Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
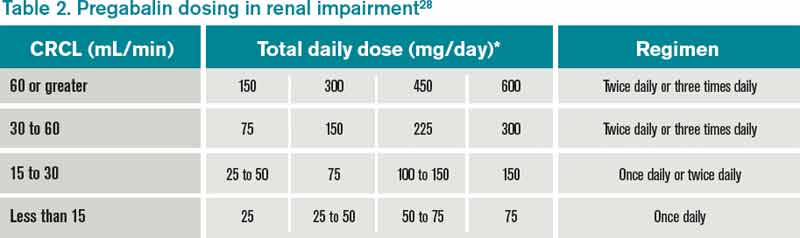
Gabapentinoids are opioid substitutes whose elimination by the kidneys is reduced as kidney function declines. To inform their safe prescribing in older adults with chronic kidney disease (CKD), we examined the 30-day risk of serious adverse events according to the prescribed starting dose. Population-based cohort study. Kidney Function: If a child has kidney problems, the dose needs to be lower. Ages ≥12 years : Adjust based on creatinine clearance and weight. Dosage Adjustment : Lower doses required; consult a paediatric specialist. Per Lexicomp, Gabapentin’s recommended dose in patients with renal impairment is as follows: CrCl >15 to 29 mL/minute: 200 to 700 mg once daily. CrCl 15 mL/minute: 100 to 300 mg once daily. Gabapentin’s apparent total clearance is 100 mL/min in adults with normal renal function, which is essentially equivalent to CrCl and does not suggest the involvement of tubular reabsorption. 1 Some evidence suggest that active tubular secretion mediated by organic cation transporter-1 (OCT-1) may play a role in gabapentin’s renal clearance. In rare instances, gabapentin can cause DRESS (drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms) syndrome. This is a severe allergic reaction that can cause damage to major organs, including the liver and kidneys. If you have existing kidney problems, you may need a lower dose of gabapentin. When it comes to gabapentin and kidney disease, kidney disease sufferers should be aware of the risks that are involved in taking gabapentin with kidney disease. Gabapentin is actually toxic to the kidneys. Gabapentin is frequently used as an analgesic in patients with chronic kidney disease. Usual initial gabapentin dose: 300mg q8h. Usual maintenance dose: 300-600mg q8h. Maximum dosage/day: 3600 mg. [15-29]: Dosage range: 200-700mg/day. [<15]: 100-300 mg/day. Use lower end of this range for CRCL <7.5 ml/min. TABLE 1. Gabapentin Dosage Based on Renal Function. TID = Three times a day; BID = Two times a day; QD = Single daily dose. a. With a growing chronic kidney disease epidemic, 22,23 an increasing number of patients with chronic kidney disease will be exposed to gabapentin. This study demonstrates that gabapentin dosage for patients with chronic kidney disease has been insufficiently adjusted and that the risk of gabapentin toxicity has been underrecognized. Patients with chronic kidney disease often receive inappropriately high gabapentin dosage for their kidney function, occasioning overt toxicity; advanced age and comorbidity predispose these patients for toxicity. Pain is one of the most common and distressing symptoms among patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD) . The prevalence of pain has been associated with substantially lower health-related quality of life and greater psychosocial distress, insomnia, and depressive symptoms [ 2-9 ]. Furthermore, the impact of gabapentin accumulation can be particularly pronounced in patients with end-stage renal disease (ESRD), where kidney function is severely impaired or virtually absent. Dialysis may help to some extent, but it often doesn’t clear gabapentin as effectively as healthy kidneys. Gabapentin dosing ranges from 100 to 3600 mg daily and pregabalin dosing is 25 to 600 mg daily. 1, 2 Gabapentin and pregabalin exhibit greater than 90% kidney elimination and adjustments to dose and frequency are recommended for patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD). 1, 2 For patients with a creatinine clearance (CrCl) below 60 mL/min, a do Gabapentin dosing guidelines for adult with renal impairment are summarized in Table 3. Dosing guidelines for gabapentin immediate-release are also applicable for adolescents 12 years of age and older with renal impairment. People with kidney disease. As gabapentinoids are predominantly excreted by the kidney, cautious starting doses and careful dose adjustments are required for people with acute or chronic kidney disease. When creatinine clearance is below 30 mL/minute, the half-lives of both gabapentin and pregabalin are prolonged. 8 Drug dosing requirements for antihypertensives in patients with chronic kidney disease are listed in Table 4. 4, 5 Thiazide diuretics are first-line agents for treating uncomplicated hypertension Rational dosing of gabapentin and pregabalin in chronic kidney disease. Rational dosing of gabapentin and pregabalin in chronic kidney disease J Pain Res. 2017 Jan Here are some of the most common questions about gabapentin and kidney disease: 1. Is it safe to take gabapentin if I have stage 3 kidney disease? Taking gabapentin with stage 3 kidney disease requires significant dose adjustments and close monitoring due to the risk of drug accumulation. Therefore, a reduced dosage of gabapentin is almost always necessary in cats with kidney disease, with adjustments often needing to be at least 50% of the typical dose for a cat with healthy kidneys. The specific dosage needs to be determined by a veterinarian who is familiar with the individual cat’s needs and the severity of its kidney disease. Challenges in pain management in patients with kidney disease. Pain assessment. This should start with assessment of a) pain severity using various standardized tools, most common of which is the numerical rating scale []; b) pathophysiologic evaluatio n into mechanism of injury and type of pain; c) psychosocial evaluation of co-occurring factors that contribute to pain or make treatment of
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |