Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
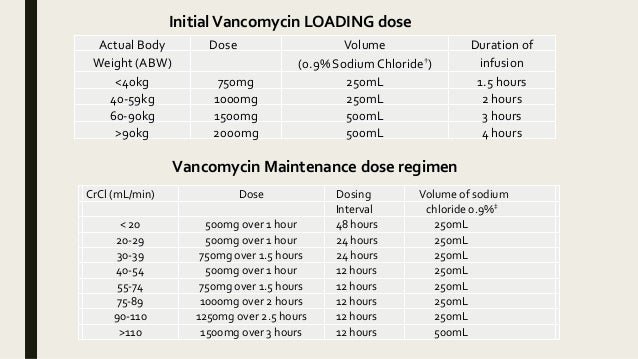
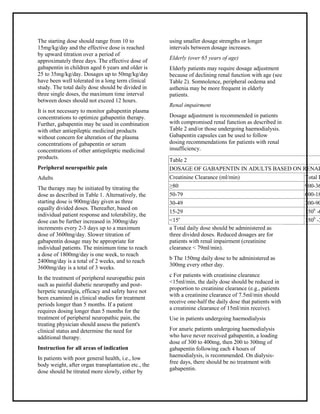
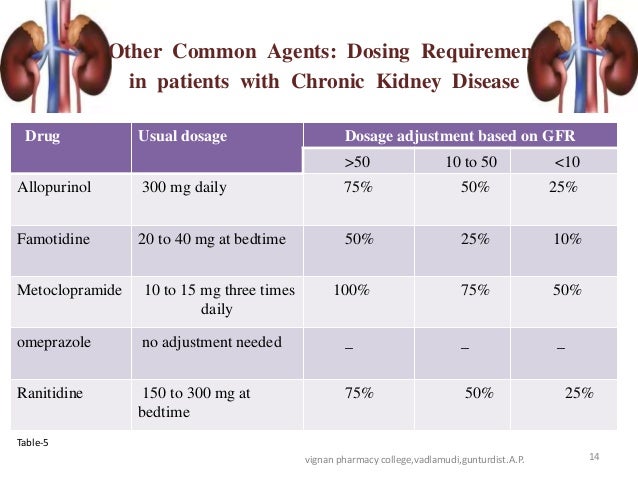
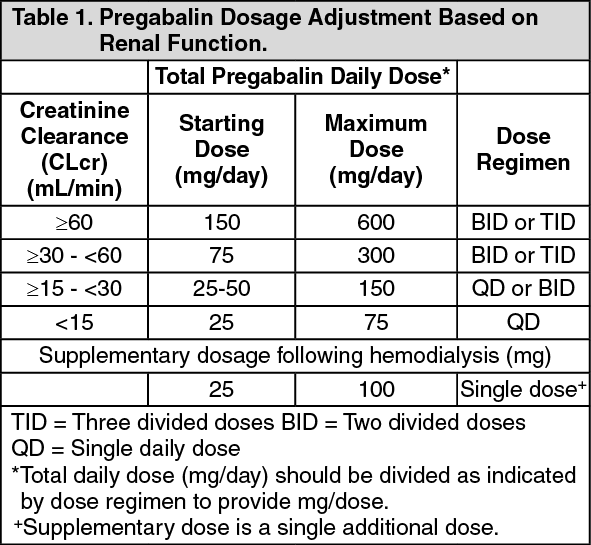
TID = Three times a day; BID = Two times a day; QD = Single daily dose. a For patients with creatinine clearance <15 mL/min, reduce daily dose in proportion to creatinine clearance (e.g., patients with a creatinine clearance of 7.5 mL/min should receive one-half the daily dose that patients with a creatinine clearance of 15 mL/min receive). Impaired kidney function (reduced creatinine clearance) increases drug accumulation, raising side effects risk. So, it's important to change the dose if your kidneys aren't working right. Levels of Kidney Problems: Dosing of Gabapentin and Pregabalin According to Creatinine Clearance as Compared to Manufacturer Recommendations. CrCl ≥60mL/min, n = 137 CrCl <60mL/min, n = 97 In the presence of cimetidine at 300 mg four times a day (N=12), the mean apparent oral clearance of gabapentin fell by 14% and creatinine clearance fell by 10%. Thus, cimetidine appeared to alter the renal excretion of both gabapentin and creatinine, an endogenous marker of renal function. For patients with creatinine clearance <15 mL/min, reduce daily dose in proportion to creatinine clearance (e.g., patients with a creatinine clearance of 7.5 mL/min should receive one-half the daily dose that patients with a creatinine clearance of 15 mL/min receive). Gabapentin Dosage Based on Renal Function. For patients with creatinine clearance <15 mL/min, reduce daily dose in proportion to creatinine clearance (e.g., patients with a creatinine clearance of 7.5 mL/min should receive one-half the daily dose that patients with a creatinine clearance of 15 mL/min receive). Gabapentin dosing guidelines for adult with renal impairment are summarized in Table 3. Dosing guidelines for gabapentin immediate-release are also applicable for adolescents 12 years of age and older with renal impairment. Gabapentin elimination half-life is 5 to 7 hours and is unaltered by dose or following multiple dosing. Gabapentin elimination rate constant, plasma clearance, and renal clearance are Pregabalin’s apparent total clearance is 67–81 mL/min in young healthy subjects and is therefore thought to undergo tubular reabsorption to some extent. 2 Hemodialysis (HD) removes approximately 35% of gabapentin and 50%–60% of pregabalin, where supplemental doses are generally recommended post-HD. 1, 2 Renal dose adjustments for gabapentin and pregabalin are ubiquitously evident in the medical literature. All manufacturers for these branded and generic dosage forms list dosing recommendations relative to creatinine clearance (CrCl) for both medications . 1,2 However, the basis of these recommendations has not been well articulated. For patients with creatinine clearance <15 mL/min, reduce daily dose in proportion to creatinine clearance (e.g., patients with a creatinine clearance of 7.5 mL/min should receive one-half the daily dose that patients with a creatinine clearance of 15 mL/min receive). b . Patients on hemodialysis should receive maintenance doses based on CrCl <15 mL/minute: Reduce daily dose in proportion to creatinine clearance based on dose for creatinine clearance of 15 mL/minute (eg, reduce dose by one-half [range: 50 to 150 mg/day] for CrCl 7.5 mL/minute) The mean gabapentin half-life ranged from about 6.5 hours (patients with creatinine clearance greater than 60 mL/min) to 52 hours (creatinine clearance less than 30 mL/min) and gabapentin renal clearance from about 90 mL/min (greater than 60 mL/min group) to about 10 mL/min (less than 30 mL/min). Manufacturer advises reduce dose to 150‒300 mg daily in 3 divided doses if creatinine clearance is less than 15 mL/minute (150 mg daily dose to be given as 300 mg in 3 divided doses on alternate days)—further dose reductions may be required in proportion to creatinine clearance, consult product literature. Hemodialysis (CrCl ; 15 mL/min): Administer supplemental dose (range 125-350 mg) posthemodialysis, after each 4 hr dialysis interval; further dose reduction should be in proportion to CrCl (eg, CrCl of 7.5 mL/min should receive one-half daily posthemodialysis dose) Drug dosing requirements for antihypertensives in patients with chronic kidney disease are listed in Table 4. 4, 5 Thiazide diuretics are first-line agents for treating uncomplicated hypertension In adults with postherpetic neuralgia, Gabapentin may be initiated on Day 1 as a single 300 mg dose, on Day 2 as 600 mg/day (300 mg two times a day), and on Day 3 as 900 mg/day (300 mg three times a day). The dose can subsequently be titrated up as needed for pain relief to a dose of 1800 mg/day (600 mg three times a day). Dose recommendations in relation to renal function given in the SPCs are in general based on endogenous creatinine clearance or estimated creatinine clearance according to the CG equation (including P-creatinine, age, sex and weight) in ml/min, an absolute value of clearance.1 This is also the case for dabigatran.38 However, different equations Renal function (creatinine clearance mL/min) Maximum daily dose mg (in 3 divided doses) ≥80: 3600 50-79: 600-1800: 30-49: 300-900: 15-29: 150-600 (150 mg daily dose to be given as 300 mg in 3 divided doses on alternate days) 15: 150-300 (150 mg daily dose to be given as 300 mg in 3 divided doses on alternate days). Further dose reductions may Patients present with symptoms such as increased sedation, confusion, unsteady gait, myoclonus, ataxia, episodic leg spasm, asterixis and tremulousness. 59 Recommendations for dose reductions based on creatinine clearance are available. 60 Patients on haemodialysis might require supplemental doses post-dialysis because dialysis removed
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |