Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |
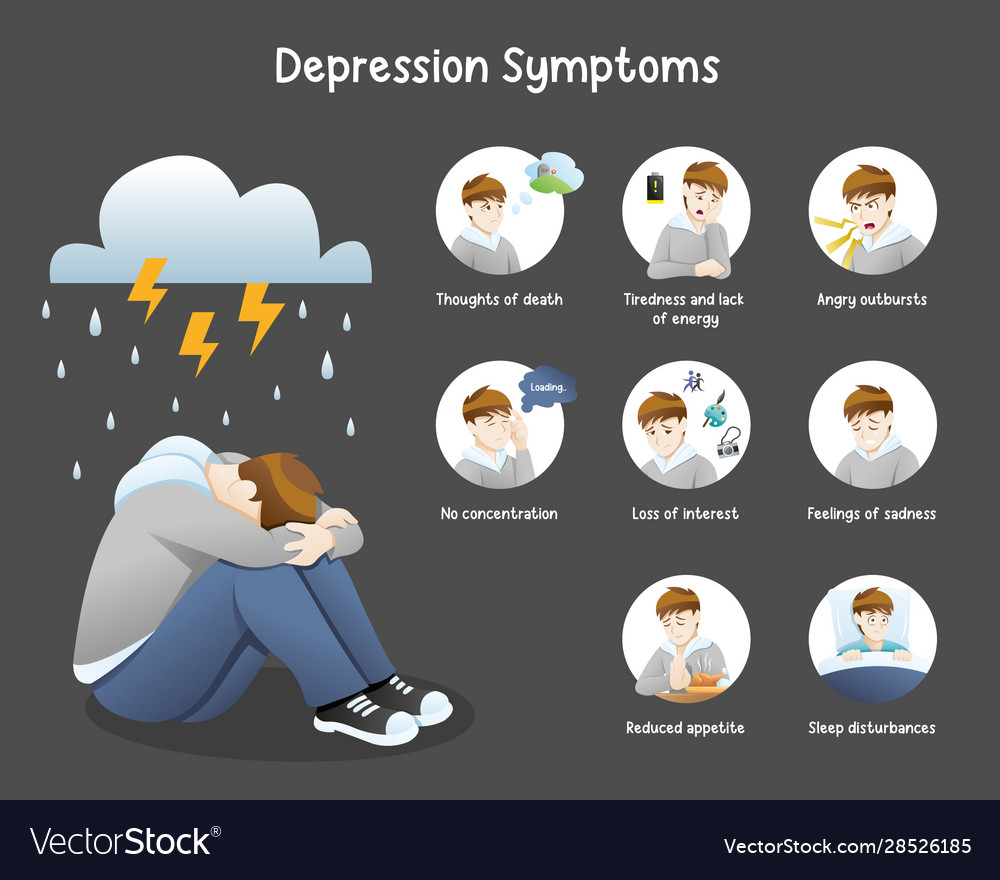
Animal studies have shown that gabapentinoids can cause respiratory depression alone and in combination with opioids. 12-14 Kozer and colleagues 12 showed that rabbits given morphine after Overall, while Gabapentin can be highly beneficial in treating various conditions, it must be used responsibly and under the guidance of a healthcare professional to minimize potential risks and adverse effects. In the context of the question, "can Gabapentin cause depression?", there is no direct evidence linking Gabapentin to depression. Considering the question of whether gabapentin can cause depression, it's also important to understand the safety concerns and withdrawal symptoms of this medication. Discontinuation Effects Gabapentin withdrawal symptoms have been reported, typically after discontinuing higher-than-recommended doses of gabapentin and for uses for which the Depression and suicidal thoughts can also make an unwelcome appearance. It’s as if gabapentin decided to invite the gloomiest rain cloud to your mental picnic. These feelings can range from a persistent low mood to more severe depressive symptoms. In some cases, patients may experience thoughts of self-harm or suicide. Abruptly stopping gabapentin can also exacerbate withdrawal symptoms like anxiety and agitation, which may worsen any underlying depression. In summary, while gabapentin has its approved uses, its connection with mood-related side effects, including depression and suicidality, necessitates vigilance and alternative treatment approaches for Research has shown that gabapentin can have varying effects on individuals with depression. Some studies suggest that gabapentin may help alleviate depressive symptoms in certain cases, while others indicate that it may not have a significant impact on mood disorders. This medicine may cause respiratory depression, a serious breathing problem that can be life-threatening, when used together with narcotic pain medicines. Check with your doctor right away if you have pale or blue lips, fingernails, or skin, difficult or trouble breathing, or irregular, fast or slow, or shallow breathing. Gabapentin isn’t usually used to treat anxiety alone. More often, it’s given to ease anxiety symptoms for someone who also has depression or bipolar disorder. (Anxiety is commonly comorbid with Gabapentin is primarily prescribed as an anticonvulsant for seizures and neuropathic pain, but its role in treating depression remains unclear. Despite being used off-label for mood disorders, significant evidence directly linking gabapentin to effective treatment of depression is lacking. While acute case studies highlight the risk of depression and suicidal ideation, controlled trials have not definitively linked gabapentin usage to a history of depression. Notably, gabapentin has been shown to influence neurotransmitters like GABA, which can affect mood. Currently, there is no direct evidence suggesting that gabapentin can cause depression outright. While it is utilized for various medical conditions, the psychiatric side effects associated with its use can be significant, including symptoms of aggression and suicidal thoughts. However, relevant research data have not proven success of newer antiepileptics. This article presents the negative side effects of gabapentin such as psychotic and depressive symptoms, which occur shortly after its use. The use of gabapentin in mood disorders is discussed through these side effects. Depression is a serious, yet uncommon, side effect of using gabapentin. It can either cause depression or make existing cases of depression worse. Individuals have a higher risk of developing depression as a side effect if they already have a history of a psychological disorder. Can Gabapentin Cause Depression? While gabapentin is primarily prescribed to manage conditions like epilepsy, neuropathic pain, and restless legs syndrome, there have been reports and studies suggesting a potential link between gabapentin use and the development or exacerbation of depressive symptoms in some individuals. Gabapentin has been associated with various psychiatric side effects, including depression. Patients taking this medication have reported significant personality changes and heightened feelings of depression, aggression, and suicidal ideation. Some reports suggest that gabapentin can exacerbate mood issues and has been linked to depressive symptoms, highlighting a complex relationship between the medication and mental health. Gabapentin has been approved by the United States (US) Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for postherpetic neuralgia and as adjunctive therapy for focal seizures. 1 However, a recent analysis of US physician office-based prescription practices between 2011 and 2016 found that less than one percent of gabapentin prescriptions are for such indications. 2 In 2020, gabapentin was reported to be If you’re taking gabapentin and you experience any new or worsening depression, or any changes in your behavior, let your prescriber know immediately. If you or someone you know is having thoughts of suicide, you’re not alone, and help is available. For additional reading about depression risks associated with medication, visit our article on can gabapentin cause depression?. Gabapentin Usage and Mental Health Potential Impact on Depression. Gabapentin is a medication commonly used for various conditions, including nerve pain and seizures. While there is no direct evidence suggesting that
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |