Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
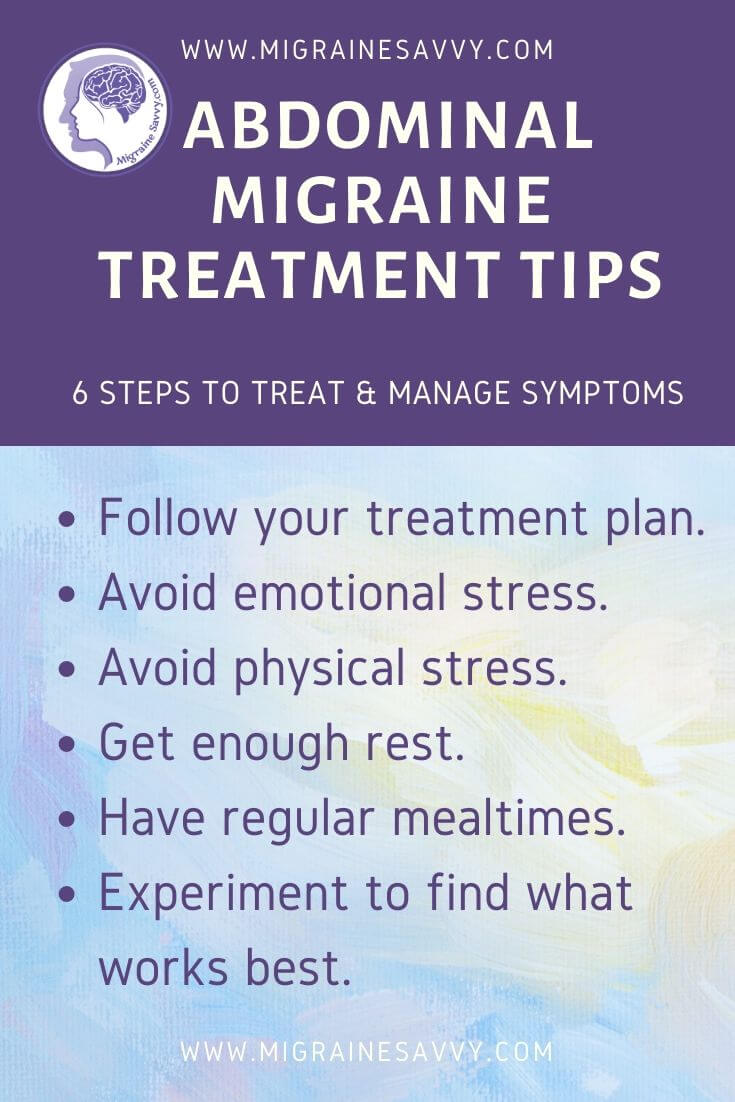
It will give you more information about gabapentin and will provide you with a full list of the side-effects which you may experience from taking it. Take gabapentin exactly as your doctor tells you to. There are several different strengths of gabapentin tablets and capsules available, and you could be prescribed more than one strength. Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant used off-label to help prevent migraine attacks. Learn about why it’s used and how it works. Many people living with migraine have not even talked to a doctor about their symptoms. If you have headaches where you have to rest in a dark room, where you might get sick to your stomach. Please talk to your healthcare professional about your symptoms. You might have migraine and we can treat migraine. Migraine is a chronic disease. Patients with mild migraine attacks – For patients with mild migraine attacks without vomiting or severe nausea, we suggest nonopioid analgesics (eg, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs [NSAIDs] such as ibuprofen or naproxen sodium and/or acetaminophen) , rather than other migraine-specific agents . Nonopioid analgesics are effective, widely Abdominal migraine is a form of migraine with abdominal pain, nausea, and vomiting episodes. It’s different from typical migraine attacks because it doesn’t usually have head pain as a symptom. This disease is mostly seen in children. Migraine is a common episodic disorder, the hallmark of which is a disabling headache generally associated with nausea and/or light and sound sensitivity. The acute treatment of migraine in adults is reviewed here. Preventive treatment of migraine in adults is discussed separately. (See "Preventive treatment of episodic migraine in adults".) Currently, some doctors are prescribing the gabapentin to prevent migraine headaches, treat nystagmus, and reduce neuropathic pain. [5, 6, 7] However, there are few studies on analgesic effects of gabapentin and other effects of it. • Most children with abdominal migraines will have migraines as adults Treatment • Dietary Modifications • Vitamins (riboflavin, magnesium, others) and supplements • Medications: • Antidepressants (amitriptyline). • Anti-nausea medication • Gabapentin • NSAIDs • Triptans- Abortive migraine treatment, NOT for prevention Discover the potential of gabapentin for preventing migraine attacks and headaches. While not a first-line treatment, it can be effective in combination with other options. Four trials with a total of 351 patients compared gabapentin in a dosage of 900 to 2,400 mg per day with placebo. The meta-analysis found no significant reduction in the frequency of migraine Gabapentin is a gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) analog that is initially developed for treating epilepsy but is currently used for various cases, including pain relief, and in particular neuropathic pain (such as headache and back pain). Gabapentin has a structure similar to gamma-butyric acid but is not converted into GABA or a GABA agonist in Studies were required to be prospective, controlled trials of gabapentin/gabapentin enacarbil or pregabalin taken regularly to prevent the occurrence of migraine attacks, to improve migraine‐related quality of life, or both. Two review authors independently selected studies and extracted data. Abdominal migraine is a difficult-to-diagnose condition characterized by stomach pain, nausea, and vomiting. Learn about symptoms and treatment. Gabapentin is used to control seizures, to treat nerve pain that can happen after having had shingles, and to treat a condition called restless legs syndrome. In addition to these FDA-approved uses, doctors sometimes prescribe gabapentin off-label. The recommendations on what information and self-care advice should be given to people with migraine are based on clinical guidelines National headache management system for adults [], Headaches in over 12s: diagnosis and management [], Primary care management of headache in adults [Becker, 2015] and Pharmacological management of migraine [], the American Headache Society updated consensus Headache subtype Diagnostic criteria Nonpharmacologic treatment options Gabapentin (Neurontin) is minimally effective at high doses, and adverse effects are common. Functional abdominal pain disorders (FAPDs) are common in childhood and include functional dyspepsia (FD), irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), abdominal migraine (AM), and functional abdominal pain–not otherwise specified (FAP-NOS) (Supplemental Table 5). 1,2 They are associated with a reduced quality of life, higher risks of anxiety and Abdominal migraine is a condition that causes episodes of moderate to severe abdominal (belly) pain lasting one to 72 hours. The condition is related to migraine headache, but doesn’t cause head pain. Children are most likely to experience abdominal migraine. What is abdominal migraine? Gabapentin (Neurontin) is FDA approved to treat certain types of seizures. It's also approved to treat nerve pain from shingles (postherpetic neuralgia). Gabapentin is also available as extended-release (ER) tablets Horizant and Gralise. These ER forms are approved to treat postherpetic neuralgia. There is limited evidence for nebivolol, bisoprolol, pindolol, carbamazepine, gabapentin, fluoxetine, nicardipine, verapamil, nimodipine, nifedipine, lisinopril, and candesartan. Acebutolol,
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |