Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |
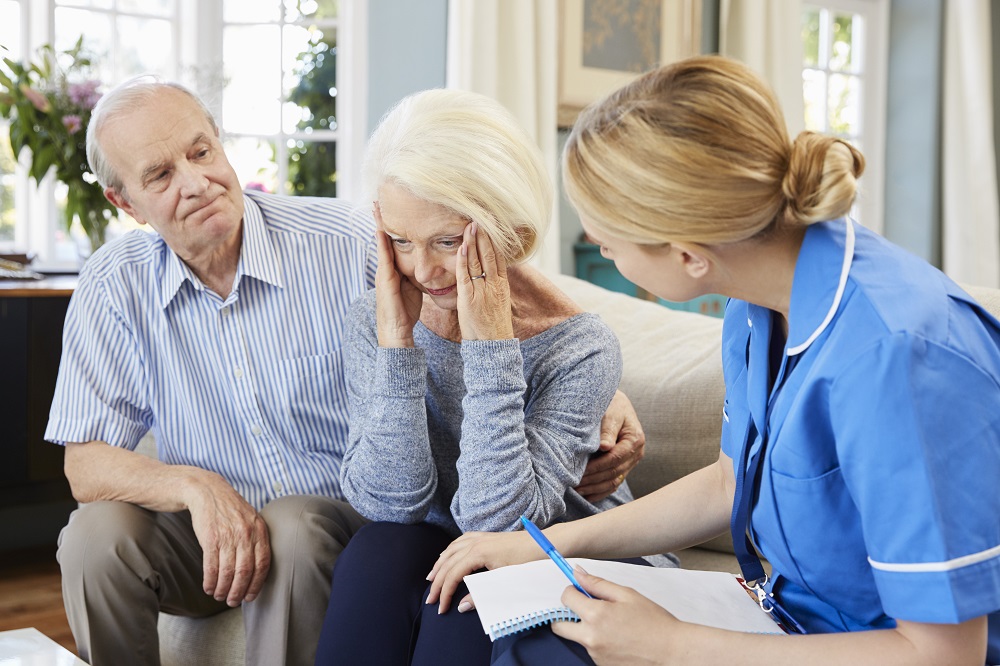
dementia patient was only followed for three weeks. Next, it is unclear whether gabapentin is equally efficacious in Alzheimer’s dementia versus concomitant Alzheimer’s and vascular dementia. Additionally, the age difference of 17?years may have also contributed to the 97-year old’s limited response to gabapentin. Since stopping gabapentin, the improvements in my girl's anxiety, fear (mostly noise fear) is amazing, and her general happiness has returned - it feels like we turned the clock back by at least a year. She can now take small walks about 10 houses up the road, whereas prior to stopping gabapentin she was too scared. low dose gabapentin can be used for treatment of patients with dementia with Lewy bodies. Purpose: To evaluate low dose Gabapentin (GBP) for treatment of disruptive behavioral symptoms in patients with moderate - severe dementia with Lewy bodies. Methods: A case series in a community setting. Eleven In a small case series, gabapentin reduced aggression among seven patients with vascular dementia or mixed vascular/AD, using daily doses ranging from 200 to 600 mg daily. Three of the seven patients were able to discontinue anti-psychotics after gabapentin initiation [ 44 ]. We present the case of a patient with incipient vascular dementia accompanied by nocturnal agitation, which was successfully treated with gabapentin. Gabapentin appears to be useful and well-tolerated in this indication. Several case reports describe using gabapentin, an anti-epileptic and FDA-approved treatment for neuropathic pain, as an off-label treatment for BPSD. BPSD in some patients may be driven by unreported neuropathic pain, which gabapentin can treat effectively. The authors describe the use of gabapentin in the treatment of 4 outpatients with dementia-associated agitation. On the basis of clinical case reports and the Overt Agitation Severity Scale, all 4 patients had reduced agitation with gabapentin. Pregabalin also has favorable results at 50 to 600 mg/d without serious adverse effects in dementia patients [4], [11], and it can decrease anxiety symptoms in patients with LBD when administered at 75 to 150 mg/d [15]. Gabapentin 100 mg can be given as needed one to three times daily to treat anxiety, and it can be used at night to promote sleep. The evidence is not very robust for gabapentin, although it is commonly used given its tolerability in the elderly. Be aware that gabapentin is renally cleared, so check creatinine clearance before prescribing. We describe a case where gabapentin was used to treat a patient with mixed Alzheimer's/vascular dementia presenting with severe aggression requiring hospitalization. The case is followed by a systematic review of current literature of the use of these drugs in aggression in patients with dementia. Another 41% of the people in the three-or-more medication group were taking a benzodiazepine, such as lorazepam (Ativan), often used for anxiety or agitation in people with dementia. Maust’s past work on benzodiazepine prescribing in older adults focused on long-term use , variation by geographic region , and the effects of national efforts We would like to show you a description here but the site won’t allow us. Gabapentin has been administered to several geriatric patients with bipolar disorder and patients with dementia. It has also been reported to be successful in the treatment of a 13-year-old boy with behavioural dyscontrol, a finding that suggested a possible role for gabapentin in the treatment of other behavioural disorders. Neuropsychiatric symptoms in Alzheimer disease (AD) and other types of dementia are extremely common and often much more troubling than cognitive symptoms [1]. This topic will review the causes and treatment of behavioral disturbance and other neuropsychiatric symptoms related to dementia. In two separate large population studies, both benzodiazepines (a category that includes medications for anxiety and sleeping pills) and anticholinergics (a group that encompasses medications for allergies and colds, depression, high blood pressure, and incontinence) were associated with an increased risk of dementia in people who used them for Overall, the risk of being hospitalized with altered mental status after initiating gabapentin remains low, but may be reduced through the judicious use of gabapentin, use of the lowest dose to control pain, and vigilance for early signs of altered mental status. I’ve struggled with anxiety for over 7 years. Tried many SSRI’s and SNRI’s and buspar. Minimal help. Supplemented with klonopin (posted this recently as a topic). I just started using 300 mg gabapentin (100 mg in morning and 200 mg) in evening). Seems to be helping. Anyone else using it? Behavioral and Psychiatric Symptoms of Dementia (BPSD) increase patient mortality, healthcare costs and caregiver burnout. While behavioral interventions are the most effective treatment for BPSD, many patients are not able to regulate their agitation using only behavioral interventions, and therefore require pharmacotherapy. Various agents such as risperidone, quetiapine and trazodone have Cox proportional hazards regression models were used to investigate the associations between exposure to gabapentin or pregabalin and the quartiles of cDDDs of gabapentin or pregabalin exposure and the risk of dementia, adjusting other potential confounders and estimating the hazard ratios (HR) and 95% confidence intervals (CIs). The authors describe the use of gabapentin in the treatment of 4 outpatients with dementia-associated agitation. On the basis of clinical case reports and the Overt Agitation Severity Scale, all 4 patients had reduced agitation with gabapentin. Three of 4 patients were successfully titrated to a full dose of 2,400mg/day. These findings suggest a possible role for gabapentin in the behavioral
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |