Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |
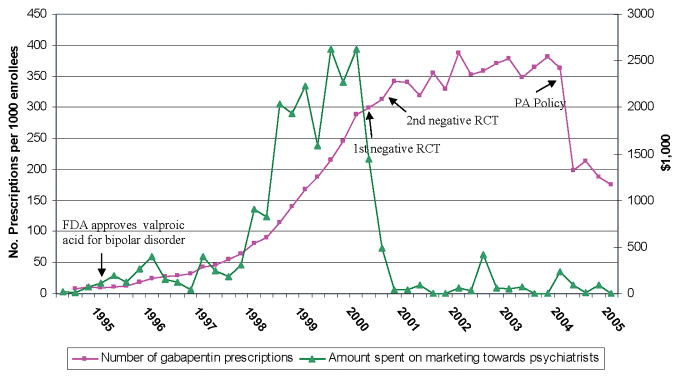
Flowchart of included and excluded studies. Bipolar disorder (BD) Four DB-RCTs investigating the efficacy of gabapentin in BD were identified. 101 patients were randomised to receive gabapentin, 81 to placebo, 30 to lamotrigine and 19 to carbamazepine. Gabapentin isn’t usually used to treat anxiety alone. More often, it’s given to ease anxiety symptoms for someone who also has depression or bipolar disorder. (Anxiety is commonly In an open-label trial (n = 22), Wang et al 33 reported success in treating mild to moderate bipolar depression with adjunctive gabapentin (mean dose of 1,725 mg/d) for 12 weeks. Background: Gabapentin, a new anti-epileptic agent, has been anecdotally reported to be effective in the treatment of mania. We systematically assessed the response rate in bipolar patients being treated adjunctively with gabapentin for manic symptoms, depressive symptoms, or rapid cycling not responsive to standard treatments. gabapentin (Neurontin) Doctors most often prescribe lithium for treating bipolar disorder symptoms. (2018). Antidepressants in bipolar depression: An enduring controversy. https: Gabapentin may be a useful drug for the add-on treatment of bipolar patients with poor response to other mood stabilizers. Gabapentin may improve depressive residual symptoms such as irritability, social withdrawal or anxiety. These results should be confirmed in randomized clinical trials. Lithium and gabapentin. Gabapentin is currently being studied as a treatment for bipolar disorder, and there have been favorable reports regarding its potential as a mood stabilizer (82, 83). The advantages of gabapentin include the lack of interactions with other drugs in the cytochrome P450 system and the lack of protein binding . Since there We identified 40 open-label studies on the use of GBP in at least 600 patients with bipolar disorder (BP), manic, depressed, or mixed episodes and unipolar depression and four controlled studies. It is crucial to monitor any changes in mood or depression while taking the medication and seek medical attention if necessary.Additionally, gabapentin can interact with other medications, including opioids and certain stomach acid medications, so it is important to inform healthcare providers about all medications being taken. Background: with increasing awareness of lithium’s limitations, several new anticonvulsants had been tested for their mood stabilisation during recent years. Among the innovative third generation mood stabilizing anticonvulsants, gabapentin (GBP) seems to have a broad spectrum of efficacy, although no certain data are available as to its efficacy and use in clinical practice. Depression and Bipolar Support Alliance: Gabapentin “was used frequently for treatment of bipolar disorder, but controlled studies found it was no more effective than a placebo.” American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry : Gabapentin has “not been shown to effectively treat mania or depression associated with bipolar disorder.” Gabapentin: Gabapentin is indicated for postherpetic neuralgia and serves as adjunctive therapy for managing partial seizures (with or without secondary generalization) in adults and pediatric patients aged 3 or older. other parts of the bipolar spectrum (bipolar disorder, type II, and bipolar disorder, NOS; 11/27, 41%) was over twice that of bipolar disorder type I (2/13, 15%, p = .16, Fisher’s exact test) or unipolar major depressive disorder (2/10, 20%, p = .44, Fisher’s exact test), but these differ-ences were not statistically significant. Gabapentin was significantly more effective than lamotrigine and carbamazepine in reducing depressive symptoms on the Minnesota Multiphasic Personality Inventory-2 (MMPI-2) depression Results: Gabapentin was moderately to mark-edly effective in 30% (15/50) of patients, with statistically nonsignificant differences between patients with bipolar disorder type I, bipolar dis-order type II and NOS, and unipolar major de-pressive disorder. 70% reported side effects, mainly sedation, with 16% of the total sample discontinuing treat A psychiatrist answers common questions about mood stabilizers for bipolar depression. Other medications, like topiramate (Topamax) or gabapentin (Neurontin), may be prescribed in some cases Evidence does not support the use of gabapentin for bipolar disorder, major depressive disorder (MDD), posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD), obsessive compulsive disorder (OCD), stimulant use disorder, or opioid withdrawal. Gabapentin may be a useful drug for the add-on treatment of bipolar patients with poor response to other mood stabilizers. Gabapentin may improve depressive residual symptoms such as irritability, social withdrawal or anxiety. These results should be confirmed in randomized clinical trials. Despite of the lack of evidence, reviews of gabapentin prescribing patterns in the United States show that this medication is still being used with alarming frequency for bipolar disorder. There are now five medications with specific, FDA approval for acute bipolar depression. Background: Gabapentin (GBP) may be useful in bipolar disorders, including as adjunctive therapy for bipolar depression, although controlled studies suggest inefficacy as primary treatment for mania or treatment-resistant rapid cycling.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |