Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
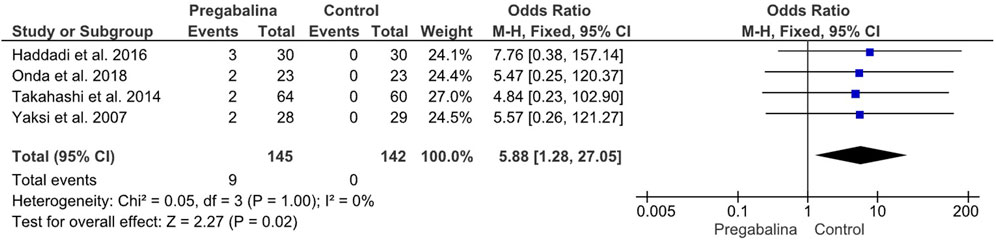
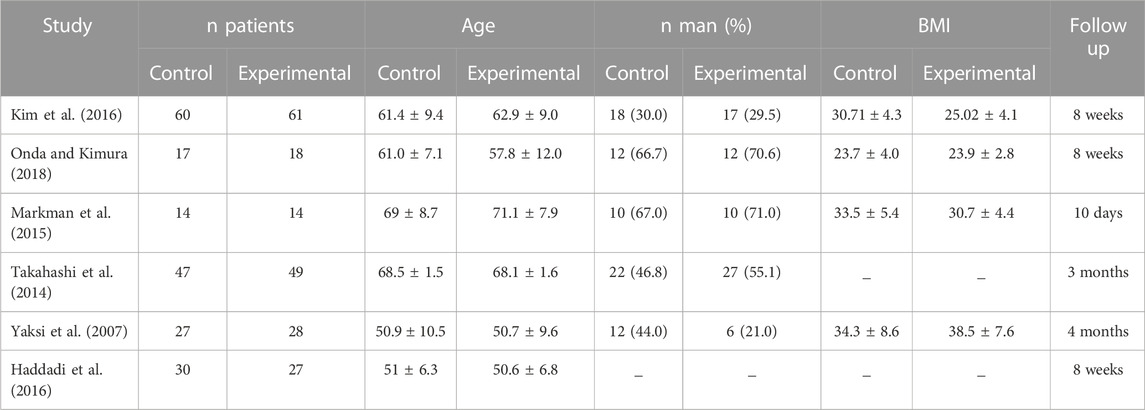
If you have lumbar spinal stenosis and have nerve pain in your legs that is reducing your ability to walk, your doctor may prescribe a neuropathic agent, such as gabapentin (Neurontin). Unfortunately, antidepressants can take several weeks to provide significant relief from spinal stenosis pain. Certain anti-seizure medications, including gabapentin and pregabalin, can help alleviate pain stemming from nerve damage. Epidural steroid injections are commonly used for lower back pain caused by inflammation in the spinal nerves. The efficacy of gabapentin monotherapy was investigated against both acute or chronic radicular pain caused by lumbar disk hernia (LDH) or lumbar spinal stenosis (LSS). Seventy-eight patients with radicular pain, 10 males and 68 females aged 23 to 76 years (mean 49.4 years), caused by LSS in 45 pati According to research, Gabapentin can often alleviate back problems caused by a herniated disc or spinal stenosis. Spinal herniation occurs when a disc between adjacent spinal vertebrae slips out of place and pinches a nerve. Spinal stenosis is a degenerative condition that causes the lower spinal canal to narrow in people over the age of 60. Certain medications are safer and more effective than others for treating spine pain in older adults, according to a recent study. Among these are the over-the-counter drugs acetaminophen (Tylenol) and ibuprofen (Advil) and some nerve pain drugs, muscle relaxants, and antidepressants. Gabapentin is a commonly tried drug for spinal stenosis, but effectiveness varies among individuals. 4.0% of members reported high effectiveness, while 44.0% reported no effect. Common combinations include paracetamol (acetaminophen) and physiotherapy. About 5% to 10% of people with low back pain have sciatica, 2 in which the leg pain follows the sciatic nerve and can be accompanied by strength, sensory and reflex changes in the leg. 3 A smaller proportion of people have neurogenic claudication, in which the leg pain is associated with spinal stenosis and symptoms are exacerbated with Keywords: Lumbar Spinal Stenosis, Nonsurgical Treatment, Epidural Steroid Injection, Interspinous Lumbar Decompression, Minimally Invasive, Algorithmic Approach. Introduction. Lumbar spinal stenosis (LSS) is described as a condition in which there is diminished space available for the neural and vascular elements in the lumbar spine . LSS may After taking a dose, IR gabapentin starts to work in the body within two to three hours. However, the full effects of gabapentin can take one to two weeks to become noticeable, and some people may need to wait longer to experience significant pain reduction. It may depend on your dose and individual response to the medication. Detailed Gabapentin dosage information for adults and children. Includes dosages for Restless Legs Syndrome, Epilepsy and Postherpetic Neuralgia; plus renal, liver and dialysis adjustments. Davis RJ, Errico TJ, Bae H, et al. Decompression and Coflex interlaminar stabilization compared with decompression and instrumented spinal fusion for spinal stenosis and low-grade degenerative spondylolisthesis: two-year results from the prospective, randomized, multicenter, Food and Drug Administration Investigational Device Exemption trial. Gabapentin is most effective in relieving neuropathic pain conditions caused by disk herniation, spinal stenosis, diabetic neuropathy, and postherpetic neuralgia. It provides limited sciatica and fibromyalgia relief, and is ineffective for reducing arthritis-related chronic low back pain. Gabapentin is a medication especially used for nerve pain. Where you have spine pain it is typical for a doctor to prescribe Gabapentin. For the spine has quite a few nerves in and around the discs. Also, diarrhea is a very common side effect of Gabapentin. Gabapentin can be very effective in treating various types of back pains, including: Sciatica; Spinal Stenosis; Nerve Pain from Various Causes; Post-Surgery Back Pain; Arthritis-related back pain; Fibromyalgia; Is Gabapentin a Long-Term Solution for Back Pain? Keywords: lumbar spinal stenosis, pregabalin, gabapentin, gabapentinoids, treatment. Citation: Martínez T, Mariscal G, de la Rubia Ortí JE and Barrios C (2023) Efficacy and safety of pregabalin and gabapentin in spinal stenosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Pharmacol. 14:1249478. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1249478 I have been taking Gabapentin for years. I have DJD, had spinal stenosis in my neck but had surgery to correct that, and Osteoarthritis and peripheral neuropathy. The Gabapentin really helps with my peripheral neuropathy leg pain. I basically have NO pain due to this wonder drug. I have been reading about a lot of side effects, but I have not One open label study concluded that compared to usual care, gabapentin reduced pain intensity and improved walking distance in lumbar spinal stenosis, a condition associated with neurologic intermittent claudication, manifest as symptoms of leg pain, numbness, and cramping precipitated by standing or walking . In any event he inclusion of non A typical gabapentin dosage is anywhere from 300 mg to 900 mg, 3 times a day. Some clinical studies have used dosages up to 1,200 mg, 3 times a day. There are a few different gabapentin products. So dosing can vary depending on which one you’re taking. For example, Gralise is only taken once a day. eHealthMe is studying from 322,815 Gabapentin users for the drug's side effects, drug interactions, effectiveness and more. Check Gabapentin in the real world. What is Spinal stenosis? Spinal stenosis (narrowing of spinal column) is found to be associated with 546 drugs and 186 conditions by eHealthMe. Check our latest studies of Spinal stenosis. Gabapentin, which has been used in the treatment of neuropathic pain, may be effective in the treatment of symptoms associated with LSS. Methods: Fifty-five patients with LSS, who had NIC as the primary complaint, were randomized into 2 groups.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |