Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
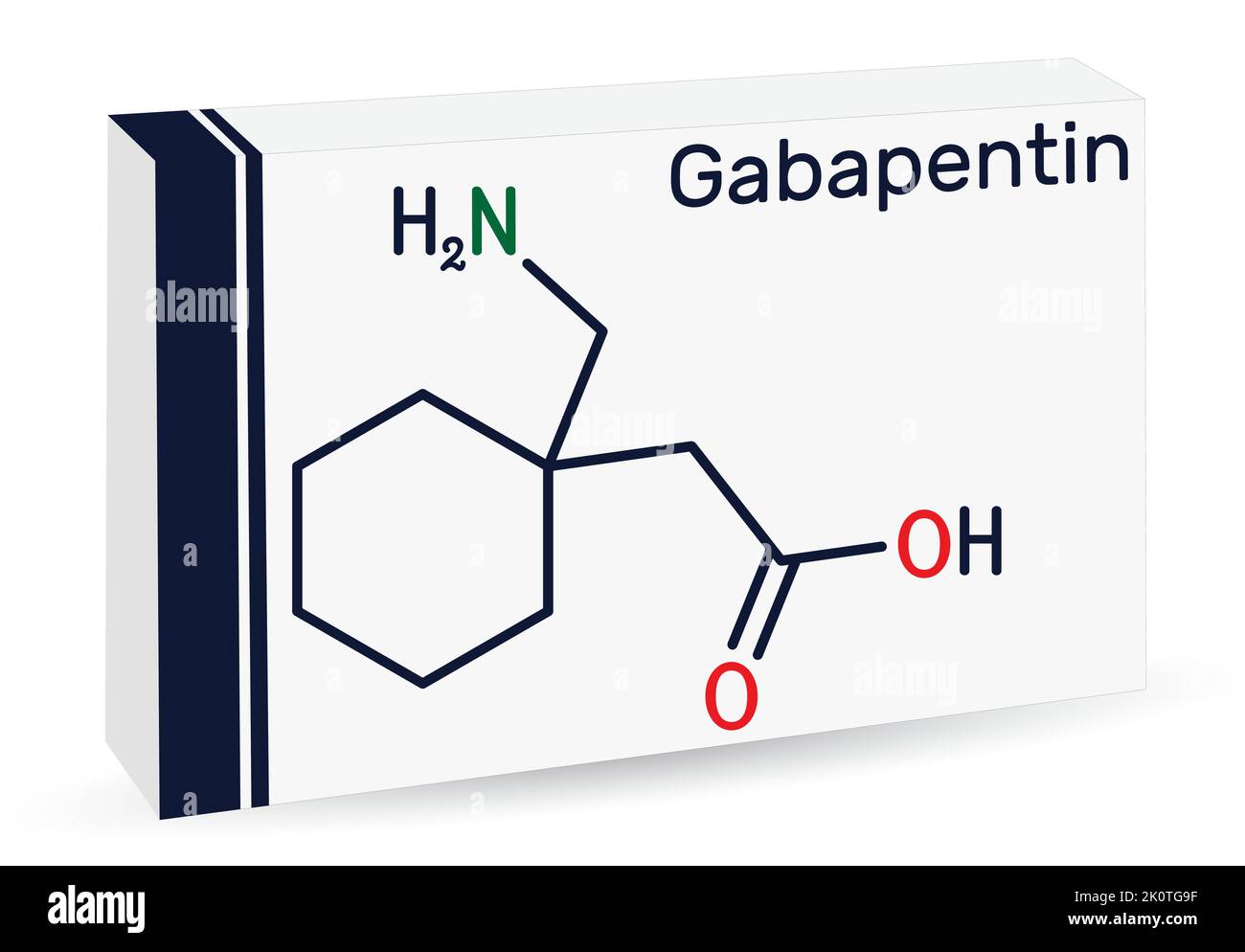
Treatment. Treating gastroparesis begins with finding and treating the condition that's causing it. If diabetes is causing your gastroparesis, your healthcare professional can work with you to help you control your blood sugar levels. In addition, chronic use may be associated with increasing abdominal pain. Tramadol, tapentadol, gabapentin, pregabalin, and nortriptyline may be alternatives for pain; however, their effect on gastric emptying is still unclear. If possible, however, try to use Gabapentin, Pregablin or tricyclics such as Nortriptyline for the abdominal pain in gastroparesis. There are patients who are refractory to all types of treatment and cannot even take in sufficient calories and fluids. Gastroenterologists at Massachusetts General Hospital have begun prescribing low-dose gabapentin for patients with functional dyspepsia because it is thought to be capable of relieving visceral pain. It is structurally related to gabapentin but has no activity at GABA or benzodiazepine receptors, though both pregabalin and gabapentin are frequently used to treat neuropathic pain. I'm on gabapentin (ostensibly) for my gastroparesis and have been for a number of years. I started at 25 mg three times a day, and gradually bumped up. My current dose is 800 mg once a day. Gastroparesis (GP) is a motility disorder characterized by symptoms and objective documentation of delayed gastric emptying (GE) of solid food without mechanical obstruction, which should be excluded by imaging studies such as upper gastrointestinal (GI) endoscopy or radiology (1,2). However, unlike the currently available literature, this report details the case of a two-month-old female with severe feeding intolerance, suspected gastroparesis, visceral hyperalgesia, and malnutrition without previous neurological conditions or cardiac surgery and the role of gabapentin in addressing her FTT. Prokinetic medications are drugs that promote gastric emptying and are an important part of managing gastroparesis. Two commonly used medications are: Erythromycin: This medicine induces forceful contractions, stimulating gastric emptying of both solid and liquid foods. You can take this medicine orally or receive it intravenously. An accurate diagnosis is necessary to treating gastroparesis, since the treatment depends on the cause.If your doctor diagnosed an underlying disease or condition that is causing the gastroparesis, the treatment will focus on correcting or reversing that condition; if there is no underlying cause or if it is not possible to treat it, then the goal of treatment is to promote gastric emptying Discussion. Gastroparesis is a disease with variable presentations ranging from mild nausea and abdominal fullness to recurrent vomiting and abdominal pain symptoms. 4 The diagnosis requires evidence of delayed GE based on a radionuclide study using an isotope-labeled solid meal for 4-hour duration in addition to the absence of mechanical obstruction. Gastroparesis is a syndrome of objectively delayed gastric emptying in the absence of a mechanical obstruction and cardinal symptoms of nausea, vomiting, early satiety, belching, bloating, and/or upper abdominal pain. This topic will review the treatment of gastroparesis. Delayed gastric emptying on objective testing defines gastroparesis, but symptoms overlap with functional dyspepsia and do not correlate well with gastric emptying delay. This review outlines a strategy for defining, diagnosing, and managing refractory gastroparesis. New to gastroparesis? Please view this post or our wiki for a detailed explanation of gastroparesis, the main approaches of treating it, and a list of neurogastroenterologists and motility clinics submitted by users of this forum. The vomiting of gastroparesis usually occurs after meals; however, with severe gastroparesis, vomiting may occur without eating due simply to the accumulation of secretions in the stomach. The characteristic vomiting happens several hours after a meal when the stomach is maximally distended by the presence of food and secretions stimulated by Gastroparesis is a condition that affects the ability of muscular contractions to effectively propel food through your digestive tract, resulting in delayed gastric emptying. Gastroparesis is typically diagnosed via a gastric emptying study (GES) and is thought to be a condition belonging on a spectrum shared with functional dyspepsia (FD Relief for gastroparesis symptoms: Gabapentin can provide relief for symptoms associated with gastroparesis, including nausea, vomiting, bloating, and abdominal pain. By targeting the nervous system, gabapentin helps to regulate the digestive process and improve gastric emptying, providing relief from these distressing symptoms. Idiopathic gastroparesis is the most common form, whereas diabetes accounts for approximately one-third of all cases of gastroparesis. 2 Other causes of nausea, vomiting, and postprandial distress symptoms (eg, early satiety, postprandial fullness, and epigastric pain) are excluded by standard endoscopy, routine laboratory studies, and computed Gabapentin as an adjunctive drug could be more effective in reducing the severity of GI symptoms in patients with dyspepsia, especially neurological symptoms (such as pain, reflux, and indigestion). Keywords: Functional dyspepsia, gabapentin, gastrointestinal disorders. The pathophysiology behind gastroparesis is varied and depends on disease etiology. Vagal and/or autonomic neuropathy play an important role in the development of diabetic gastroparesis, and it is estimated to occur in up to 20% to 40% of patients with diabetes. Gastroparesis can cause problems with blood sugar levels and nutrition.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |