Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
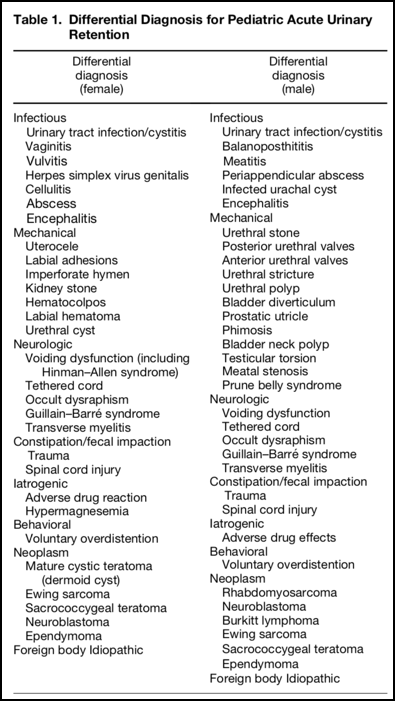
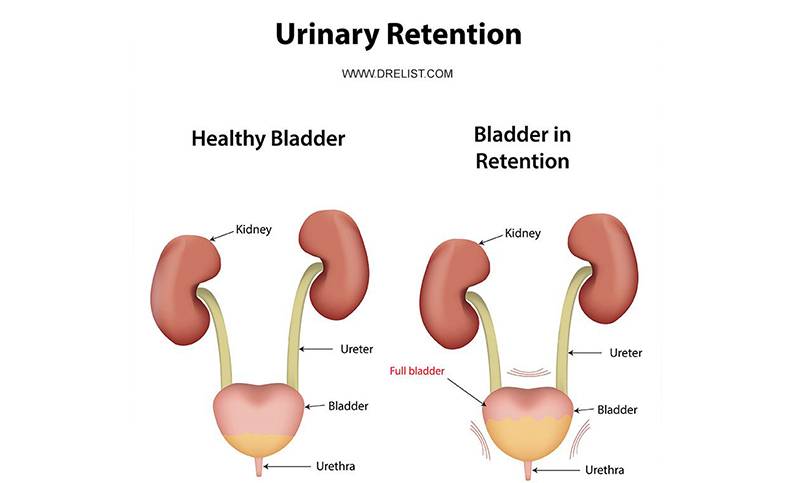
Note: This document provides detailed information about Neurontin Side Effects associated with gabapentin. Some dosage forms listed on this page may not apply specifically to the brand name Neurontin. Applies to gabapentin: oral capsule, oral solution, oral suspension, oral tablet, oral tablet extended release 24 hr. Serious side effects of Drug-induced urinary retention is generally treated by urinary catheterization, especially if acute, in combination with discontinuation or a reduction in dose of the causal drug. Acute urinary retention (AUR) is the inability to voluntarily pass urine. It is the most common urologic emergency [ 1 ]. In males, AUR is most often secondary to benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH); AUR is rare in females [ 2,3 ]. To the best of our knowledge, the literature includes just 5 cases of gabapentin-induced incontinence, 3 of which involved both rectal and urinary incontinence and 2 involved only urinary incontinence. Table 1: Drug Classes Causing Urinary Retention Drugs causing urinary retention Example medications Mechanism Anticholinergic drugs - TCAs (amitriptyline, nortryptiline) - tiotropium (Spiriva) - diphenhydramine (benadryl) - dimenhydrinate (gravol) Impaired detrusor contraction, leading to poor bladder emptying. Opioids All opioids Urinary retention is the acute or chronic inability to voluntarily pass an adequate amount of urine. The condition predominantly affects men. The most common causes are obstructive in nature, with The literature includes a few cases suggesting an association between gabapentin use and urinary incontinence. This case focuses on a previously unrecorded association between gabapentin and increased urinary frequency, which was dose dependent. In the day 1 of GBP use, the subject reported intermittent urinary incontinence. Medication was discontinued and her continence returned. One year later, in the follow-up, the subject remained continent. Conclusions: Only a few cases with GBP-associated urinary incontinence have been reported in the literature. Gabapentin has been linked to increased urinary retention, meaning that the body is having difficulty emptying the bladder. It can also cause a decrease in urine output, which can be dangerous in people with certain medical conditions. It can also lead to other urinary symptoms, such as frequent urination and burning or pain when urinating. Ten days after she began taking gabapentin to relieve her pain, she experienced daily urinary incontinence. In another instance, a 63-year-old female patient was diagnosed with complex regional pain syndrome, and seven days after the initiation of gabapentin therapy, urinary incontinence developed. Urinary retention is reported as a side effect among people who take Gabapentin (gabapentin), especially for people who are female, 60+ old, have been taking the drug for < 1 month also take Aspirin, and have Multiple sclerosis. 4. Can Gabapentin Cause Urinary Retention or Incontinence? 🚽. Gabapentin’s sedative effects may indirectly alter urination behavior: Urinary Retention: Some dogs might urinate less frequently due to gabapentin’s calming effects. Incontinence: Rare but possible if gabapentin causes significant sedation or relaxation of the bladder muscles. When you stop taking gabapentin, you'll need to reduce your dose gradually to avoid withdrawal symptoms. Do not stop taking gabapentin without talking to your doctor. Talk to your doctor if you're concerned about becoming physically dependent on gabapentin. Other side effects. These are not all the side effects of gabapentin. Urinary retention (UR) is a urological syndrome characterized by the patient’s inability to empty all the urine from the bladder. It is usually caused by obstructive diseases of the lower urinary tract (eg, benign prostatic hyperplasia [BPH] and urethral stricture), urinary tract infections and/or inflammatory diseases, and neurological disorders (eg, diabetic neuropathy, multiple sclerosis Gabapentin (GBP) is a structural analog of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) that is commonly used in palliative care for symptom management indications including neuropathic pain syndromes, hiccups, cough, and anxiety. An uncommon adverse effect of GBP is urinary incontinence (UI). We report the case Gabapentin and Urinary Retention. To determine whether there is any evidence to support an (causal) association between the administration of gabapentin and the Gabapentin, is now being prescribed for over active bladder, I sends messages from the brain to the bladder to slow down the muscles, so yes it can reduce how often you go to the toilet, cause fluid retention, and make it difficult to start a flow. Uncommon (0.1% to 1%): Hematuria, dysuria, urinary frequency, cystitis, urinary retention, vaginal hemorrhage, amenorrhea, dysmenorrhea, menorrhagia; Frequency not reported: Sexual dysfunction (including changes in libido, ejaculation disorders, and anorgasmia) Hematologic. Common (1% to 10%): Leucopenia, purpura Gabapentin side effects are usually mild, and they may be less common with gabapentin ER forms. Examples of mild side effects that can happen include: Vertigo (dizziness) Feeling fatigued or sleepy. Fluid retention. Trouble balancing or controlling movement. Diarrhea or constipation. Nausea and vomiting. Brain fog. Headache. Weight gain. Dry mouth Urinary retention (UR) is a urological syndrome characterized by the patient’s inability to empty all the urine from the bladder. It is usually caused by obstructive diseases of the lower urinary tract (eg, benign prostatic hyperplasia [BPH] and urethral stricture), urinary tract infections and/or inflammatory diseases, and neurological disorders (eg, diabetic neuropathy, multiple sclerosis
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |