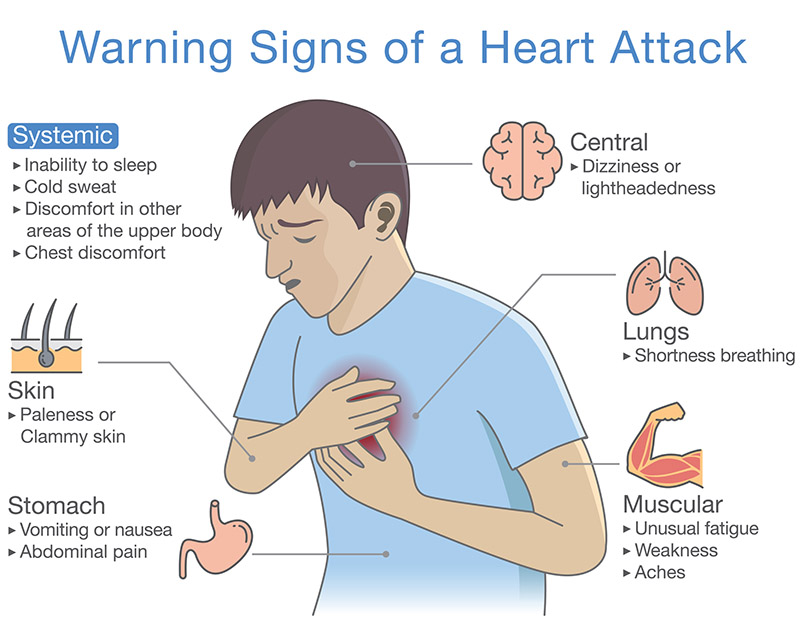 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
(The medical term for a fast heart rate is tachycardia.) If you have a fast heart rate because of a medication, you also may feel: Lightheaded or dizzy; Short of breath; Chest pain; Heart palpitations GD-Gabapentin: Gabapentin belongs to the class of medications called anti-epileptics. It is used in combination with other seizure control medications to manage and prevent seizures associated with epilepsy. Gabapentin does not cure epilepsy and only works to control seizures as long as the medication is taken. Gabapentin works by affecting the transmission of nerve signals in the brain. Gabapentin is fairly safe when you use it correctly. It does come with some possible side effects, though. People who misuse this drug are also at risk of additional side effects. Gabapentin Gabapentin is a commonly used medication used as an anti-convulsant or analgesic. The well-known side-effects of gabapentin are dizziness, drowsiness and fatigue. In rare cases, it can lead to development of new onset congestive heart failure (CHF) or decompensation of pre-existing CHF. Often, edema from gabapentin is mild and doesn’t cause serious issues. But for people with heart conditions, it can put excess stress on the heart. It can also be a problem for people with kidney or liver problems . Although the most frequent side effects of gabapentin are associated with the central nervous system, gabapentin can also affect the cardiovascular system. Case reports and observational studies have showed that gabapentin can be associated with increased risk of atrial fibrillation. Oral and intravenous gabapentin can markedly attenuate blood pressure (BP) in hypertensive rats. The nucleus tractus solitarii (NTS) is the primary integrative center for cardiovascular control and other autonomic functions in the central nervous system. Then, unilateral microinjection of gabapentin into the NTS before and after N(ω)-nitro-L-arginine methyl ester (L-NAME) treatment whether to change blood pressure and heart rate. Results: Unilateral microinjection of gabapentin into the NTS produced prominent dose-related depressor and bradycardic effects in SHR rats. Summary: Heart rate increased is reported as a side effect among people who take Gabapentin (gabapentin), especially for people who are female, 60+ old, have been taking the drug for < 1 month also take Tylenol, and have Rheumatoid arthritis. Gabapentin may affect the rate of your heartbeats in some instances. It has been shown to both increase and decrease the heart rate in different settings. A rapid heartbeat is a withdrawal symptom of the medication. Most heart-affecting side effects can be avoided with proper use and medical care. In the first experiment, we found that i.v. GBP significantly decreased BP, HR, maximal LV pressure, and maximal and minimal dP/dt, whereas it increased IRP-AdP/dt, Tau, systolic, diastolic, and cycle durations (* p < 0.05 and ** p < 0.01 vs. baseline; n = 4). Background Gabapentin and pregabalin are commonly prescribed medications to treat pain in patients with diabetic neuropathy. Gabapentin and pregabalin can cause fluid retention, which is hypothesized to be associated with cardiovascular diseases. However, whether long-term use of gabapentin and pregabalin is associated with adverse cardiovascular diseases remains unknown. This study aims to Yes, gabapentin can cause heart palpitations. Some people have experienced their heart beating too hard and fast after taking gabapentin. This side effect is most commonly experienced after an increase or decrease in dose, or when you start on a dose which is too high for you. While research indicates that gabapentin can actually reduce blood pressure and heart rate in some cases, there are also potential risks related to blood pressure, especially with long-term use and withdrawal. The key lies in understanding the nuances of how gabapentin interacts with the body, its potential side effects, and individual patient 1. Can Gabapentin cause heart palpitations? 2. Can Gabapentin cause high blood pressure? 3. Should I stop taking gabapentin if I develop swelling in my legs? 4. Can gabapentin cause blood clots? 5. Can I take gabapentin with heart medications? 6. Can gabapentin cause chest pain? 7. Does Gabapentin affect heart rate? 8. Gabapentin and pregabalin are commonly prescribed medications to treat pain in patients with diabetic neuropathy. Gabapentin and pregabalin can cause fluid retention, which is hypothesized to be associated with cardiovascular diseases. However, Our recent study showed the risk of adverse cardiovascular events increased in diabetic neuropathy patients who were prescribed gabapentin or pregabalin. Here, we investigated whether the prescription of gabapentin or pregabalin has similar cardiovascular risk in patients with fibromyalgia. Therapeutic effects of gabapentin in epilepsy or pain seem to be based on the attenuation of neuronal hyperactivity in various brain circuits by acting on α 2 δ subunit of VDCCs. 40 Gabapentin also reduced hemodynamic response to the endotracheal intubation which may cause SNS activation and catecholamine release, resulting in acute increase While studies suggest that gabapentin can lower blood pressure and heart rate acutely, it is also listed as a potential side effect to cause hypertension, or high blood pressure, particularly with long term use. 4. Can gabapentin cause heart palpitations? Yes, abnormal heartbeats or heart palpitations are a possible side effect of gabapentin Common side effects of gabapentin include: flulike symptoms such as fever or body aches. Rare but serious side effects of gabapentin include: changes in memory, ability to concentrate, or personality. Gabapentin may cause breathing problems in people who use opioid pain medicines and those with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
%2C+Newcastle+upon+Tyne%2C+UK+2+Medical+Toxicology+Centre%2C+Newcastle+University%2C+Newcastle+upon+Tyne%2C+UK..jpg) |  |
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Health-How-To-Check-Your-Heart-Rate-67f1e3c1f4a9494d9b165b8d34d0144e.jpg) | :max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/symptoms-of-iron-deficiency-5188449-V1-8373d720093241b993bc13816e3fb63c.png) |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |