Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
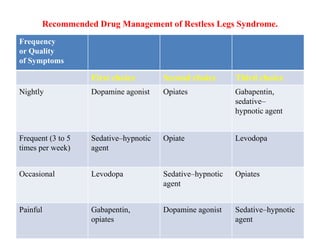 |  |
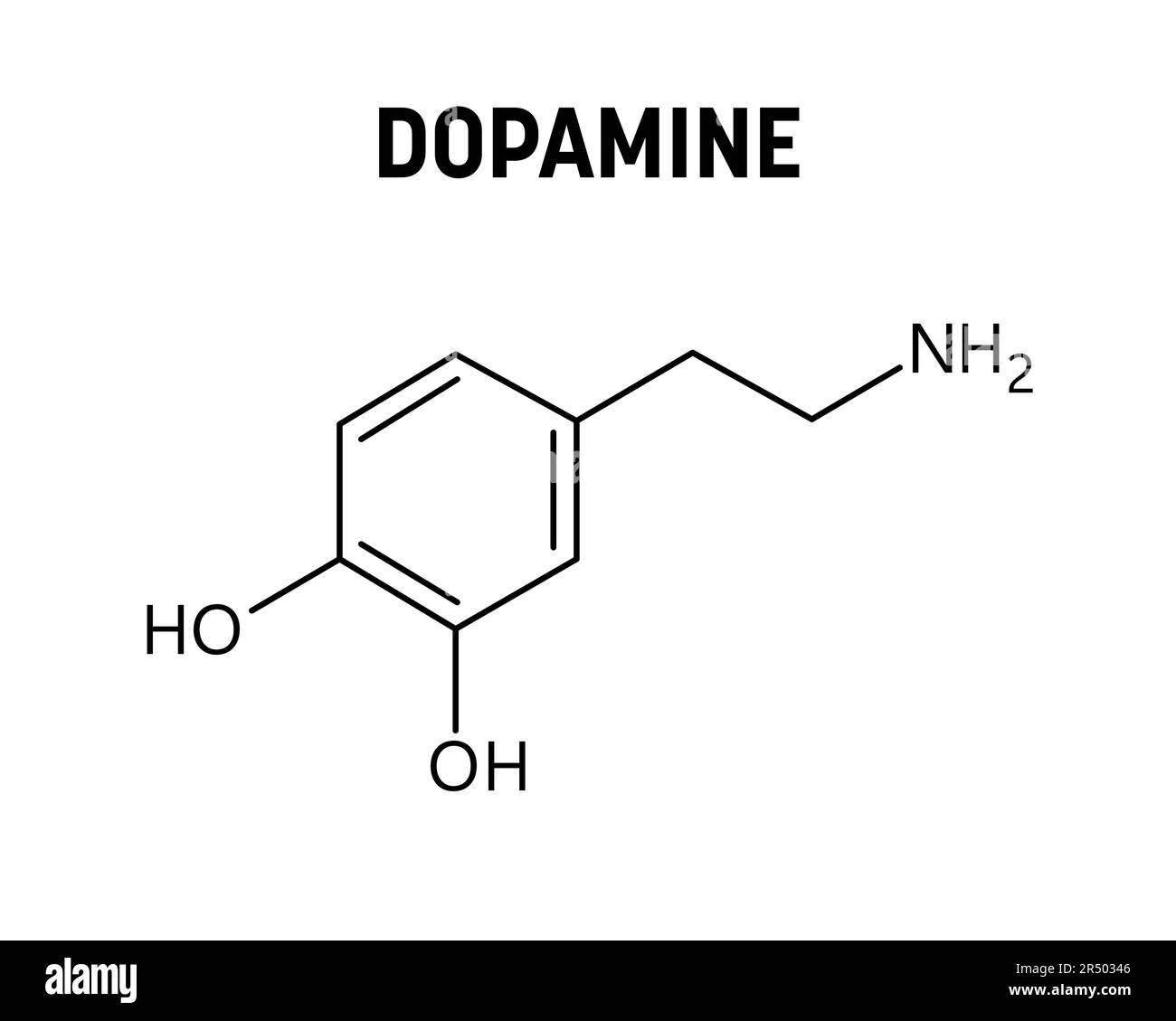
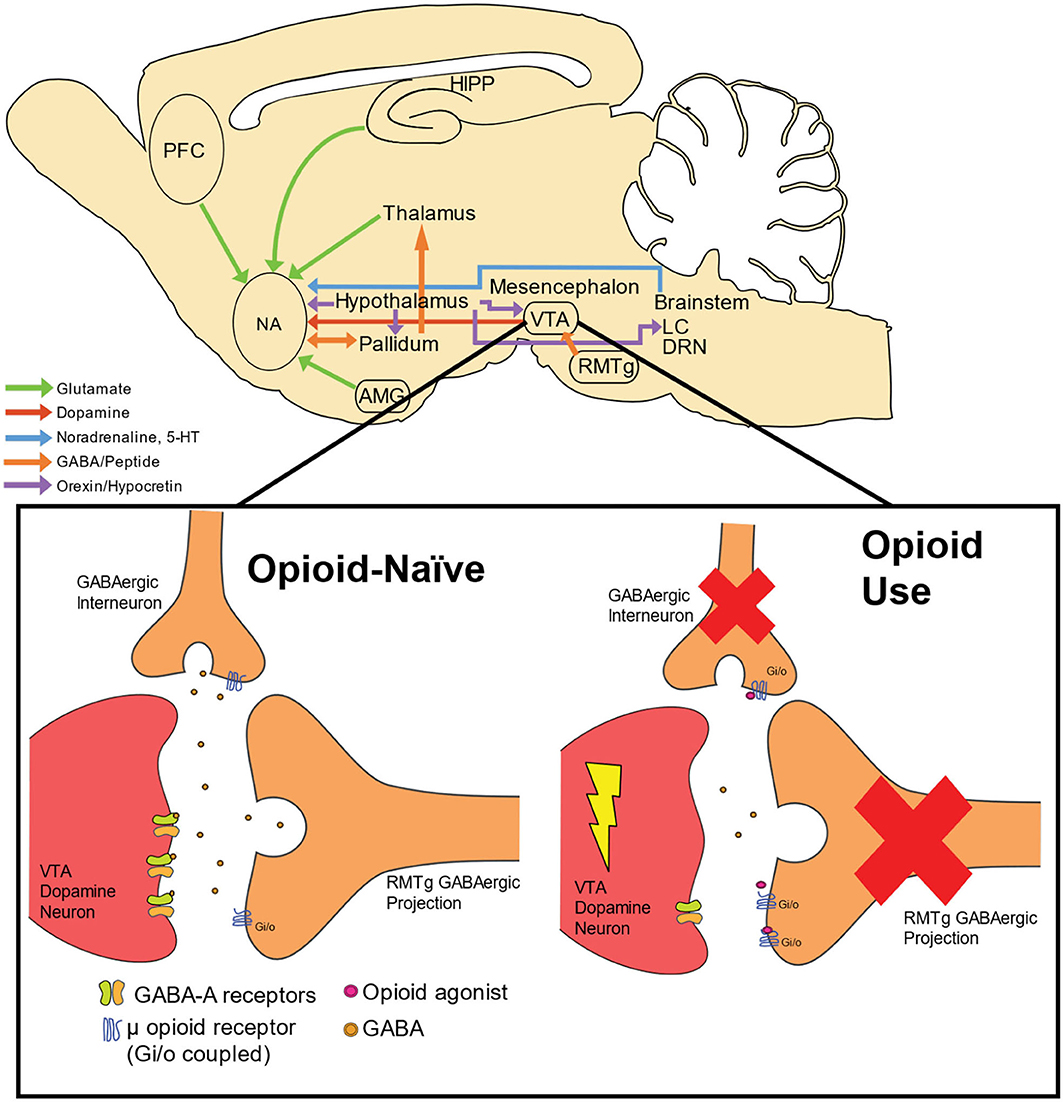
The dopamine reduction from gabapentin would be like a fraction of 1% of the dopamine reduction from the antipsychotics. I'd imagine gabapentin's dopamine modulating effects will help keep your dopamine more stable if you come off the antipsychotic, after being on them your dopamine receptors get very upregulated and sensitive. Accumulating evidence indicates that gabapentin (GBP), a prescription drug, is prone to misuse, abuse, withdrawal, and dependence. Commonly, drugs of abuse modulate the dopaminergic system to Accumulating evidence indicates that gabapentin (GBP), a prescription drug, is prone to misuse, abuse, withdrawal, and dependence. Commonly, drugs of abuse modulate the dopaminergic system to induce addiction. Research has shown that gabapentin exerts a modulating effect at neuronal receptor sites, inhib- iting the release of the neurotransmitters dopamine (5), serotonin and norepinephrine (6) and resulting in in- creased GABA concentrations in various locations throughout the brain (7). Drugs like gabapentin can mess with your dopamine levels, and with prolonged use, they may be the only source of dopamine in your body. As a result, it is highly addictive. Gabapentin, also known by the brand name of Neurontin, is a prescription pain medication that belongs to its class of drugs known as gabapentinoids. Gabapentin enacarbil is a prodrug of gabapentin, converted to gabapentin after absorption, and thus avoids the nonlinear pharmacokinetics of gabapentin. It is administered as a single daily dose of 600 mg (300 mg in patients older than 65 years) at 5 pm to target adequate therapeutic levels at bedtime. In contrast, new evidence supporting three alpha-2-delta ligand calcium channel blockers — gabapentin enacarbil, gabapentin, and pregabalin — led the task force to support them as strong recommendations for RLS treatment. These medications are not associated with the augmentation of RLS symptoms observed with the dopaminergic agents. Abstract Introduction. Recent years have seen a dramatic escalation of off-label prescribing for gabapentin and pregabalin (gabapentinoids) owing in part to generic versions of each being released over the past two decades, but also in part as a response to increasing calls for multimodal and non-opioid pain management strategies. Gabapentin (GBP) was used to explore the chronic analgesic treatment that could reverse pain-related depression. To investigate the in vivo variations of VTA DA neuron firing and LFP, multichannel acquisition processor system was used. Though it does not directly act on dopamine or serotonin receptors, studies do show that gabapentin can increase total blood levels of serotonin in some people. So it’s a very interesting drug that you will see a lot and for a variety of reasons. We’ll talk more about the uses of gabapentin in a bit. R: Routes The AASM now recommends the alpha-2-delta ligand medications gabapentin enacarbil (the other FDA-approved drug for RLS), gabapentin, and pregabalin (the latter two when prescribed off-label) as first-line therapy and recommends against the three FDA-approved dopamine agonists—pramipexole, rotigotine, and ropinirole—as well as dopaminergic GABA’s activity has vital consequences for dopamine function and subsequent behavior, especially those relating to outcomes that are motivationally relevant for the individual. It is suggested Gabapentin is a structural analog of the inhibitory neurotransmitter γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA). Its anticonvulsant, analgesic and anxiolytic properties suggest that it increases GABAergic inhibition; however, the molecular basis for these effects is unknown as gabapentin does not directly modify GABA type A (GABA A) receptor function, nor does it modify synaptic inhibition. Ativan, a benzodiazepine that enhances GABA activity, can influence dopamine release and contribute to its addictive potential. Similarly, gabapentin and dopamine interactions highlight how drugs designed to mimic GABA can have complex effects on other neurotransmitter systems. Dopamine (DA) is the key regulator of reward behavior. The DA neurons in the ventral tegmental area (VTA) and their projection areas, which include the prefrontal cortex (PFC), nucleus accumbens (NAc), and amygdala, play a primary role in the process of reward-driven behavior induced by the drugs of While some studies suggest that gabapentin may indirectly increase dopamine levels in certain brain regions, others have found no significant effect or even a potential decrease in dopamine activity. Although the cellular mechanisms of pharmacological actions of gabapentin (Neurontin) remain incompletely described, several hypotheses have been proposed. It is possible that different mechanisms account for anticonvulsant, antinociceptive, anxiolytic and neuroprotective activity in animal models. Gabapentin, marketed for the treatment of seizures and neuropathic pain, has been shown to increase in vivo GABA concentration in the brain of both rodents and humans. Gabapentin effects on glutamate are not known. Drugs of abuse represent a growing public health crisis. Accumulating evidence indicates that gabapentin (GBP), a prescription drug, is prone to misuse, abuse, withdrawal, and dependence. Commonly, drugs of abuse modulate the dopaminergic system to induce addiction. In this study, we used the condit Shortly after, gabapentin was shown in vitro to reduce the release of the neurotransmitter dopamine from slices of rat caudate nucleus (striatum). [110] This study provided evidence that the action of gabapentin, unlike baclofen, did not arise from the GABA B receptor.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |