Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 | %2C+Newcastle+upon+Tyne%2C+UK+2+Medical+Toxicology+Centre%2C+Newcastle+University%2C+Newcastle+upon+Tyne%2C+UK..jpg) |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | 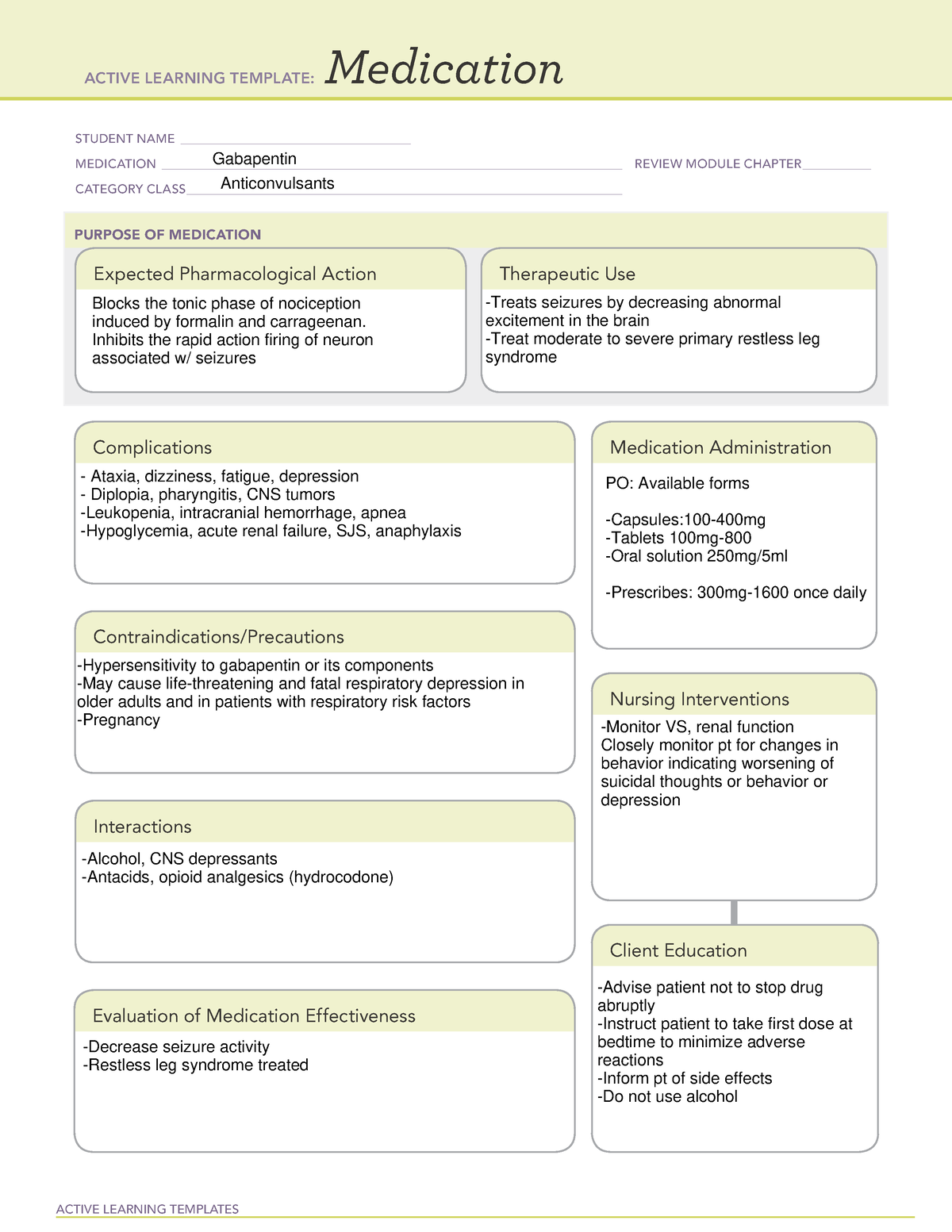 |
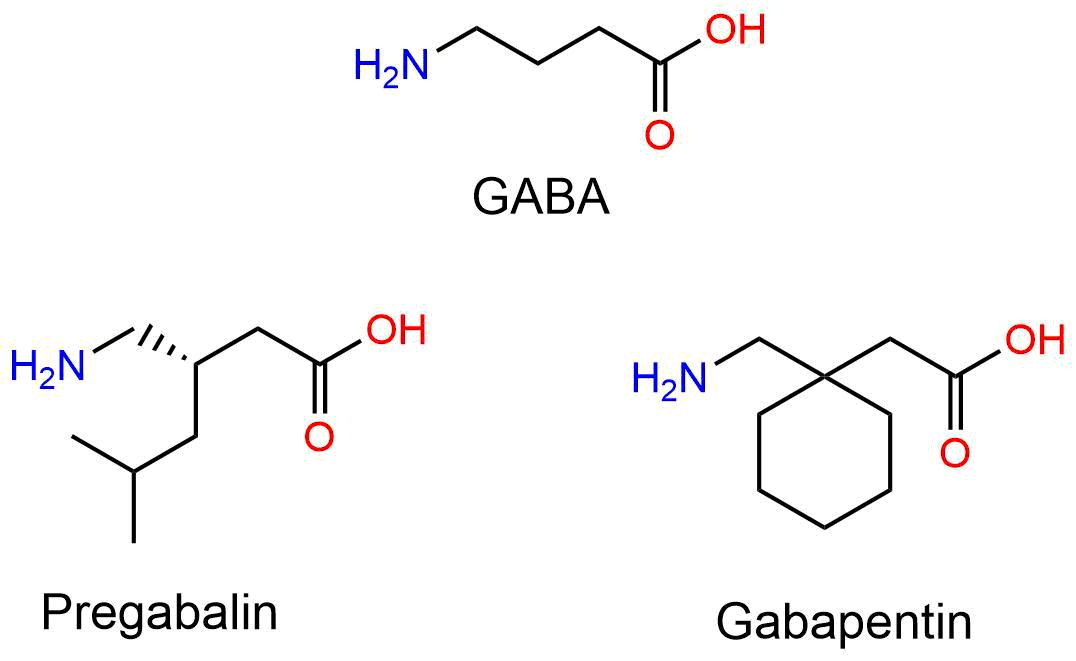
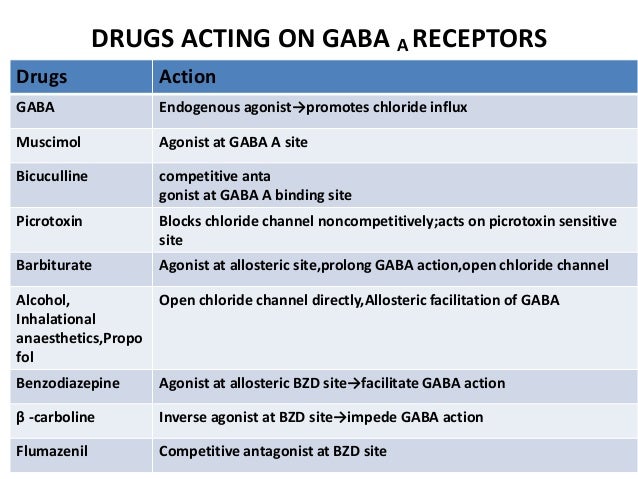
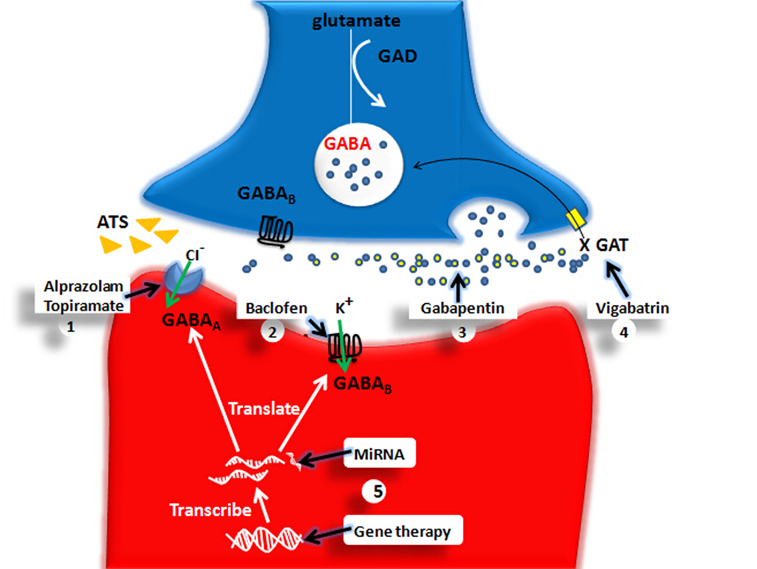
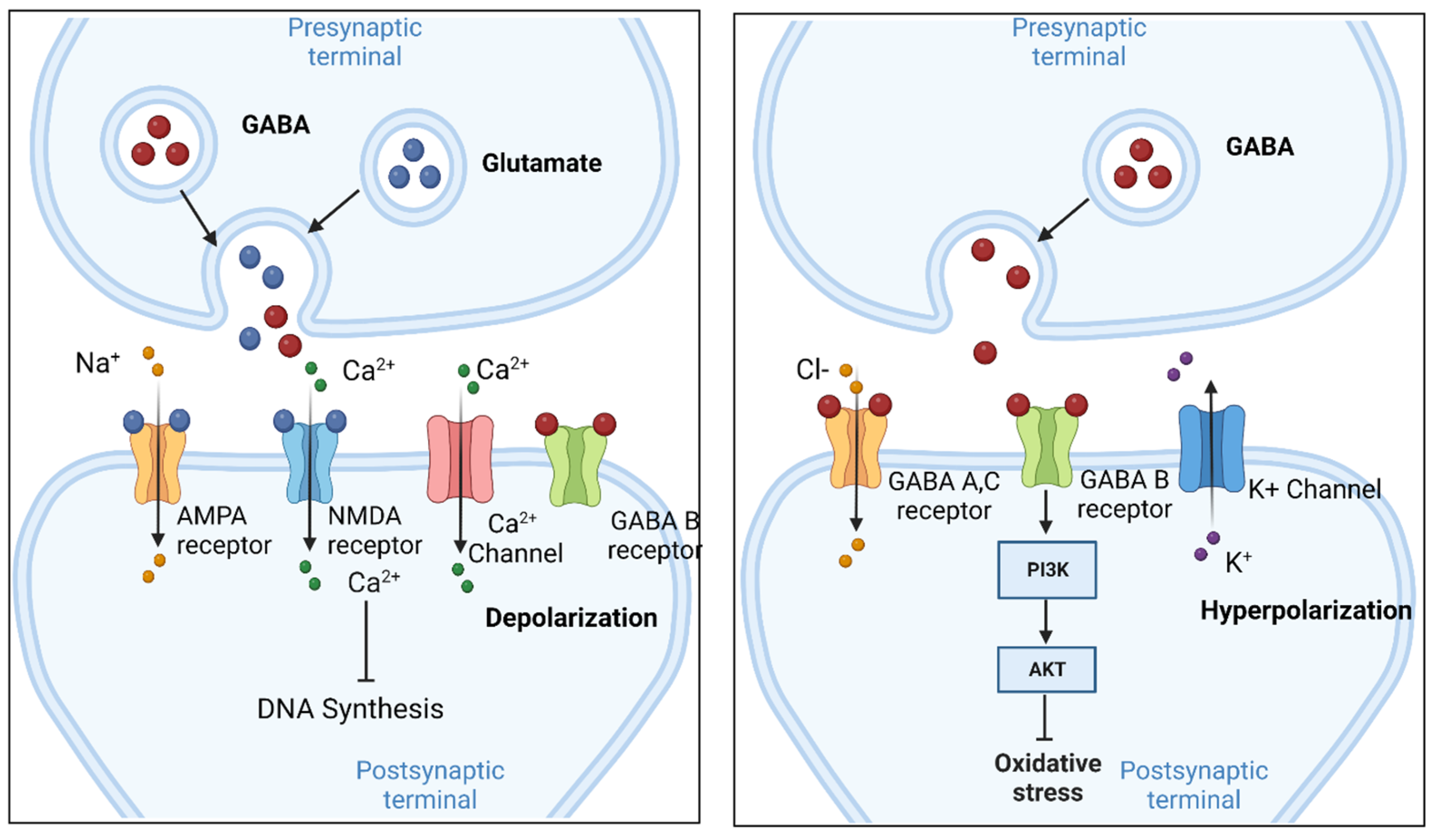
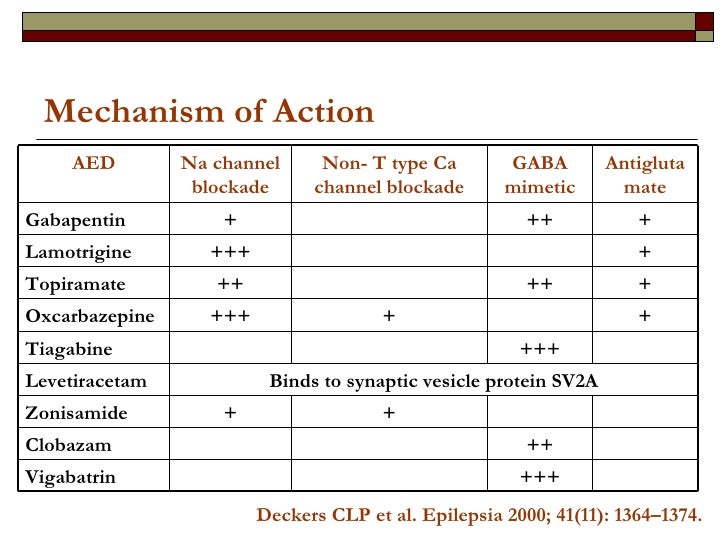
Gabapentin: Gabapentin (Neurontin) was originally approved by the US FDA in 1993 for the adjunctive treatment of partial seizures. This was then followed up with the approval for postherpetic neuralgia in 2002. Gabapentin was originally developed to be a γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) neurotransmitter analogue but it was We summarise the studies that have been performed which demonstrate that gabapentin appears to interact with a novel binding site expressed at high density within the central nervous system (CNS), namely the α2δ voltage-dependent calcium channel subunit. Gabapentinoids bring relief in only 35% of patients (Moore and others 2014). Gabapentin was designed as a GABA mimetic with increased lipophilicity so as to improve access to the cen-tral nervous system. gabapentin pregabalin gabapentinoids โรคลมชัก อาการปวดเส้นประสาทส่วนปลาย gamma-aminobutyric acid GABA-mimetic properties Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency MHRA ยาผิดกฎหมาย illegal drugs Misuse of Drugs Act 1971 Schedule Brain GABA levels appeared to be higher in patients taking high-dose gabapentin (3,300-3,600 mg/day) than in those taking standard doses (1,200-2,400 mg/day). Gabapentin appears to increase human Gabapentin, known by brand names like Neurontin and Gralise, is a bit of a pharmaceutical chameleon. Originally developed to treat epilepsy, it’s now prescribed for a smorgasbord of conditions, from nerve pain to restless leg syndrome. Despite chemical similarity to the inhibitory neurotransmitter γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) and despite the effort to increase lipophilicity of this GABA-mimetic agent, gabapentin neither mimics GABA nor acts specifically at GABA receptors or GABA synapses. 1,2 Current evidence suggests that the most probable mechanism for the functional To substantiate the notion that cocaine behavioral effects may be influenced by γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) neurotransmission male Wistar rats were injected with gabapentin (a cyclic GABA analogue), tiagabine (a GABA reuptake inhibitor), or vigabatrin (a GABA transaminase inhibitor) before acute or repeated treatment with cocaine evoking either locomotor hyperactivation or sensitization. Gabapentin was originally designed as an anti-convulsant g-aminobutyric acid (GABA) mimetic capa-ble of crossing the blood-brain barrier. In the present re-view we show that although gabapentin is not a GABA mimetic, it has great utility as an add-on therapy for epilepsy and as a first-line treatment for neuropathic pain. Gabapentin was originally designed as an anticonvulsant γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) mimetic capable of crossing the blood-brain barrier. In the present review we show that although gabapentin is not a GABA mimetic, it has great utility as an add-on therapy for epilepsy and as a first-line treatment for neuropathic pain. We summarise the studies that have been performed which demonstrate that In this targeted narrative review, we aim to disabuse pain physicians and other clinicians, pharmacists, and policymakers of both the positive and negative myths concerning gabapentinoid medications. Gabapentin was originally designed as an anti-convulsant gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) mimetic capable of crossing the blood-brain barrier. In the present review we show that although gabapentin is not a GABA mimetic, it has great utility as an add-on therapy for epilepsy and as a first-line treatm Gabapentin enhanced expression of δGABA A receptors and increased a tonic inhibitory conductance in neurons. This increased expression likely contributes to GABAergic effects as gabapentin caused ataxia and anxiolysis in wild-type mice but not δ subunit null-mutant mice. Physicians who administer gabapentin should inform their patients about the potential risk of gabapentin-induced incontinence and its negative impact on quality of life. 1. Introduction. Gabapentin is a structural analogue of gamma aminobutyric acid (GABA) and was originally designed as an anticonvulsant . Maneuf YP, Gonzalez MI, Sutton KS, Chung FZ, Pinnock RD, Lee K. Cellular and molecular action of the putative GABA-mimetic, gabapentin. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2003. 60:742–750. 22. Although gabapentin was developed as a GABA-mimetic compound subsequent studies have shown that it does not have a major effect on GABA receptors or other GABA mechanisms. In animal models gabapentin is effective against chemically-induced seizures, maximal electroshock seizures and kindled Gabapentin’s effects on brain GABA, phosphomonoesters, and bioenergetics: A 31P-MRS study. Cellular and molecular action of the putative GABA-mimetic Gabapentin functions as a γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA)-mimetic agent, binding to the alpha-2-delta subunit of the voltage-gated calcium channels, purportedly inferring antinoceptive, anticonvulsant, and anxiolytic properties. 1 Gabapentin was originally approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 1993 for epilepsy and later The drug is a GABA analog, but is not a GABA mimetic, although some neurons that respond to gabapentin are GABAergic. Gabapentin, at relevant concentrations, binds to an auxiliary protein of voltage-gated calcium channels (a2/3) and apparently, as a result, modulates the action of calcium channels and neurotransmitter release. GBP, was formerly known as an anticonvulsant γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) mimetic, is considered as a safe and well-tolerated antiepileptic drug (AED) with promising pharmacokinetic properties and a wide therapeutic index.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 | %2C+Newcastle+upon+Tyne%2C+UK+2+Medical+Toxicology+Centre%2C+Newcastle+University%2C+Newcastle+upon+Tyne%2C+UK..jpg) |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |