Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
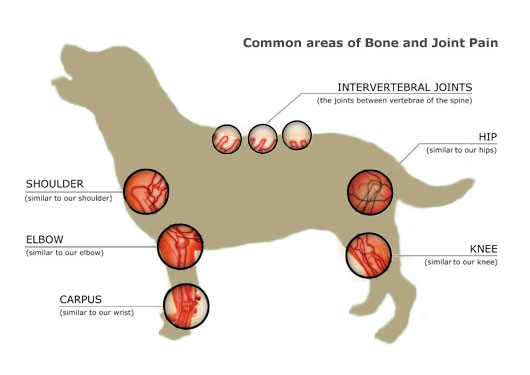
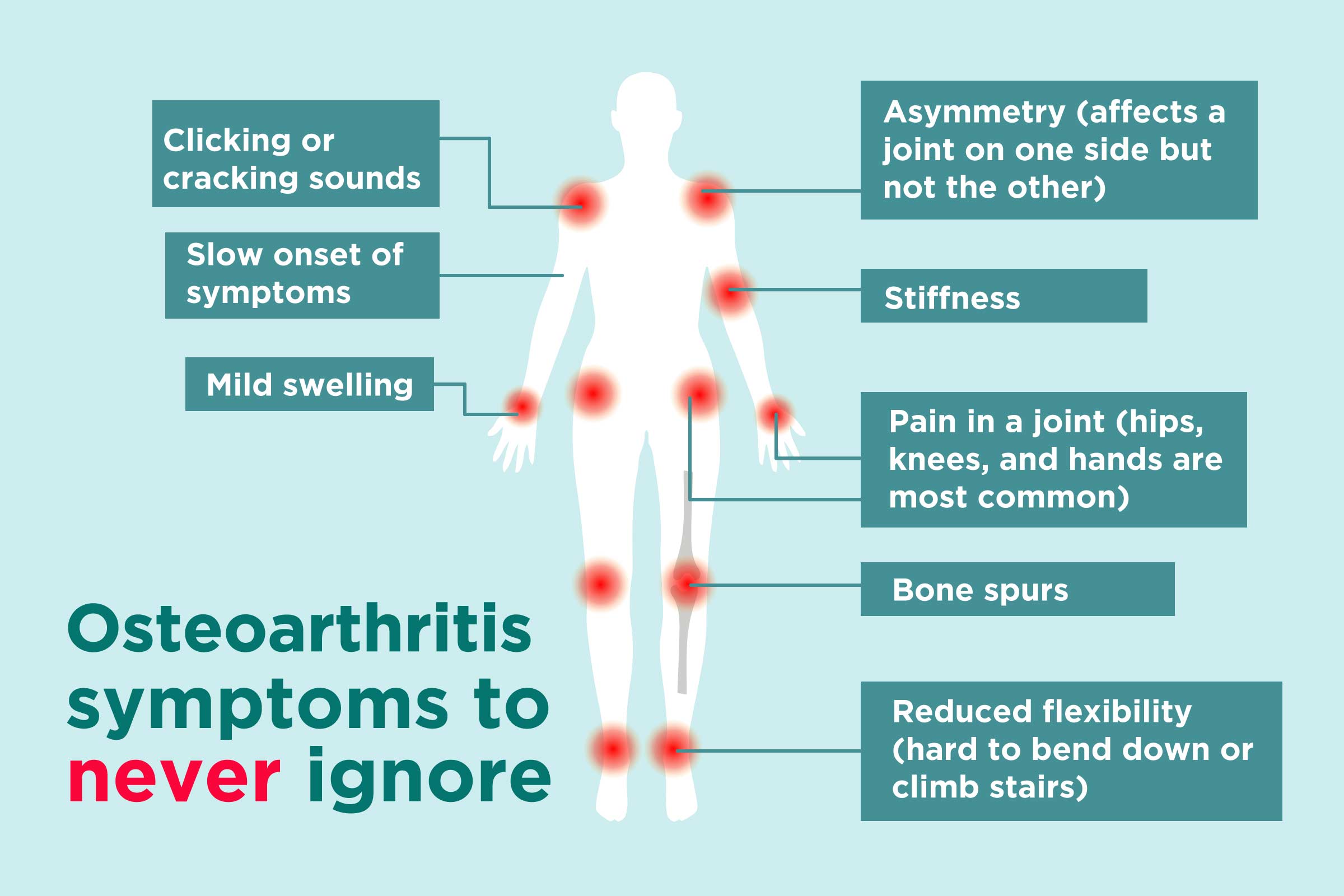
Gabapentin is prescribed for long-term pain control. It isn't used to treat short-term pain. Researchers aren't sure exactly how it works, but it may change how your body feels and reacts to pain. Back pain is very common and usually doesn’t have a serious cause. Download versus Arthritis - Back pain information Gabapentin and pregabalin aren’t Abstract. Gabapentin is prescribed for analgesia in chronic low back pain, yet there are no controlled trials supporting this practice. This randomized, two-arm, 12-week, parallel group study compared gabapentin (forced titration up to 3600 mg daily) to inert placebo. While potentially useful for treating severe knee OA, there is no strong evidence that gabapentin can provide relief from autoimmune forms of arthritis, such as rheumatoid arthritis and psoriatic arthritis. Gabapentin is also used to manage a condition called postherpetic neuralgia, which is pain that occurs after shingles. Gabapentin works in the brain to prevent seizures and relieve pain for certain conditions in the nervous system. It is not used for routine pain caused by minor injuries or arthritis. Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant. Gabapentin (generic for Neurontin), is commonly prescribed for neuropathy. Neuropathy is pain felt along the nerve endings. Many diabetics suffer from neuropathy. Gabapentin is also an anti seizure med. 300 mg at bedtime is a small dosage but sleepiness is a common side effect of the medicine so at the very least it may help promote sleep. Gabapentinoids are anticonvulsant medications that have shown benefit as antispasticity agents in studies in involving patients with spinal cord injuries. Both gabapentin and pregabalin inhibit the α²δ subunit of L-type voltage-gated Ca²⁺ channels, which are thought to inhibit glutamate release. Nerve pain medication: Gabapentin (Neurontin) and pregabalin (Lyrica) may help reduce neck and back nerve pain, especially sciatica. Begin with low doses to avoid daytime drowsiness and fall risk. Muscle relaxants. Tizanidine (Zanaflex) and baclofen (Lioresal) may reduce pain from muscle spasms. Gabapentin is occasionally taken as a pain relief option, but what’s the science behind it? This article will determine whether gabapentin is effective for arthritis pain, how it works, and how to make the most of it. A systematic review of the global prevalence of low back pain. Arthritis Rheum. 2012;64(6):2028–37. pmid:22231424 . View Article PubMed/NCBI Google Scholar 4. Morlion B. Chronic low back pain: pharmacological, interventional and surgical strategies. Symptoms usually begin within hours of combining the drugs and include confusion, agitation, irregular heartbeat, unstable blood pressure, tremors, muscle rigidity, nausea and vomiting. If you have these symptoms, stop taking your medication and seek immediate medical help. It’s most effective for treating neuropathic back pain caused by disk herniation and consequent sciatica, as well as spinal stenosis, diabetic neuropathy, and postherpetic neuralgia. It’s largely ineffective in treating non-specific chronic pain and arthritis, but may relieve fibromyalgia. The role of gabapentin for back pain works in the following way: Reduces the release of several neurotransmitters, decreasing the transmission of pain signals in the nervous system Prevents pain responses in animal models of hyperalgesia, indicating its ability to modulate the perception and processing of pain Background Chronic low back pain (CLBP) is a global health problem, and gabapentin and pregabalin are often used in the treatment of patients without associated radiculopathy or neuropathy. Therefore, determining their efficacy and safety is of enormous value. "I suffer from Rheumatoid Arthritis and I've been in constant pain since my diagnosis 4 years ago. The rheumatoid arthritis medications curbed the pain, but it was still 7 on a scale of 1-10 and it was debilitating. I've been on gabapentin for just 2 weeks and the pain is now down to a 2 on a scale of 1-10. Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant used to treat nerve related back pain, such as sciatica. Rheumatoid Arthritis; Thyroid Disorders; Treating neuropathic sciatic pain with gabapentin is According to research, Gabapentin is inefficient in treating back pain caused by chronic conditions like arthritis. Gabapentin is ineffective in the treatment of lumbar pain that isn’t radicular or non-radicular. Gabapentin is a remedy for nerve pain that’s also prescribed for back pain. See how it works and if it can help back pain from sciatica, shingles, and more. Arthritis-related back pain: Studies suggest gabapentin’s limited effectiveness in treating back pain associated with chronic conditions like arthritis, regardless of whether the pain is radicular or non-radicular. You might get some relief from joint and muscle pain using a non-burning capsaicin cream on the market in the US called Capsadyn. Even at the maximum concentration allowed by the FDA (0.25%), it was clinically demonstrated to not burn.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |