Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
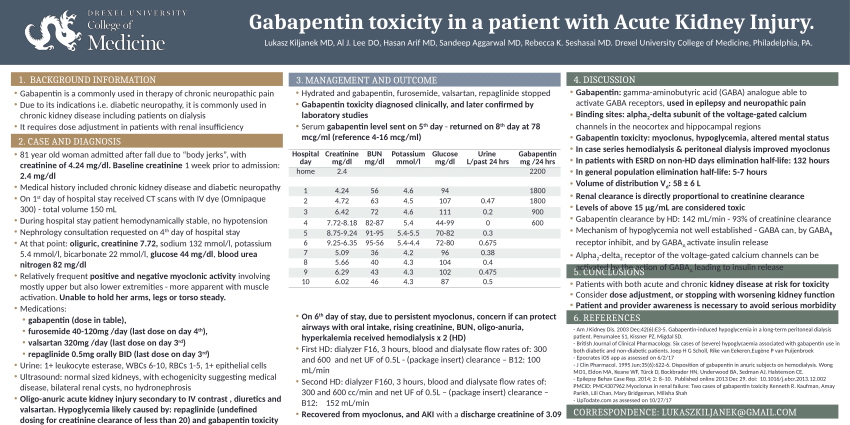
Gabapentinoids are eliminated from the body solely by the kidney, and pharmacokinetic studies show a stepwise prolongation in the elimination half-life of gabapentin and pregabalin as kidney function declines. 9, 10 Gabapentinoids should therefore be started at lower doses in patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD; guidelines are summarized The short answer is: yes, gabapentin can be problematic for individuals with kidney failure and chronic kidney disease (CKD). While gabapentin is often prescribed for pain management, particularly nerve pain, and sometimes for seizures, its primary elimination pathway is through the kidneys. Gabapentin is frequently used as an analgesic in patients with chronic kidney disease. Although gabapentin is well known for its favorable pharmacokinetics, it is exclusively eliminated renally, and patients with chronic kidney disease are at risk for toxicity. Existing literature on such risk is lacking. Pain is one of the most common and distressing symptoms among patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD) . The prevalence of pain has been associated with substantially lower health-related quality of life and greater psychosocial distress, insomnia, and depressive symptoms [ 2-9 ]. Challenges in pain management in patients with kidney disease. Pain assessment. This should start with assessment of a) pain severity using various standardized tools, most common of which is the numerical rating scale []; b) pathophysiologic evaluatio n into mechanism of injury and type of pain; c) psychosocial evaluation of co-occurring factors that contribute to pain or make treatment of The half-life of gabapentin immediate-release formulation is 5–7 hours in patients with normal renal function and is prolonged up to 52 hours in patients with CrCl<30 mL/min. 26 The half-life of pregabalin is 16.7 hours in patients with CrCl 30–59 mL/min, 25 hours in patients with CrCl 15–29 mL/min, and 48.7 hours in patients with CrCl<15 To protect your kidneys while taking Gabapentin, consider the following recommendations: Inform your healthcare provider about any pre-existing kidney conditions or medications you are taking. Stay hydrated by drinking an adequate amount of water throughout the day. Per Lexicomp, Gabapentin’s recommended dose in patients with renal impairment is as follows: CrCl >15 to 29 mL/minute: 200 to 700 mg once daily. CrCl 15 mL/minute: 100 to 300 mg once daily. In summary, gabapentin can be used in patients with stage 3 kidney disease, but only under careful medical supervision and with appropriate dosage adjustments. Never attempt to self-medicate or adjust dosages without consulting your doctor. For adults with normal kidneys: Pain Relief: Start with 300 mg three times a day. The doctor might increase the dose to up to 3600 mg per day, taken in divided doses. Seizures: Start with 300 mg once a day, then increase to 900 mg per day, taken in three doses. 4. Renal Dosing Recommendations. Dose Adjustment: 900 - 3600 mg / TID. Gabapentin is not absolutely contraindicated in kidney disease, but it demands meticulous management. The key to its safe use is careful dose adjustments, rigorous monitoring for toxicity, and an open dialogue with your healthcare provider. NSAIDs have the most potential for risk when it comes to your kidneys. The best pain med for you depends on a variety of factors, including kidney health. Let's discuss: .table_layout tbody td{ font-size:0.95em;} Usual Gabapentin Dosing (Adults) Usual initial gabapentin dose: 300mg q8h. Usual maintenance dose: 300-600mg q8h. Maximum dosage/day: 3600 mg Gabapentin Renal Dosing [>60 ml/min]: Give usual dosage : Dosage range: 400-1400mg/day (divided doses - Usually bid) : Dosage range: 200-700mg/day. : 100-300 mg/day. Use lower end of this range for CRCL In most cases, gabapentin doesn’t hurt the liver or kidneys, though proper dosing is important to prevent side effects. Learn how gabapentin affects the liver and kidneys here. Gabapentin is widely used in the management of pain. It is entirely excreted through the renal system so this needs to be considered in any patient becoming acutely ill and developing renal failure. We describe a patient who developed significant deterioration in her conscious level due to iatrogenic gabapentin overdose. Conclusion. Gabapentin is frequently used as an analgesic in patients with chronic kidney disease. Although gabapentin is well known for its well recieved pharmacokinetics, it is exclusively eliminated renally, and patients with chronic kidney disease are at risk for toxicity. Gabapentin can be used in cats with advanced kidney disease, but dosages may need to be adjusted to account for decreased kidney function. 11. Can gabapentin be used in conjunction with other pain medications in cats with kidney disease? Yes, gabapentin can be used in combination with other pain medications to provide comprehensive pain relief Gabapentinoids are opioid substitutes whose elimination by the kidneys is reduced as kidney function declines. To inform their safe prescribing in older adults with chronic kidney disease (CKD), we examined the 30-day risk of serious adverse events according to the prescribed starting dose. Patients with chronic kidney disease often receive inappropriately high gabapentin dosage for their kidney function, occasioning overt toxicity; advanced age and comorbidity predispose these patients for toxicity.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |