Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
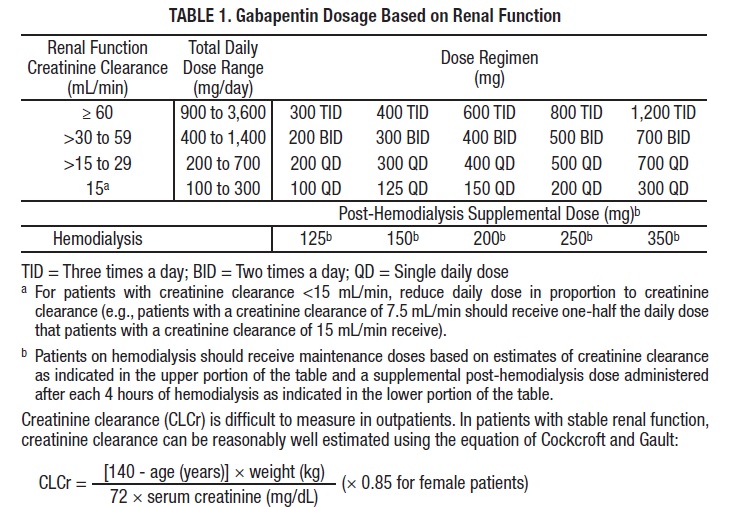
The exact way that gabapentin works for nerve pain or seizures is unknown. Gabapentin may block certain signals from nerves. While less common, the most serious side effects of gabapentin are Gabapentin for other types of nerve pain. Gabapentin can also treat nerve pain from PHN, which is the most common complication of shingles. It’s also used off-label to treat diabetes-related nerve pain. If you have nerve pain from other causes — like back injury, nerve injury, or after surgery — it still may help. This summary uses a Cochrane review, updated in 2014, to address the efficacy of gabapentin compared with placebo to palliate neuropathic pain. 3 The Cochrane review includes 37 trials enrolling Gabapentin is a prescription medication known as a gamma aminobutyric acid (GABA) analogue. GABA reduces the excitability of nerve cells (neurons) in the brain, which play a role in seizures and the transmission of pain signals. Gabapentin mirrors the effects of GABA calming excited neurons. Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. The typical starting dose of gabapentin for sciatic nerve pain for most patients is 300mg once a day. Your physician may increase the dosage up to three times a day. It is imperative to take the For treating nerve pain, one may recommend three doses of Gabapentin in a day divided into morning, afternoon, and evening doses. One may start with a low dose of 100 mg at night. The typical starting dosage of gabapentin for seizures is 300 mg by mouth three times a day, with or without food. Your prescriber may adjust your gabapentin dosage to up to 600 mg 3 times a day (1,800 mg per day). The maximum gabapentin dosage is 3,600 mg per day, but higher doses are more likely to cause side effects.Restless legs syndrome Detailed Gabapentin dosage information for adults and children. Includes dosages for Restless Legs Syndrome, Epilepsy and Postherpetic Neuralgia; plus renal, liver and dialysis adjustments. Gabapentin can help relieve nerve pain in some people with postherpetic neuralgia (nerve pain after shingles) and peripheral diabetic neuropathy (nerve pain in the feet in people with diabetes). Gabapentin is licensed for the treatment of peripheral neuropathic pain such as painful diabetic neuropathy and postherpetic neuralgia in adults [ABPI, 2020a].However, the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) recommends gabapentin as a first-line treatment option for adults with all neuropathic pain (except trigeminal neuralgia) [NICE, 2019a]. Gabapentin for Neuropathic Pain Initial dose: 300 mg once daily, with gradual increases as needed. Maintenance dose: 900-3600 mg per day, divided into three doses. Below is a general guideline for dosing: Gabapentin is primarily used for: Neuropathic Pain: Effective in alleviating pain from nerve damage. Postherpetic Neuralgia: Reduces pain following shingles. Seizure Disorders: Acts as an adjunctive therapy for partial seizures. For immediate-release gabapentin (Neurontin), dosing may be initiated with 300 mg on day 1, doubled on day 2 (300 mg twice a day), and tripled on day 3 (300 mg 3 times a day). The dose can then be titrated up as needed for pain relief to a maximum dose of 1,800 mg daily (divided into 3 daily doses). Gabapentin is commonly used to treat neuropathic pain (pain due to nerve damage). This review updates a review published in 2014, and previous reviews published in 2011, 2005 and 2000. To assess the analgesic efficacy and adverse effects of Pharmacodynamics. Gabapentin is an anti-convulsant medication that inhibits the release of excitatory neurotransmitters, allowing for its use against pathologic neurotransmission such as that seen in neuropathic pain and seizure disorders. 16,19 It has a wide therapeutic index, with doses in excess of 8000 mg/kg failing to cause a fatal reaction in rats. 21 Introduction. Gabapentin is an anticonvulsive medication that is primarily used to treat seizures and nerve pain. It was initially developed as a muscle relaxer and anti-spasmodic medication, but its anticonvulsive properties were discovered later. If you've been prescribed gabapentin for nerve pain, you may begin to feel pain relief within one to two weeks of starting it, depending on your dosage. However, for some people, it can take longer to see benefits. The established therapeutic dosing for gabapentin in neuropathic pain is 1800-3600 mg/day in 3 divided doses in patients with normal renal function. View complete list of side effects. 4. Bottom Line. Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant with pain-relieving effects that may be used to treat certain seizure disorders or relieve nerve pain. Common side effects include dizziness or drowsiness and it may cause a withdrawal syndrome on discontinuation so should not be stopped abruptly. 5. Tips The usual dose to treat nerve pain in adults is 900mg to 3,600mg a day, split into 3 doses. To prevent side effects, your doctor will prescribe a low dose to start with and then increase it over a few days. Once you find a dose that suits you, it will usually stay the same.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |