Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
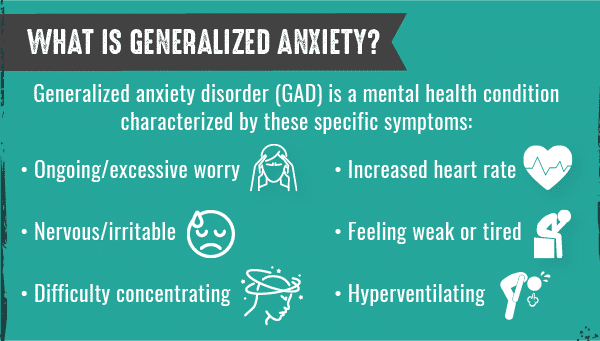 |  |
 | :max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/dsm-5-criteria-for-generalized-anxiety-disorder-1393147-final-5cde49b87f644d4a9eb25ad7ab1ceae0.png) |
 |  |
 | +and+Gabapentin+(Neurontin).jpg) |
 |  |
Both gabapentin and pregabalin are used off-label for the treatment of various anxiety disorders, especially those that fail to respond to antidepressants and/or benzodiazepines. Pregabalin is currently approved for the treatment of generalized anxiety disorder (GAD) by the European Medicines Agency, but not by the U.S. FDA. Panic disorder, generalized anxiety disorder, social anxiety disorder: Anticholinergic and antihistaminergic side effects; strong CYP2D6 inhibitor; difficult discontinuation, taper slowly Paroxetine CR (Paxil CR) 12.5: 25–75: Panic disorder, generalized anxiety disorder, social anxiety disorder: Same as paroxetine Fluvoxamine (Luvox) 25: 100 While gabapentin is increasingly being used to treat generalized anxiety disorder (GAD), little is known about its effectiveness on GAD symptoms. The patient presented here has a relatively straightforward psychiatric history, with GAD playing a prominent role. But there’s little evidence that gabapentin can help with symptoms of generalized anxiety disorder (GAD). According to a 2020 review, about 1 to 10% of people may experience a sense of Anxiety disorders are the most common type of psychiatric illness, with a 12-month prevalence approaching 1 in 5 adults (18.1%). 1 Generalized anxiety disorder (GAD) is the most frequent anxiety disorder, affecting about 5% of adults in the primary care setting. 2 Often suffering since childhood or adolescence, 2 individuals with GAD experience a constant state of worry and anxiety on most Gabapentin is not registered for use in the management of anxiety in the U.S. However, doctors use it off-label to treat anxiety disorders. While there are some studies showing its efficacy for certain types of anxiety, more studies need to be done to properly evaluate the effectiveness of gabapentin in treating generalized anxiety disorder. These disorders can significantly impact daily life, affecting an individual’s emotions, behaviors, and physical health. Common anxiety disorders include generalized anxiety disorder (GAD), panic disorder, social anxiety disorder, and specific phobias. The Rise of Gabapentin for Anxiety GAD is one of the more common mental disorders seen in primary medical care, and is associated with increased use of health services. 7 Comorbidity with major depression or other anxiety disorders is exceedingly common. 1 GAD and major depression have a similar degree of functional impairment 8, 9 but patients with comorbid major depression and In cases of generalized anxiety disorder, pregabalin may also be preferred due to its stronger evidence base and quicker symptom relief. Gabapentin, while slower, may still be effective for individuals with specific anxiety profiles, such as social anxiety. Whether you’re already taking gabapentin for an anxiety disorder or are curious if you might benefit from it, you may be wondering how effective it is, how it works, and if there are side effects. Here we’ll cover everything you need to know about gabapentin for anxiety. Previously presumed to have a low abuse and misuse potential, gabapentin has been commonly prescribed for the treatment of anxiety disorders. 10,11 While pregabalin has shown efficacy for generalized anxiety disorder (GAD) in two RCTs, 12,13 the authors could find no such RCTs done for gabapentin. 9 One randomized, double-blind, placebo-controll Recent research indicates that gabapentin has proven to be an effective treatment for anxiety sufferers. Nevertheless, there are few case reports and no randomized controlled trials regarding this medication’s efficacy in treating generalized anxiety disorder (GAD). People with generalized anxiety disorder who take Gabapentin have been shown to be less irritable, reduce the use of alcohol as self-medication, have fewer depression symptoms, feel less anxious anticipating the future, improve in phobic avoidance (going out in public more, and experience a significant decrease in panic disorder and reduction In this review, the author examines the evidence for psychopharmacologic treatments among adults for generalized anxiety disorder, panic disorder, and social anxiety disorder derived from clinical trials. For each disorder, major categories of drugs are reviewed, and then the evidence-based medications in each category are discussed. The author reviews key safety and tolerability This review's first aim is to summarize current pharmacological treatments (both approved and off-label) for panic disorder (PD), generalized anxiety disorder (GAD), social anxiety disorder (SAD), and specific phobias (SP), including selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), serotonin norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs Treatment of generalized anxiety disorder with gabapentin. Case Reports in Psychiatry. Mason, B. J., et al. (2012). A proof-of-concept randomized controlled study of gabapentin: Effects on cannabis use, withdrawal and executive function deficits in cannabis-dependent adults. Neuropsychopharmacology. Matsuda, K. M., et al. (2016).
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 | :max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/dsm-5-criteria-for-generalized-anxiety-disorder-1393147-final-5cde49b87f644d4a9eb25ad7ab1ceae0.png) |
 |  |
 | +and+Gabapentin+(Neurontin).jpg) |
 |  |