Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/VWH-GettyImages-1348724431-3f5c216541064d2a85f13ddc273fb650.jpg) |  |
 |
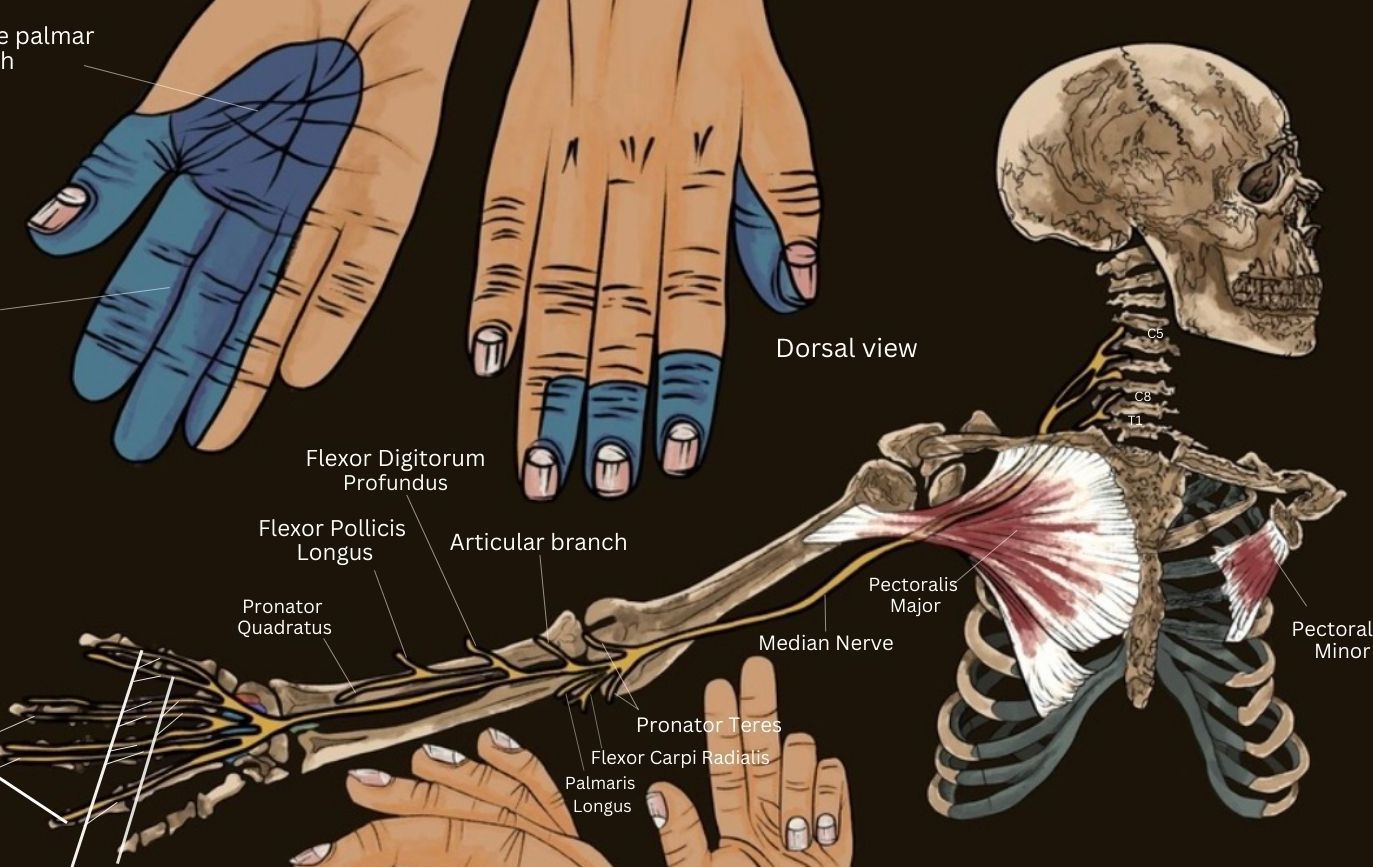
Severe: any disturbances in nerve conduction studies mentioned above, along with evidence of axon loss, defined as: (a) lack or decreased amplitude of sensory nerve action potential or mixed nerve action potential of median nerve (b) lack of or decreased amplitude of thenar compound muscle action potential; or (c) the presence of fibrillation Substance P plays a role in how you perceive pain. Gabapentin dosage for sciatica nerve pain. Gabapentin dosages for sciatica nerve pain typically start at 300 mg to 900 mg by mouth 3 times a day. This dosage is slowly increased by your prescriber depending on your response to the medication. Common side effects of gabapentin Treatment for nerve pain generally requires a prescription, but these four OTC medications are also available. Learn more. (gabapentin, pregabalin) tricyclic antidepressants (amitriptyline) Carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) is a neuropathy due to the compression of the median nerve. It is shown that gabapentin in high doses is effective in treatment of CTS patients. In this study we evaluated the efficacy of low doses of gabapentin in treatment of CTS patients. Ninety patients with CTS were Gabapentin can help relieve nerve pain in some people with postherpetic neuralgia (nerve pain after shingles) and peripheral diabetic neuropathy (nerve pain in the feet in people with diabetes). The established therapeutic dosing for gabapentin in neuropathic pain is 1800-3600 mg/day in 3 divided doses in patients with normal renal function. Using antidepressants for nerve pain can have an added benefit, considering that chronic pain often coincides with depression.Chronic pain can make a person depressed, and depression can often Pain relievers. Medicines available without a prescription, such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, can improve mild symptoms. Anti-seizure medicines. Medicines such as gabapentin (Gralise, Neurontin, Horizant) and pregabalin (Lyrica), developed to treat epilepsy, often improve nerve pain. Side effects can include drowsiness and dizziness. For treating nerve pain, one may recommend three doses of Gabapentin in a day divided into morning, afternoon, and evening doses. One may start with a low dose of 100 mg at night. If you've been prescribed gabapentin for nerve pain, you may begin to feel pain relief within one to two weeks of starting it, depending on your dosage. However, for some people, it can take longer to see benefits. Nerve pain medications. A variety of drugs can be added to conventional pain relievers to reduce nerve pain. Adding one of these nerve pain medications won't completely take the pain away, but it may help. Anticonvulsants: These medications were developed to control seizures, but they also help to blunt pain signals in the nerves. Several are Gabapentin can help relieve nerve pain in some people with postherpetic neuralgia (nerve pain after shingles) and peripheral diabetic neuropathy (nerve pain in the feet in people with diabetes). That’s the situation for millions of people who suffer from idiopathic sensory polyneuropathy. The term “idiopathic” means that no cause can be identified; “sensory” refers to the type of nerve, in this case those carrying nerve signals such as pain or temperature; “poly” means “many” and “neuropathy” means nerve disease. Gabapentin is FDA-approved as Neurontin to treat partial seizures in adults and children with epilepsy. Partial seizures are convulsions that originate from a single location in the brain. Neurontin is also approved to treat a type of nerve pain called postherpetic neuralgia, or PHN. The purpose of this report is to review the clinical evidence on the efficacy, safety and guidelines for use of gabapentin in adults with neuropathic pain, and to examine evidence on the misuse or abuse of gabapentin and other drugs for neuropathic pain. Gabapentin in low doses is a useful drug in treatment of CTS symptoms with no side effects and intolerance. Gabapentin with dose of 300 mg/day is more effective than the dose of 100 mg/day. Key Words: Gabapentin, Carpal tunnel syndrome, BCTQ, VAS. Gabapentin provides pain relief of a high level in about a third of people who take if for painful neuropathic pain. Adverse events are frequent, but mostly tolerable. Titrate dose as needed for pain relief; Maintenance dose: 900 to 1800 mg/day orally in 3 divided doses Maximum dose: 1800 mg per day Extended-release: Gralise (gabapentin) 24-hour extended-release tablets: Initial dose: Day 1: 300 mg orally with the evening meal Day 2: 600 mg orally with the evening meal Gabapentin is commonly used to treat neuropathic pain (pain due to nerve damage). This review updates a review published in 2014, and previous reviews published in 2011, 2005 and 2000. To assess the analgesic efficacy and adverse effects of Gabapentin alleviates affective pain after traumatic nerve injury. Neuroreport . 2015;26(9):522–527. doi: 10.1097/WNR.0000000000000382 (13) Khan J, Noboru N, Imamura Y, Eliav E. Effect of Pregabalin and Diclofenac on tactile allodynia, mechanical hyperalgesia and pro inflammatory cytokine levels (IL-6, IL-1β) induced by chronic constriction
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/VWH-GettyImages-1348724431-3f5c216541064d2a85f13ddc273fb650.jpg) |  |
 |