Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 | 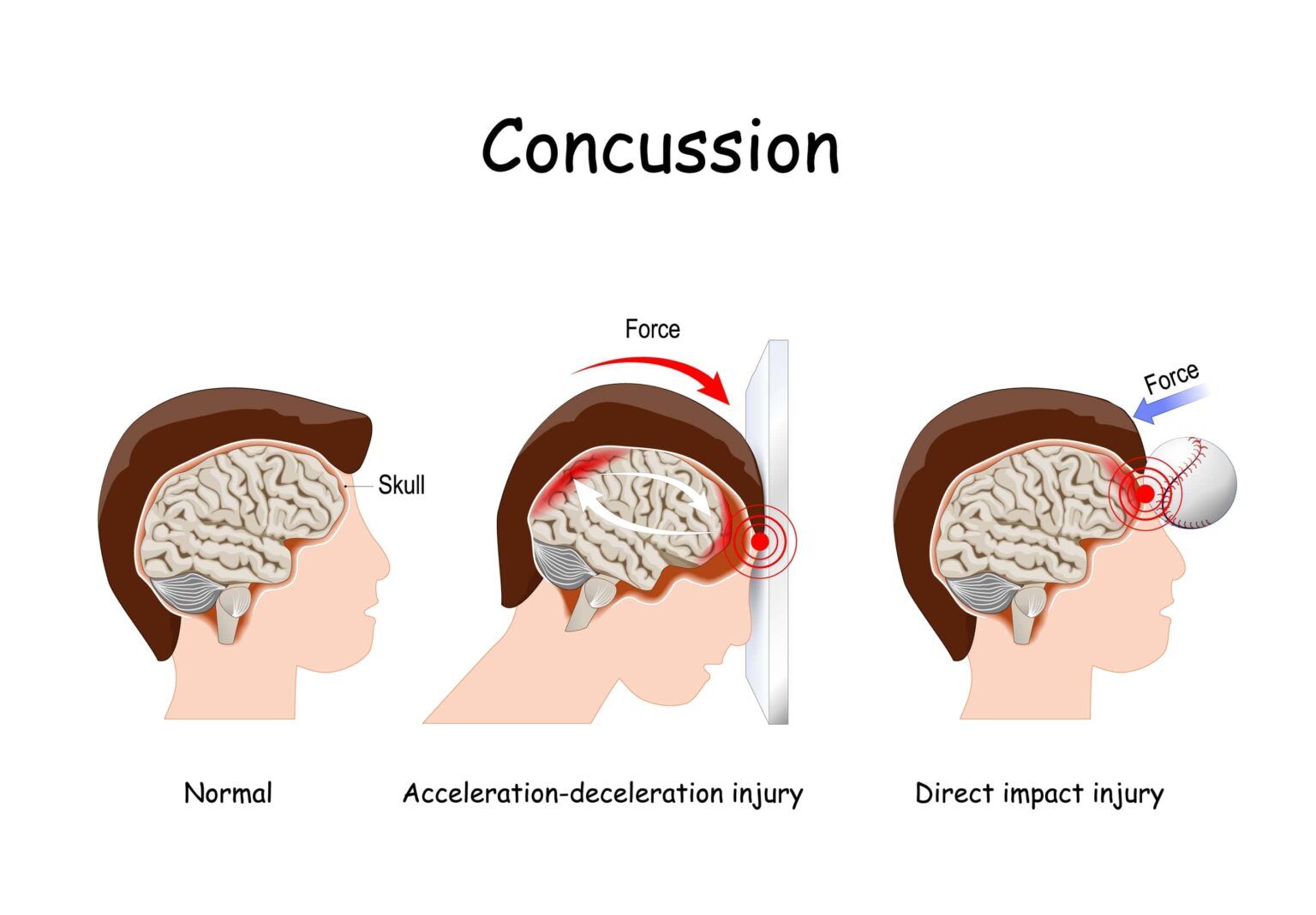 |
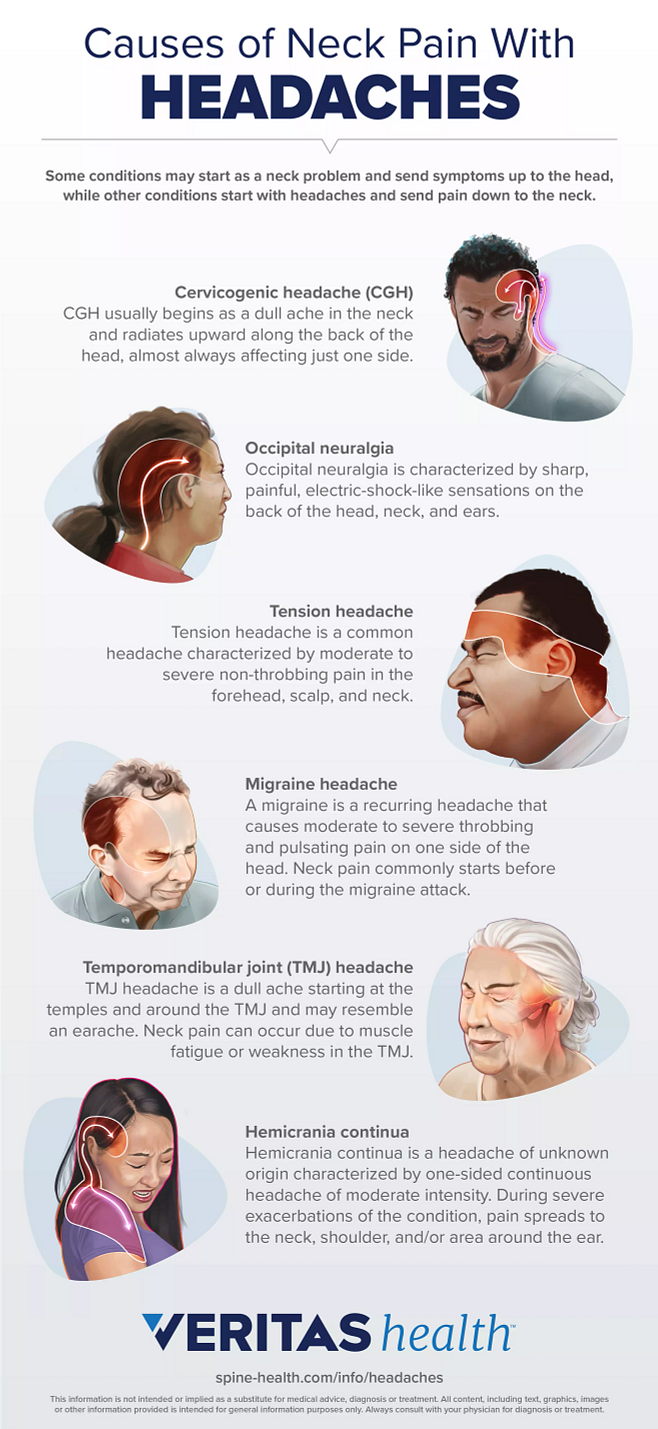
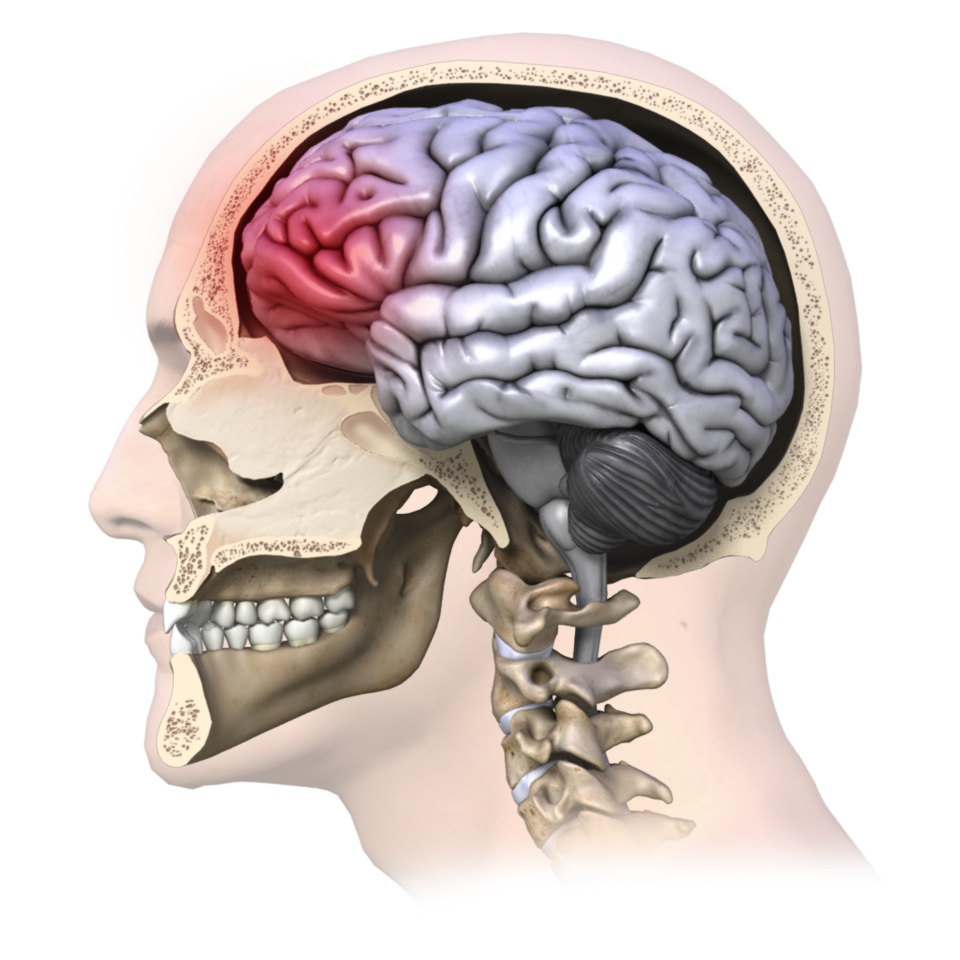
Gabapentin (GBP), originally an antiepileptic drug, is more commonly used in the treatment of pain, including headache disorders. Off-label GBP is used in headache disorders with some success, some failure, and much debate. This distinction between post-concussion headaches and concussion-related headaches also highlights the importance of baseline testing. If a clinician has a valid baseline test at his disposal for a given patient who has suffered a brain injury, he will much more easily be able to determine the clinical significance of his patient’s post Disease/ Disorder Definition. Acute headache attributed to trauma or injury to the head and/or neck is defined by the International Headache Society (ICHD 3) as a headache occurring within 7 days of a head or neck trauma, within 7 days after regaining consciousness, and/or within 7 days of being able to report pain after the injury but lasting less than 3 months. The most common headache quality was a combined throbbing and pressing headache (45%) followed by “pure” pressing headache (32%) and “pure” throbbing headache (18%). Continuous photophobia and phonophobia was reported by 46% and 60% of the subjects, respectively [ 18 ]. 87% ( N = 100) of the surveyed MTBI subjects in the study indicated Gabapentin or TCAs were prescribed to some patients during their follow‐ups for headache treatment, based on physician judgment. Patients were classified into 3 groups: (1) no medication; (2) To examine the association of commonly prescribed post-concussive medications, namely gabapentin and tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs), with symptom reduction after concussion. Background. Concussion is a common diagnosis in modern medicine. Headaches are the most common symptom associated with concussions and many providers will treat post concussive headaches with medications besides acetaminophen or NSAIDs. Headaches related to concussions are sometimes separated into tension-type headaches and migraine-type headaches (3). Post-traumatic headaches (PTHA) are a common sequela of traumatic brain injury (TBI) and may progress to chronic and possibly debilitating conditions.[1] PTHA can be further subdivided into 2 general categories. Acute PTHA is attributed to TBI that resolves within 3 months, and persistent PTHA has not resolved within 3 months.[2] There are several potentially overlapping phenotypes of PTHA. Some brain injury patients may experience heightened anxiety and restlessness when taking gabapentin. Mood swings, irritability, or depression have been reported with Gabapentin. Although gabapentin is not considered highly addictive, it does cross the blood-brain barrier and has a risk for physical dependence. Treating Brain Damage with Gabapentin Several drugs are often used to treat symptoms of concussion, including an epilepsy drug, gabapentin (Neurontin), amitriptyline (Elavil) and other antidepressants. A recent study by doctors at the University of Utah in Salt Lake City examined the role of medications in the treatment of concussions. To date, the FDA has not approved any medication specifically for treatment of concussion, but patients are frequently prescribed either gabapentin or a tricyclic antidepressant (TCA) such as amitriptyline or nortriptyline. Sutton KG, Martin DJ, Pinnock RD, Lee K, Scott RH. Gabapentin inhibits high-threshold calcium channel currents in cultured rat dorsal root ganglion neurones. Br J Pharmacol. 2002;135(1):257–265. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0704439. [PMC free article] [Google Scholar] 8. Rose MA, Kam PC. Gabapentin: Pharmacology and its use in pain management. To examine the association of commonly prescribed post-concussive medications, namely gabapentin and tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs), with symptom reduction after concussion. Concussion is a common diagnosis in modern medicine. Patients recover from a concussion with time, regardless of medication. Gabapentin and TCAs appear to have immediate effects on improving symptom burden, but long-term outcomes show similar improvement compared to those who are not prescribed medication. Headache subtype Diagnostic criteria Nonpharmacologic treatment options Gabapentin (Neurontin) is minimally effective at high doses, and adverse effects are common. Headaches are one of the most common persisting symptoms following a concussion. Post-traumatic headaches are defined as the onset of a headache within 7 days following concussion and are either acute (first 3-months of β-Blockers, calcium channel blockers, valproic acid, topiramate, triptans, dihydroergotamine, and gabapentin, have all been discussed as potential medical therapies for persistent headaches after concussion and may make reasonable choices in the appropriate circumstances. 41,42,44,48,49 We would like to show you a description here but the site won’t allow us. Gabapentin, amitriptyline, and nortriptyline can produce sedation, which can help those suffering from sleep disturbance. If a provider is not comfortable prescribing these medications or doesn’t prescribe them regularly, the patient should be referred to a concussion or headache specialist more familiar with their use. Data sources. We searched PubMed and Embase databases for articles on acute and prophylactic pharmacological PTH treatment. The search was performed on January 16, 2019 with the following search string: (post traumatic headache OR post-traumatic headache OR posttraumatic headache OR post traumatic migraine OR post-traumatic migraine OR posttraumatic migraine OR post concussion headache OR post
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |