Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
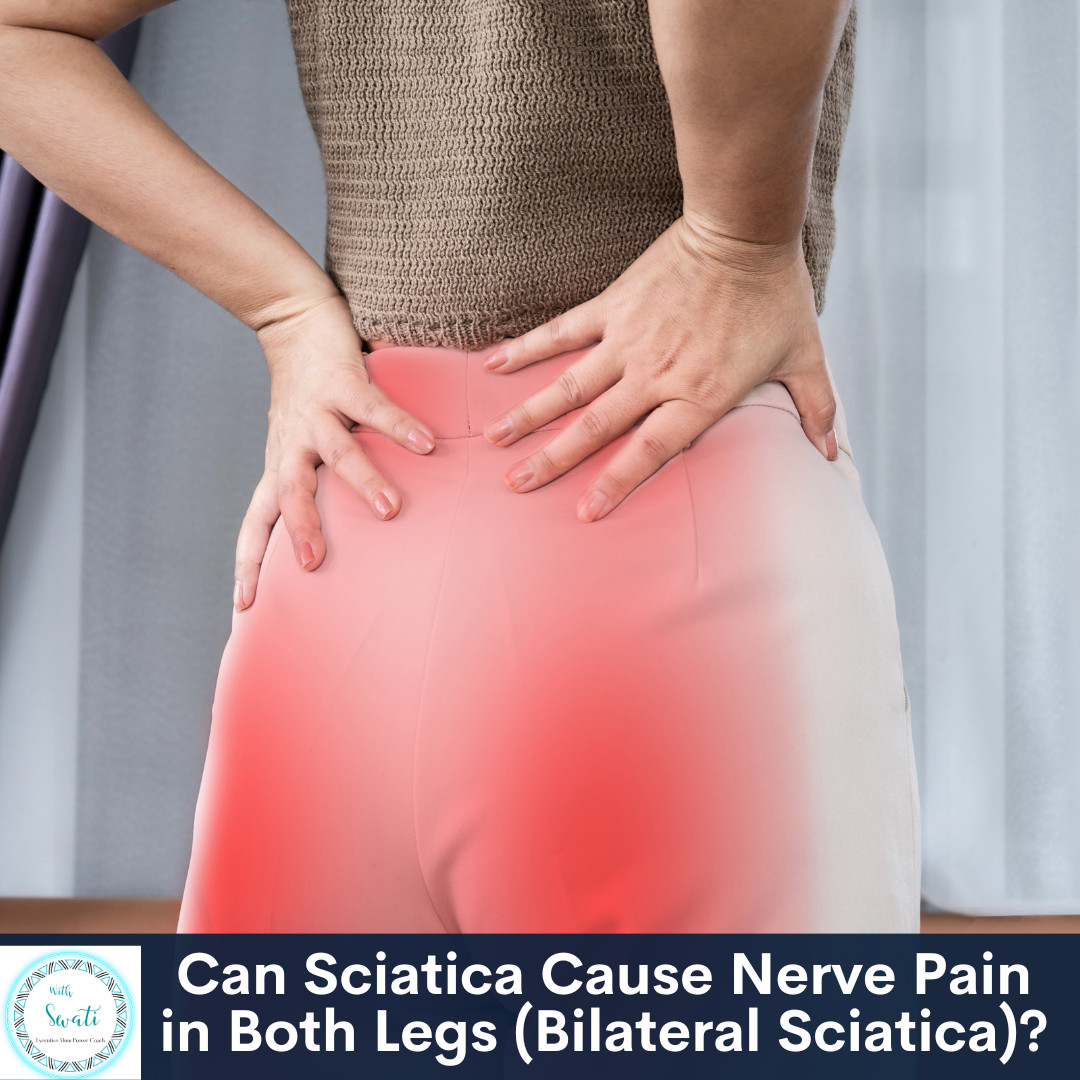
Chronic sciatica (CS) is sciatica which has been present for more than 3 months despite active conservative management, including physical therapy. CS may complicate previous chronic low back pain; however, it may also present purely as an isolated phenomenon [ 1 , 4 ]. Findings This randomized clinical trial of pregabalin vs gabapentin in 18 patients with chronic sciatica found that gabapentin was superior to pregabalin with greater reduction of leg pain intensity and fewer adverse events. Gabapentin can help relieve sciatica, intense pain that runs along the sciatic nerve from the lower back through the hips and buttocks (12). Sciatica affects one side of the body and is usually caused by disk herniation or spinal stenosis (12). Prescribing gabapentin for chronic, non-specific low back pain is not recommended. Patients who suffer from nerve pain, numbness, and tingling in the legs from sciatica or have diabetic Deyo RA, Weinstein JN. Low back pain. The New England journal of medicine. 2001;344(5):363–70. pmid:11172169 . View Article PubMed/NCBI Google Scholar 2. Hooten WM, Cohen SP. Evaluation and Treatment of Low Back Pain: A Clinically Focused Review for Primary Care Specialists. In this randomized, double-blind, double-dummy, cross-over trial of pregabalin versus gabapentin for management of chronic sciatica (CS), 20 patients with unilateral CS were randomized to receive gabapentin (400 mg to 800 mg, 3 times daily) then pregabalin (150 mg to 300 mg twice daily, plus once-daily placebo for blinding) or vice versa, each "The most important finding is that the widespread use of pregabalin or gabapentin for chronic non-specific low back pain, which is the most common chronic pain ailment today, is not supported by evidence," said study author Harsha Shanthanna, MD, MBBS, MSc, PhD, associate professor of anesthesiology and a chronic pain physician at St. Joseph's Gabapentin is a remedy for nerve pain that’s also prescribed for back pain. See how it works and if it can help back pain from sciatica, shingles, and more. For those with contraindications or intolerable side effects from tricyclic antidepressants or SNRIs, gabapentin represents an effective alternative oral medication for chronic sciatica according to IASP guidelines. Combining gabapentin with non-pharmacologic approaches like physical therapy and exercise may allow for lower therapeutic doses A small study comparing gabapentin to pregabalin for chronic sciatica found that gabapentin might be the better option. The study showed that treatment with gabapentin resulted in more pain relief and had less risk of side effects when compared to pregabalin. For chronic low back pain and neurogenic claudication, similar recent reviews also did not find any treatment benefit for anticonvulsants. 5, 14 Unlike our review, which focuses on comparisons with placebo-controlled trials, Shanthanna and colleagues 14 compared anticonvulsants with other active treatments for chronic low back pain, and found a Both gabapentin (GBP, Neurontin) and pregabalin (PGB, Lyrica) are used to treat chronic sciatica (CS). Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) is an important pain-related neurotransmitter, although neither GBP nor PGB affect the GABA receptor. Background Chronic low back pain (CLBP) is a global health problem, and gabapentin and pregabalin are often used in the treatment of patients without associated radiculopathy or neuropathy. Therefore, determining their efficacy and safety is of Previous trials of pregabalin and gabapentin in patients with chronic low back pain or sciatica did not show a beneficial effect over placebo. 10,11 Our trial extends this finding by the inclusion Chronic sciatica (CS), like most neuropathic pain states, is often resistant to simple treatment regimens. 1,2 Chronic sciatica is sciatica lasting longer than 3 months. 3 Neuropathic pain states are typically managed by super-adding anticonvulsant drugs onto simple drug regimens. The drugs most commonly used are gabapentin (GBP) or pregabalin Gabapentin is prescribed for analgesia in chronic low back pain, yet there are no controlled trials supporting this practice. This randomized, two-arm, 12-week, parallel group study compared gabapentin (forced titration up to 3600 mg daily) to inert placebo. Despite the specific indications of gabapentinoids, there is a notable increase in the off-label prescription of, which has raised the concern about the misuse of these drugs since the benefits remain unclear. 17, 18, 19 To our knowledge regarding their use on sciatica, pain relief only has been reported in one trial comparing gabapentin with placebo 20 and in no one of those investigating A 2016 double-blind RCT (N = 108) investigated gabapentin as a treatment for chronic low back pain with and without a radicular component. 2 This RCT was included in the 2017 meta-analysis but is Is chronic non-specific low back pain chronic? definitions of a problem and problems of a definition. Br J Gen Pract. 1999;49(442):358-362. - PMC - PubMed Robertson KL, Marshman LA. Gabapentin superadded to a pre-existent regime containing amytriptyline for chronic sciatica. Nerve pain medication: Gabapentin (Neurontin) and pregabalin (Lyrica) may help reduce neck and back nerve pain, especially sciatica. Begin with low doses to avoid daytime drowsiness and fall risk. Muscle relaxants. Tizanidine (Zanaflex) and baclofen (Lioresal) may reduce pain from muscle spasms.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |