Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
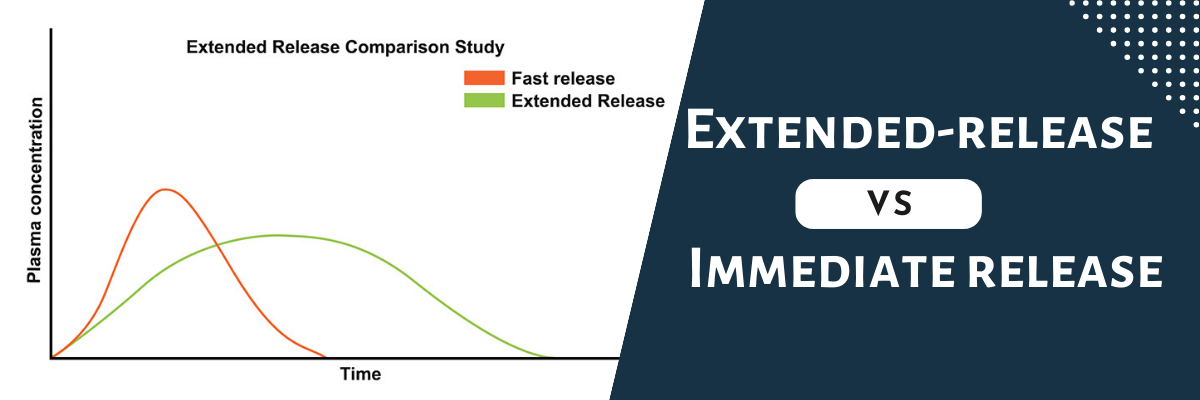
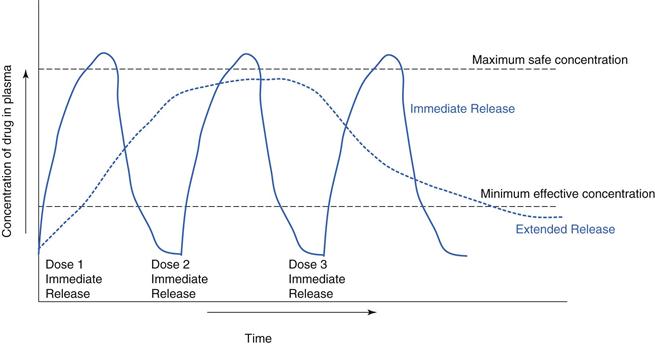
Navigating the maze of “Extended-release vs Immediate release: making informed medication choices” can be complex, but you’re now armed with knowledge. Remember that your unique health needs and preferences play a critical role in this decision. Over the past 3 decades there has been a substantial increase in the number of licensed anti-seizure medications (ASMs) [1]; to date, over 30 ASMs are available for the treatment of epilepsy which, alongside the advent of extended-release (ER) delivery systems, has dramatically increased the epilepsy armamentarium. ER drug delivery systems have a number of advantages compared with immediate The IASP guidelines recommend both immediate- and extended-release gabapentin IASP [Finnerup 2015]. In contrast, a guideline from the American Academy of Neurology Objectives: To compare gabapentin extended-release, a gastro-retentive formulation, in relieving postamputation pain among gabapentin-experienced and gabapentin-naïve patients. Design: Open-labeled pilot study. Gabapentin (Neurontin) has shown efficacy in relieving vasomotor symptoms and is used as off-label for this indication. A new extended-release formulation of gabapentin has also shown efficacy in treating hot flashes and improving sleep quality with possibly fewer side effects than regular gabapentin. Gabapentin is available in two extended-release formulations in addition to the immediate release: a gastric retentive formulation (GBP-GR) and a gastro-retentive prodrug gabapentin enacarbil that are approved for the management of postherpetic neuralgia. Swearingen D, Aronoff GM, Ciric S, et al. Pharmacokinetics of immediate release, extended release, and gastric retentive gabapentin formulations in healthy adults. Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2018;56(5):231-238. Antacids containing aluminum or magnesium may interfere with the absorption of this medication. If you are also taking an antacid, it is best to take gabapentin at least 2 hours after taking the antacid. Different forms of gabapentin (such as immediate-release, sustained-release, enacarbil sustained-release) are absorbed in the body differently. Gabapentin, an immediate-release formulation, has demonstrated clinical efficacy in DPN patients but also a relatively high incidence of somnolence and dizziness at the doses required for effective treatment of DPN pain (1, 2). An average percent of pain relief with gabapentin extended-release was noted to be significant (p < 0.01) after 8 weeks of therapy among gabapentin-experienced (81.25 ± 16.42%) and gabapentin-naïve groups (85 ± 17.73%) when compared to baseline for gabapentin-experienced (31.25 ± 29%) and gabapentin-naïve groups (36.25 ± 34.2% The two trials had a very similar design and identical twice-daily dosing regimens, but carbamazepine was administered in an immediate-release (IR) formulation in trial A and in extended-release (ER) formulation in trial B. Abbreviations: IR, immediate release; ER, extended release; N, number of subjects in the intent-to-treat population. Objective: Gabapentin immediate release (GBP-IR), gabapentin gastric retentive (GBP-GR), and the prodrug gabapentin enacarbil extended release formulation (GEn) have been approved for management of postherpetic neuralgia (PHN) in adults. This is the first pharmacokinetic (PK) comparison of all three formulations using FDA-recommended doses for PHN. Pharmacokinetics of gabapentin after a single day and at steady state following the administration of gastric-retentive- extended-release and immediate-release tablets: a randomized, open-label, multiple-dose, three-way crossover, exploratory study in healthy subjects Objective: The aim of this study was to compare the pharmacokinetics of an oral, gastric-retentive, gabapentin extended-release (G-ER) formulation with a gabapentin immediate-release (G-IR) formulation after single and multiple daily doses in healthy subjects. When GRALISE (1800 mg once daily) and gabapentin immediate release (600 mg three times a day) were administered with high-fat evening meals (50% of calories from fat), GRALISE had a higher C max and lower AUC at steady state compared to gabapentin immediate release. Objective: Gabapentin immediate release (GBP-IR), gabapentin gastric retentive (GBP-GR), and the prodrug gabapentin enacarbil extended release formulation (GEn) have been approved for management of postherpetic neuralgia (PHN) in adults. Gabapentin enacarbil (Horizant™) extended release tablets received FDA approval in April 2011 for the treatment of moderate-to-severe primary Restless Legs Syndrome in adults. 1 Gabapentin immediate release (Neurontin) was first approved by the FDA in 1994 for the adjunct treatment of partial seizures and is also FDA approved for the Horizant and Gralise are gabapentin medications that last longer in the body than immediate-release gabapentin. These products are effective for nerve pain from shingles (Horizant and Gralise) and restless leg syndrome (Horizant only). Objective: Gabapentin imme-diate release (GBP-IR), gabapentin gastric retentive (GBP-GR), and the prodrug ga-bapentin enacarbil extended release formu-lation (GEn) have been approved The time to reach maximum plasma concentration (t (max)) was extended for gabapentin delivered from the gastric-retentive extended-release formulation compared with the immediate-release formulation.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |