Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
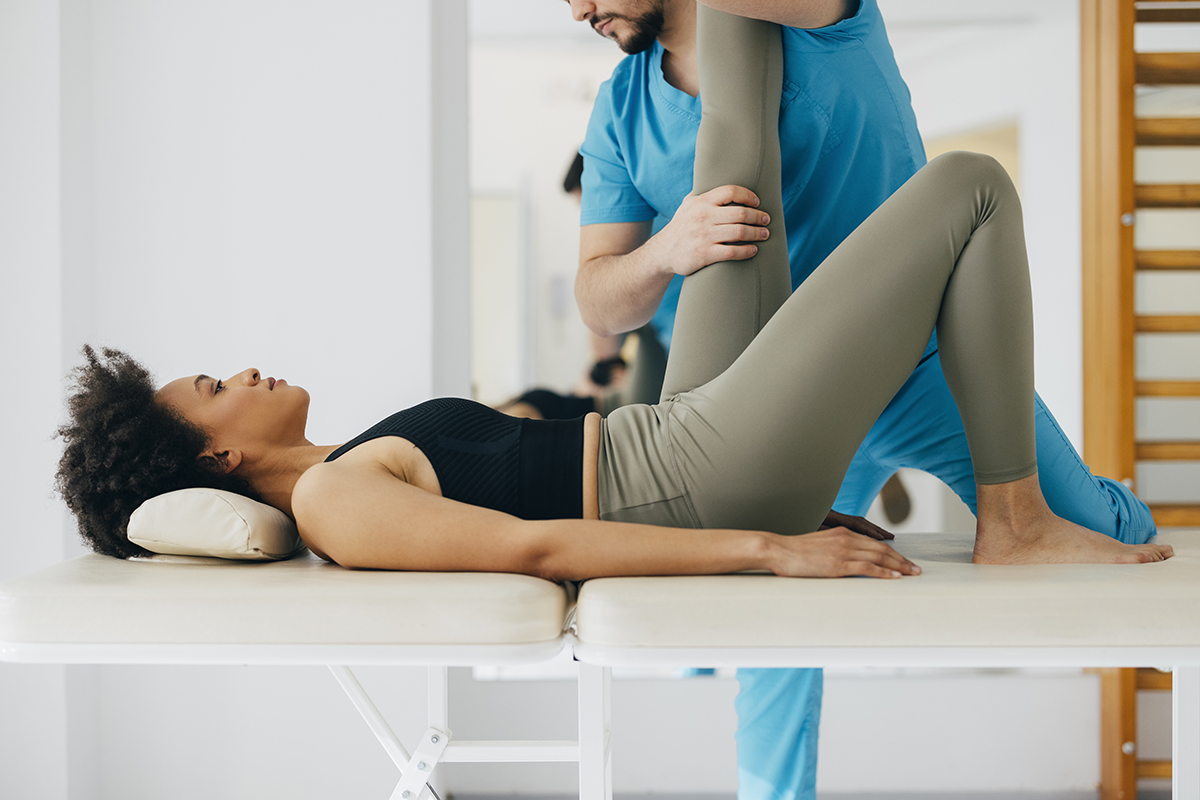 |  |
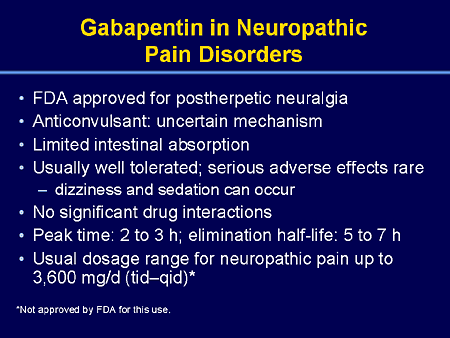
Gabapentin can be very effective in treating various types of back pains, including: Gabapentin for Sciatica: Sciatica, marked by sciatic nerve compression, presents as lower back pain radiating down one or both legs. Anti-seizure medications, such as gabapentin (Neurontin), are sometimes prescribed to help control chronic low back pain. They may be especially useful for nerve pain, such as sciatica or peripheral neuropathy, caused by the degenerated disc. We conducted a 12-week, two-arm, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial to examine the efficacy of gabapentin in patients with chronic low back pain with or without leg pain. Prescribing gabapentin for chronic, non-specific low back pain is not recommended. Patients who suffer from nerve pain, numbness, and tingling in the legs from sciatica or have diabetic neuropathy Fourteen of 15 comparisons found anticonvulsants were not effective to reduce pain or disability in low back pain or lumbar radicular pain; for example, there was high-quality evidence of no effect of gabapentinoids versus placebo on chronic low back pain in the short term (pooled mean difference [MD] −0.0, 95% confidence interval [CI] −0.8 Background Chronic low back pain (CLBP) is a global health problem, and gabapentin and pregabalin are often used in the treatment of patients without associated radiculopathy or neuropathy. Therefore, determining their efficacy and safety is of enormous value. Nerve pain medication: Gabapentin (Neurontin) and pregabalin (Lyrica) may help reduce neck and back nerve pain, especially sciatica. Begin with low doses to avoid daytime drowsiness and fall risk. Muscle relaxants. Tizanidine (Zanaflex) and baclofen (Lioresal) may reduce pain from muscle spasms. Gabapentin is a remedy for nerve pain that’s also prescribed for back pain. See how it works and if it can help back pain from sciatica, shingles, and more. Background and objective: Chronic Low Back Pain (CLBP) is very common, with a lifetime prevalence between 51% and 80%. In majority, it is nonspecific in nature and multifactorial in etiology. Pregabalin (PG) and Gabapentin (GB) are gabapentinoids that have demonstrated benefit in neuropathic pain conditions. Chronic Low Back Pain (CLBP) is very common, with a lifetime prevalence between 51% and 80%. In majority, it is nonspecific in nature and multifactorial in etiology. Pregabalin (PG) and Gabapentin (GB) are gabapentinoids that have demonstrated According to research, Gabapentin is inefficient in treating back pain caused by chronic conditions like arthritis. Gabapentin is ineffective in the treatment of lumbar pain that isn’t radicular or non-radicular. Gabapentinoids are anticonvulsant medications that have shown benefit as antispasticity agents in studies in involving patients with spinal cord injuries. Both gabapentin and pregabalin inhibit the α²δ subunit of L-type voltage-gated Ca²⁺ channels, which are thought to inhibit glutamate release. Pregabalin (PG) and Gabapentin (GB) are gabapentinoids that have demonstrated benefit in neuropathic pain conditions. Despite no clear rationale, they are increasingly used for nonspecific CLBP. They necessitate prolonged use and are associated with adverse effects and increased cost. Graded treatment recommendations can be found in treatment topics for specific chronic pain conditions (eg, chronic back pain, postherpetic neuralgia, fibromyalgia). The general approach to the management of chronic non-cancer pain and nonpharmacologic therapies for chronic pain are discussed separately. If your back pain is nerve-related, then the anticonvulsant drug gabapentin may be a good choice for you. This article will explain how gabapentin works, detail its uses, and go over potential side effects, so that you can assess with your doctor whether this drug may be right for you. 1.1 Back Pain Risk factors and probability of Fracture or Malignancy [1] 1.2 Red Flag Symptoms of Low Back Pain [2] 1.3 Red Flag Signs of Low Back Pain [3] 2 Clinical Features. 2.1 Symptoms by Causes of Low back pain; 2.2 Waddell's Signs of Non-Organic Low back pain [4] 3 Differential Diagnosis. 3.1 Lower Back Pain; 4 Evaluation. 4.1 Exam; 4.2 Improved lumbar spine alignment; Lower Back Pain Medication. Lower back pain medication for severe spinal stenosis pain may include NSAIDs, antidepressants, anti-seizure medication, or corticosteroid shots. Medication can provide near-immediate relief from severe spinal stenosis pain, but may carry the risk of side effects and complications. NSAIDs The role of gabapentin for back pain works in the following way: Reduces the release of several neurotransmitters, decreasing the transmission of pain signals in the nervous system Prevents pain responses in animal models of hyperalgesia, indicating its ability to modulate the perception and processing of pain A 2016 double-blind RCT (N = 108) investigated gabapentin as a treatment for chronic low back pain with and without a radicular component. 2 This RCT was included in the 2017 meta-analysis but is The efficacy of gabapentin monotherapy was investigated against both acute or chronic radicular pain caused by lumbar disk hernia (LDH) or lumbar spinal stenosis (LSS). Seventy-eight patients with radicular pain, 10 males and 68 females aged 23 to 76 years (mean 49.4 years), caused by LSS in 45 pati
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |