Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
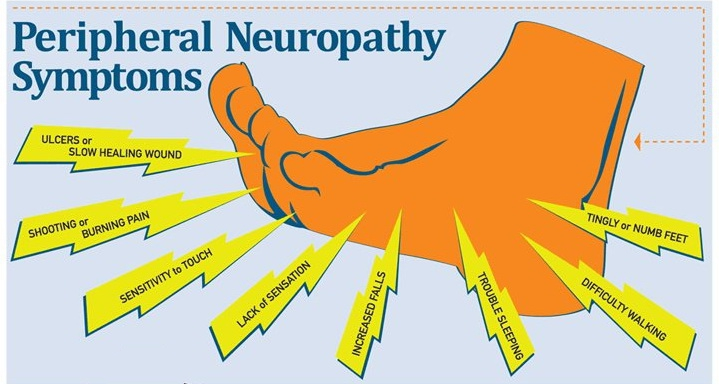
Researchers publishing in JAMA Neurology describe the results of a unique trial in which 402 people with idiopathic sensory polyneuropathy were randomly assigned to one of four medications: duloxetine, mexiletine, nortriptyline, or pregabalin. Alcoholic neuropathy, also known as alcoholic peripheral neuropathy, refers to damage of the nerves due to chronic and excessive alcohol consumption. Affected nerves include the peripheral nerves, primarily located in the arms and legs, and the autonomic nerves, which help regulate our internal body functions. This increases the risk of foot problems and other neuropathy complications. Eat healthy meals. Good nutrition is especially important to make sure that you get important vitamins and minerals. Include fruits, vegetables, whole grains and lean protein in your diet. Avoid excessive alcohol. Alcohol can make peripheral neuropathy worse. Gabapentin enacarbil available under the trade name Horizant is the only gabapentin product approved for treatment of Restless Legs Syndrome (RLS). A daily dose of 1200 mg provided no additional benefit compared with the 600 mg dose, but caused an increase in adverse reactions. Evidence from single-site studies lend support to the safety and efficacy of gabapentin as a novel treatment for alcohol use disorder, with unique benefits for alcohol-related insomnia and negative affect, relative to available treatments. AUD patients for which gabapentin should be considered are those with comorbid neuropathy (typically alcoholic neuropathy or even diabetic neuropathy). It inhibits excitatory calcium channels and potentiates inhibitory GABA-B receptors. It was difficult to give up but mixing gabapentin, Cymbalta, and supplements with alcohol also causes problems so why risk it? I find my neuropathy is staying the same at least and not progressing, my memory is 10 times better and I lost 20 lbs which puts less pressure on my feet. Observations that neuropathy can develop even in the setting of normal thiamine levels 70 and that the early stages of alcoholic neuropathy are characterized by painful paresthesia 71 have led scientists to postulate that alcohol and its metabolites have direct neurotoxic effects on small C fibers . 72, 73 Acetaldehyde is a known neurotoxin Diagnosing Alcoholic Neuropathy. While there is not one specific test to diagnose alcoholic neuropathy, there are a number of tests that will help to rule out other potential causes for neuropathy, including: diabetes test; heavy metal poison test; HIV test; syphilis test; Other tests that are used to ‘rule-in’ alcoholic neuropathy may be Alcohol takes away my neuropathy. But when I get sober the pain comes back even worse than normal. So I have to take more Kratom and CBD oil , which I supplement with my prescribed gabapentin. Evidence from single-site studies lend support to the safety and efficacy of gabapentin as a novel treatment for alcohol use disorder, with unique benefits for alcohol-related insomnia and negative affect, relative to available treatments. Alcoholic neuropathy is a condition of bilateral degeneration of peripheral nerves. The incidence of neuropathy in chronic alcoholism has ranged widely in the literature from 9 to 67% [1]. It manifests by altered superficial sensations and pain. In this guideline, gabapentin is suggested for patients with moderate to severe AUD who wish to reduce alcohol consumption or achieve abstinence, who prefer gabapentin or do not tolerate or respond to naltrexone and acamprosate, and for whom gabapentin is not contraindicated. a side effect of certain medicines or drinking too much alcohol; People who are known to be at an increased risk of peripheral neuropathy may have regular check-ups so their nerve function can be assessed. Treating peripheral neuropathy. Treatment for peripheral neuropathy depends on the symptoms and underlying cause. Ammendola A, Gemini D, Iannaccone S, et al. Gender and peripheral neuropathy in chronic alcoholism: a clinical-electroneurographic study. Alcohol Alcohol. 2000 Jul-Aug. 35(4):368-71. [QxMD MEDLINE Link]. Chopra K, Tiwari V. Alcoholic neuropathy: possible mechanisms and future treatment possibilities. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2012 Mar. 73(3):348-62. Alcohol-induced PN can be managed with antiseizure medication, which has an anticholinergic effect on the central and peripheral nervous systems and blocks the uptake of serotonin and norepinephrine to decrease pain perception. Gabapentin, pregabalin, and carbamazepine are commonly used to alleviate burning and stabbing dysesthesias. Painful dysesthesias associated with alcoholic neuropathy can be treated using gabapentin or amitriptyline with other over the counter pain medications, such as aspirin or acetaminophen. However these drugs are being used only for the management of acute pain and are ineffective in targeting the basic pathological pathways involved in alcoholic Gabapentin has been shown to be safe and effective for mild alcohol withdrawal but is not appropriate as mono-therapy for severe withdrawal owing to risk of seizures. During early abstinence, gabapentin may improve sleep, cravings, and mood—factors associated with relapse. Gabapentin works for me. Also No alcohol and I try to reduce sugar to 0. I take B1 and B12 but i think Gabapentin and diet change is the best option for me. Alcohol was the reason for my neuropathy though so i guess depending on the cause might have different remedies. Total recorded alcohol consumption per capita of individuals 15 years or older, in liters of pure alcohol. Alcoholism is the main cause of alcoholic polyneuropathy. In 2020 the NIH quoted an estimate that in the United States 25% to 66% of chronic alcohol users experience some form of neuropathy. [7]
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |