Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | 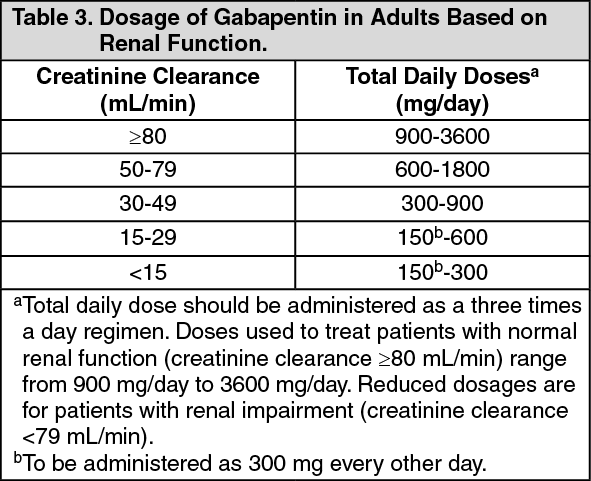 |
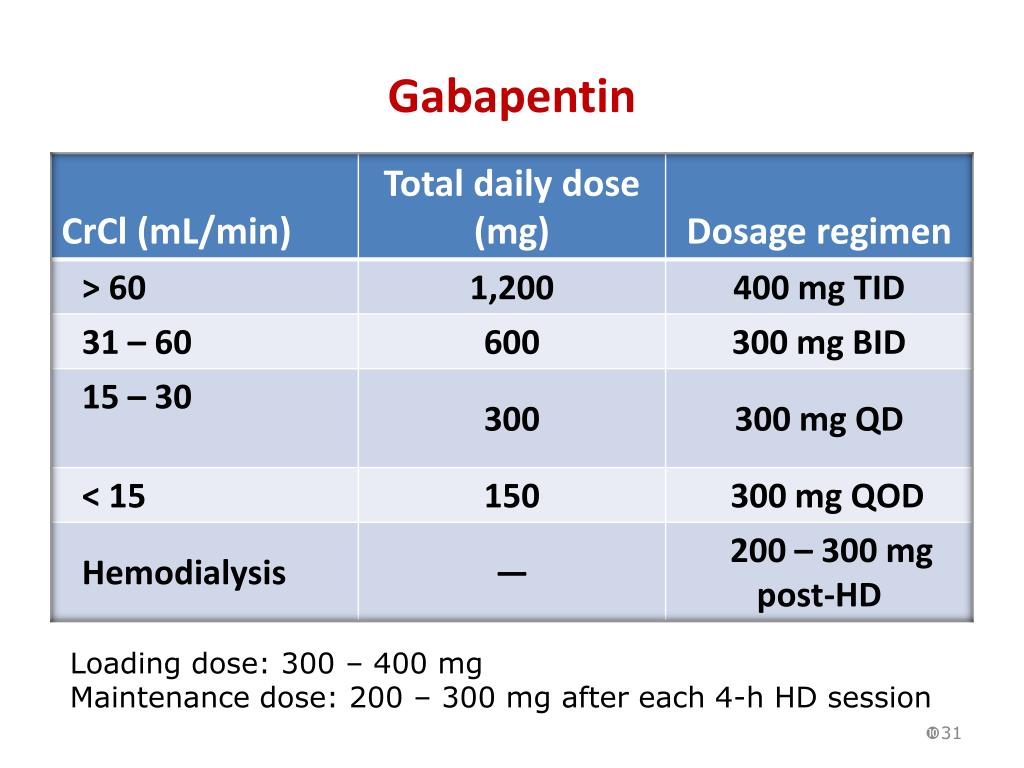
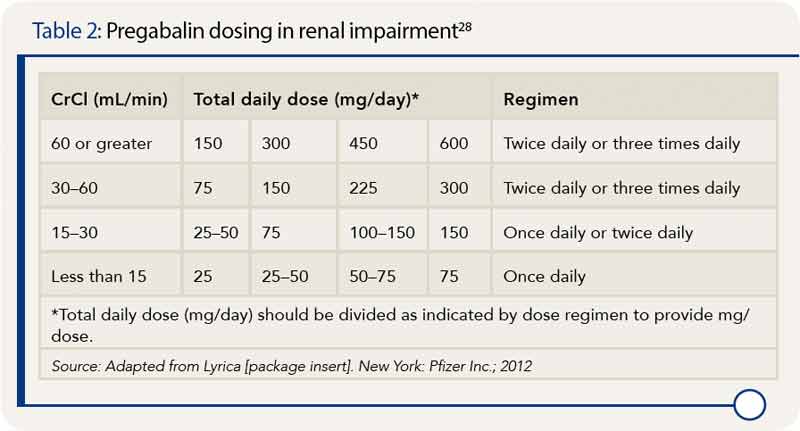
Suggested maintenance dosing schedule for doses ≥600 mg/day: One-third of total daily dose given midday, remaining two-thirds of the total daily dose given in the evening (Garcia-Borreguero 2002; Happe 2003; IRLSSG/EURLSSG/RLS-F [Garcia-Borreguero 2016]; Saletu 2010; Silber 2018; Vignatelli 2006). For adults, your gabapentin dosage varies depending on your medical conditions and which form you’re taking. The maximum dosage is 3,600 mg per day. For children, the dosage is based on age and body weight. Gabapentin is available as a lower-cost generic. But certain products are brand-only. Medscape - Seizure dosing for Neurontin, Gralise (gabapentin), frequency-based adverse effects, comprehensive interactions, contraindications, pregnancy & lactation schedules, and cost Gabapentin. Please read the leaflet included in your prescription. What is Gabapentin? Gabapentin is an anti-epileptic / anti-convulsant drug that can be used in to treat pain caused by damage to the nerves (neuropathic). How to take Gabapentin Gabapentin needs to be gradually increased over a period of time until a maximum daily dose of 600mgs Administration of 4 different doses of gabapentin during the initial titration in outpatients with neuropathic pain resulted in a significant reduction in awakening from breakthrough pain and a reduction in the adverse effects of the medication. Keywords: Ambulatory care, Drug administration schedule, Gabapentin, Neuropathic pain. A tapering schedule is a plan that outlines how to gradually reduce the dosage of Gabapentin over a set period. The process involves careful planning and consideration of individual patient factors, such as the current dosage, the time the medication has been used and the patient’s overall health and response to medication changes. dose until your follow up. c. Continue the titration schedule to the goal of 1800 mg/day of GABAPENTIN . d. You may stop titration early at the dose where you no longer have bothersome pain or at a pain level more acceptable for you. Not all patients will require the full schedule for pain relief. For immediate-release gabapentin (Neurontin), dosing may be initiated with 300 mg on day 1, doubled on day 2 (300 mg twice a day), and tripled on day 3 (300 mg 3 times a day). The dose can then be titrated up as needed for pain relief to a maximum dose of 1,800 mg daily (divided into 3 daily doses). Table 2. Dosage Adjustments for Renal Impairment in Adults Receiving Gabapentin Gastroretentive Tablets60; Cl cr (mL/minute). Adjusted Dosage Regimen. 30–60. 600 mg to 1.8 g once daily; initiate at 300 mg once daily and may titrate according to same schedule recommended for those with normal renal function based on individual patient response and tolerability Absorption of gabapentin is solely dependent on LAT that are easily saturable, resulting in dose-dependent pharmacokinetics. As the dose of gabapentin increases, the area under the plasma concentration–time curve (AUC) does not increase proportionally. Child 6–11 years 10 mg/kg once daily (max. per dose 300 mg) on day 1, then 10 mg/kg twice daily (max. per dose 300 mg) on day 2, then 10 mg/kg 3 times a day (max. per dose 300 mg) on day 3; usual dose 25–35 mg/kg daily in 3 divided doses, some children may not tolerate daily increments; longer intervals (up to weekly) may be more appropriate, daily dose maximum to be given in 3 divided Risk of death with co-use of opioids and gabapentin is up to 60 percent greater with doses of gabapentin over 900 milligrams per day. Antacids with aluminum and magnesium like Maalox and Mylanta Examples of gabapentin dosing schedules are below. The usual target dose for pain management is approximately 1800 mg/day (e.g., 600 mg three times a day). The maximum dose of gabapentin is 3600 mg/day. • Gabapentin may be taken with or without food. first. Doses ≥120mg OME daily should be highlighted as a priority. Take into account ‘when required’ doses of opioid medication on an individual basis, ensuring dose is not escalated while reduction of regular analgesic medication occurs. Make small dose changes, which are less likely to cause withdrawal symptoms and will build confidence in If using gabapentin for epilepsy, some studies recommend to decrease your dose slowly (over months) to avoid recurrent seizures. Data indicates that seizures most often occur in the first six months after beginning to taper. If using gabapentin for other indications, it is recommended to taper gabapentin for at least one week. Emotional Stress: Mood swings or panic attacks may occur without a taper schedule to soften the transition. Gabapentin Taper Schedule. Gabapentin taper schedule isn’t one-size-fits-all. Some individuals can lower their dose in a matter of weeks, while others may need months for a more comfortable transition. TABLE 1. NEURONTIN Dosage Based on Renal Function; TID = Three times a day; BID = Two times a day; QD = Single daily dose * For patients with creatinine clearance <15 mL/min, reduce daily dose in proportion to creatinine clearance (e.g., patients with a creatinine clearance of 7.5 mL/min should receive one-half the daily dose that patients with a creatinine clearance of 15 mL/min receive). Enter the table at the appropriate dose level Pregabalin is available in the following formulations: 25mg, 50mg, 75mg, 100mg, 150mg, 200mg, 225mg and 300mg capsules and tablets. An alternative regime is to take the same dose reduction (25mg per dose) across the day. Effective Dose: Reached by upward titration over a period of approximately 3 days; the effective dose in patients 5 years of age and older is 25 to 35 mg/kg/day in divided doses (3 times a day). The effective dose in pediatric patients ages 3 and 4 years is 40 mg/kg/day and given in divided doses (3 times a day). Detailed Gabapentin dosage information for adults and children. Includes dosages for Restless Legs Syndrome, Epilepsy and Postherpetic Neuralgia; plus renal, liver and dialysis adjustments.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |