Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
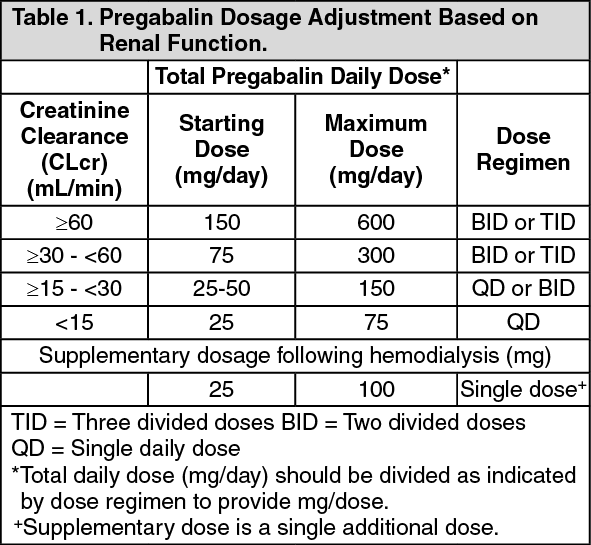
Adjust the dose for people with renal impairment (see Table 2). Consult the manufacturer's Summary of Product Characteristics if the person is undergoing haemodialysis. Table 2. Recommended dosage adjustment for gabapentin in people with renal impairment. Nonopioid analgesics, including acetaminophen, topical analgesics, gabapentinoids, serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors, and tricyclic antidepressants may be considered based on pain etiology and type, with careful dose considerations in kidney disease. NSAIDs may be used in CKD and ESKD for short durations with careful monitoring. normal renal function on maximum recommended dosing yielded concentrations of 5–8 mg/L for gabapentin and ~ 2.8–8.2 mg/L for pregabalin. 22–25 The elimination half-lives of gabapentin and pregabalin are prolonged with renal impairment leading up to accumulation with repeated dosing. The half-life of gabapentin immediate-release Majority drugs, including Gabapentin, are eliminated by the kidneys and will accumulate to a toxic level in renally compromised patients as in this case. Per Lexicomp, Gabapentin’s recommended dose in patients with renal impairment is as follows: CrCl >15 to 29 mL/minute: 200 to 700 mg once daily. CrCl 15 mL/minute: 100 to 300 mg once daily Dosing Modifications Renal impairment (Neurontin) CrCl >60 mL/min: 300-1200 mg PO TID Renal impairment: Gabapentin dose reduction may be required, depending on - ESAS-r:Renal; RELATED TOPICS. Approach to the management of chronic non-cancer pain in adults; Arteriovenous graft creation for hemodialysis and its complications; Epidemiology and pathogenesis of analgesic-related chronic kidney disease; Evaluation of chronic pain in adults; NSAIDs: Acute kidney injury; NSAIDs: Electrolyte complications Gabapentin dosing guidelines for adult with renal impairment are summarized in Table 3. Dosing guidelines for gabapentin immediate-release are also applicable for adolescents 12 years of age and older with renal impairment. The absolute bioavailability of gabapentin drops from 60% to 33% as the dosage increases from 900 to 3600 mg/day, while the absolute bioavailability of pregabalin remains at <-90% irrespective View gabapentin information, including dose, uses, side-effects, renal impairment, pregnancy, breast feeding, monitoring requirements and important safety information. The half-life of gabapentin immediate-release formulation is 5–7 hours in patients with normal renal function and is prolonged up to 52 hours in patients with CrCl<30 mL/min. 26 The half-life of pregabalin is 16.7 hours in patients with CrCl 30–59 mL/min, 25 hours in patients with CrCl 15–29 mL/min, and 48.7 hours in patients with CrCl<15 Download Table | Recommended dose adjustments based on varying degrees of renal impairment from publication: Rational dosing of gabapentin and pregabalin in chronic kidney disease | Mena Raouf,1 Dosage Adjustment in Patients with Renal Impairment [Package insert] Dosage adjustment in patients 12 years of age and older with renal impairment or undergoing hemodialysis is recommended, as follows (see dosing recommendations above for effective doses in each indication): The Renal Dosage is an educational tool designed by an experienced physician, Dr. Safwan Sayyal in consultation with nephrologists to ascertain the appropriate medication dosage based on a patient's kidney function. This will help to eliminate dosing errors in individuals with renal impairment. The risk of respiratory depression should be assessed when initiating gabapentin in patients with respiratory comorbidities, neurological disease, renal impairment and in combination with other respiratory depressants such as opioids. Loading dose of 300–400 mg in patients who have never received gabapentin. Maintenance dose of 100–300 mg after each HD : session and increase according to tolerability. In patients with normal renal function, the maximum dose of gabapentin is 3600mg daily in divided doses. However, gabapentin is renally cleared and so the dose needs to be adjusted according to the GFR. For patients on dialysis, the recommended dose is 100-300mg post dialysis on dialysis days only. Dosage adjustment in patients 12 years of age and older with renal impairment or undergoing hemodialysis is recommended, as follows (see dosing recommendations above for effective doses in each Gabapentin Dosage Based on Renal Function. For patients with creatinine clearance <15 mL/min, reduce daily dose in proportion to creatinine clearance (e.g., patients with a creatinine clearance of 7.5 mL/min should receive one-half the daily dose that patients with a creatinine clearance of 15 mL/min receive). Doses often need to be reduced in renal impairment to prevent accumulation and toxicity. Examples of drugs that should be reduced in renal impairment are the gabapentinoids: gabapentin and pregabalin. Table 1 shows maximum recommended dose of gabapentin in renal impairment: Table 2 shows the maximum recommended dose of pregabalin in renal Dosing recommendations for individual drugs can be found in Drug Prescribing in Renal Failure: Dosing Guidelines for Adults. 4 The guidelines are divided into three broad GFR categories (less than
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |