Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
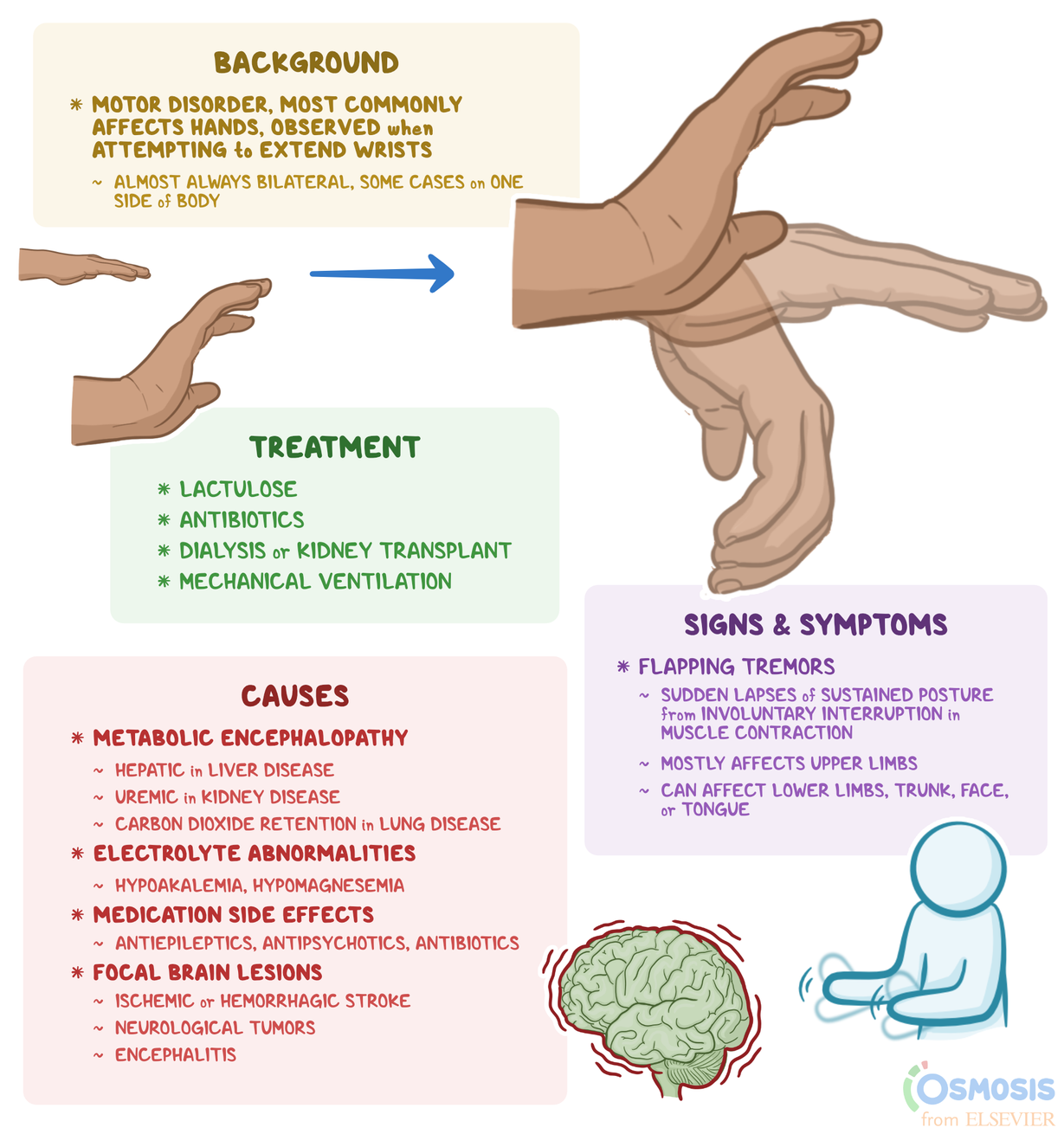
The most common starting daily dose of gabapentin was the equivalent of 50 mg (44.1%) or 100 mg (38.2%) daily, with the median daily dose of 100 mg (range 39–455 mg Chronic pruritus is a distressing symptom that is often refractory to treatment. Patients frequently fail topical therapies and oral over-the-counter antihistamines, prompting the clinician to consider alternative therapies such as neuroactive agents. Herein, the use of gabapentin and pregabalin, 2 medications well known for treating neuropathic pain and epilepsy that are occasionally used for Gabapentin is a promising and a well-tolerated treatment option for patients with UP. We recommend it as a first line therapy with a maintenance post-HD dose of 100-300 mg. We also recommend the 5-D scale in the assessment of the severity of pruritus. Due to this slow metabolism, administering an adequate dose of gabapentin before sleep should help provide relief from pruritus throughout the night. The authors recommend an initial nighttime dose of 100 mg that can be titrated up to 300 mg within weeks. Lau et al., assessed the effect of gabapentin for pruritus in hemodialysis patients and reported that dose of 100 mg gabapentin after hemodialysis decrease adverse events in these patients (23). Based on findings of this study, gabapentin is a promising medication for the treatment of uremic pruritus. Gabapentin, an anticonvulsant, may control pruritus with neuropathic origin. The objectives of this study were to assess the efficacy of gabapentin in reducing pruritus scores of patients with uremic pruritus and evaluate its safety among dialysis patients. Despite advances made in treatment, uremic pruritus remains a common and distressing symptom in patients on hemodialysis (HD). Gabapentin is an effective drug in the management of neuropathic pain. Considering that neuropathic pain and pruritus share similar pathogenic mechanisms, we conducted this Uremic pruritus is a common condition among dialysis-dependent patients, affects patient's quality of life, and is associated with shorter survival time. 28, 29 The cause of uremic pruritus has been attributed to multiple factors including sensitization to itch by uremic neuropathy. 30 Therefore, clinicians hypothesized that neuroactive agents Interestingly, one of the major pruritic conditions treated by gabapentin and pregabalin is uremic pruritus in patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD) . Although uremic pruritus is not classically considered to be a neuropathic form of pruritus, it has been shown that 65% of patients with CKD exhibit peripheral nerve disorders, such as The association of uremic pruritus and restless leg syndrome in dialysis patients and successful treatment with gabapentin implies the role of neuropathy in uremic pruritus . In addition, increasing evidence suggests that both central and peripheral opioid receptors contribute to uremic pruritus. Gabapentin is likely effective for uremic pruritus but adverse events are common. Starting at a low dose of 100 mg orally after hemodialysis and titrating to effect may best provide effective and safe outcomes. Gabapentin or pregabalin relieved itching in 85% of 71 consecutively treated CKD patients. Patients should be advised about side effects and the drug initiated at a low dose. Patients intolerant of gabapentin may tolerate pregabalin. Gabapentin is a well-established treatment option for itch with a reassuring safety profile that does not require continued lab monitoring. Generalized itching is a common cause of visits to the dermatologist and can be difficult to treat, leading to sleepless nights and inability to function. In summary, 100 mg of gabapentin is generally considered a low dose across various clinical contexts. It is effective for conditions like uremic pruritus and carpal tunnel syndrome, though higher doses may be required for optimal symptom control in some cases. (n=31), vs. routine care (n=32) on the pruritus score of hemodialysis patients.13 Pruritus improved in both baby oil groups, with no differences were found in the baby oil temperature. Capsaicin (topical) In a double-blind, placebo-controlled, crossover trial14 of 34 hemodialysis patients with uremic pruritus, 1 Uraemic pruritus is an itch affecting large bilateral surface areas with no associated primary skin lesion. It can be generalised or localised to the back, face and arms, and occurs on a near-daily basis. General management advice Assess for non-uraemic causes of itch such as allergic or drug reactions, psoriasis, atopic eczema, fungal infections, scabies, Clinicians should consider prescribing pregabalin and gabapentin for pruritus, potentially replacing conventional treatments while refining dosing strategies and monitoring patient safety based on the reported outcomes. Pruritus is a common dermatological symptom that causes an unpleasant skin sensation and the desire to scratch. the use of gabapentin and pregabalin as antipruritic agents are explored. They are found to be promising alternative treatments for the relief of several forms of chronic pruritus, particularly uremic pruritus and neuropathic or neurogenic itch, in patients who fail conservative therapies. (J Am Acad Dermatol 2016;75:619-25.) Gabapentin reduced symptoms of pruritus (P < 0.001) and RLS (P < 0.05). There was no statistical difference when comparing HD and conservatively managed patients for daily starting dose (P = 0.88), median dose (P = 0.84), and final dose (P = 0.18). Uremic pruritus is most commonly described as a daily or near-daily occurrence of itch that spans large bilaterally symmetrical surface areas. It does not exhibit a dermatomal pattern and there is no asso-ciated primary skin lesion.5-7 Uremic pruritus can vary from a generalized itch to a localized itch affecting the back, face, and arms.5
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |