Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
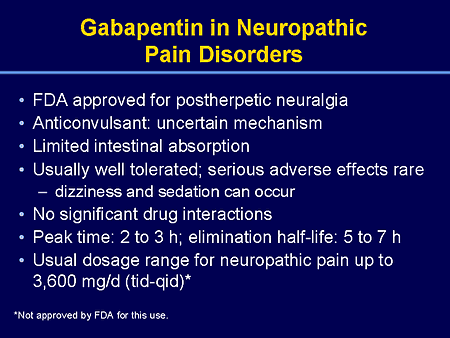
Gabapentin, an antiepileptic drug, is frequently used off-label to manage postoperative nerve pain due to its antiallodynic and antihyperalgesic properties. This article synthesizes research findings on the optimal dosage and efficacy of gabapentin for managing nerve pain after surgery. Yu L, Ran B, Li M, et al. Gabapentin and pregabalin in the management of postoperative pain after lumbar spinal surgery: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Spine 2013; 38:1947–1952. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ] Gabapentin 250 mg is statistically superior to placebo in the treatment of established acute postoperative pain, but the NNT of 11 for at least 50% pain relief over 6 hours with gabapentin 250 mg is of limited clinical value and inferior to commonly used analgesics. Similarly, aside from 24 h after surgery, gabapentin significantly reduced pain with movement (25–27,31,34,35,37,38) by 18% to 28% (VAS 8.2 mm to 10.2 mm) after surgery . The pooled effects on VAS pain scores displayed significant heterogeneity, which was not explained by subgroup analyses based on surgical procedure, gabapentin dose or study However, sometimes medication can play a role in managing nerve pain after spine surgery. These may include: Analgesics: These pain relievers, such as acetaminophen, can help reduce mild to moderate nerve pain. Nerve pain medications: gabapentin, pregabalin (Lyria), as well as amitriptyline can all be used to calm down your nerve pain. Gabapentin, pregabalin, and duloxetine have potential to further decrease post-operative pain and lower opioid dependency. This review creates an opening for further research in hand surgery to assess an updated protocol for pain management to reduce opioid dependency. We defined new postoperative gabapentin as fills for 7 days before surgery until 7 days after discharge. We excluded patients whose discharge disposition was hospice or death. The primary outcome was prolonged use of gabapentin, defined as a fill>90 days after discharge. While gabapentin may have some benefit in the short-term and some older adults may have persistent pain that warrants prolonged use of gabapentin, particularly after spinal surgery, we speculate that a large proportion of this prolonged use is not intentional, and that the system needs to be improved to prevent both polypharmacy and In people over 50, shingles commonly cause postherpetic neuropathy, a burning pain that lasts after shingles’ symptoms disappear . Studies show that extended-release gabapentin may successfully treat post-shingles pain (18, 21). Post-surgery Back Pain Gabapentin and the related, more potent compound pregabalin have been shown to be beneficial in the treatment of neuropathic pain as well as postoperative pain following spinal surgery and hysterectomy. A less-invasive version called a nerve block delivers an anesthetic injection to a nerve root to temporarily cut off pain signals. Peripheral nerve field stimulation, which uses electrical pulses to ease chronic nerve pain may also help, although the benefits are uncertain. Summary Pain after hernia repair surgery is not uncommon. We recommend being selective with regard to using gabapentinoids for acute postoperative pain management after careful consideration of the potential side effect profile based on patient comorbidities as well as the expected severity of postoperative pain. Evaluation of the optimal preemptive dose of gabapentin for postoperative pain relief after lumbar diskectomy: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. J Neurosurg Anesthesiol. 2005;17(2):65–68. doi: 10.1097/01.ana.0000151407.62650.51. Would you want to take Lyrica (pregabalin) or Neurontin (gabapentin) for pain relief after a major surgery? Both drugs belong to a class of nerve medication called gabapentinoids that are increasingly being prescribed to patients perioperatively (after surgery) as an alternative to opioid medication. Gabapentin is commonly indicated in the treatment of seizures. 27 Gabapentin, which acts on the nociceptive processes involved in central sensitization, has been shown to reduce hypersensitivity associated with nerve injury (hyperalgesia) and postoperative pain and inflammation in animal models. 28 Interestingly, gabapentin’s antiemetic Peri-operative gabapentin administration is effective in reducing pain scores, opioid requirements and opioid-related adverse effects in the first 24 hours after surgery. No serious side-effects were observed, though sedation was associated with gabapentin use. How Long Does Gabapentin Take to Work for Nerve Pain? After taking a dose, IR gabapentin starts to work in the body within two to three hours. However, the full effects of gabapentin can take one to two weeks to become noticeable, and some people may need to wait longer to experience significant pain reduction. What Helps With Nerve Pain After Surgery? Treatment options for nerve damage and pain after surgery include: Orthobiologics (e.g. platelet-rich plasma — PRP) Physical therapy may help. Medications that are commonly used to treat nerve damage after surgery include: Neurontin (Gabapentin) (12) Lyrica (Pregabalin) (13) Elavil (Amitriptyline) (14) Gabapentin and other anticonvulsant medications have been established as an effective treatment for chronic neuropathic pain and are commonly used for such conditions as herpetic neuralgia, diabetic neuropathy, and phantom limb pain following amputation. Gabapentin has also been shown to reduce immediate postoperative pain following mastectomies and other breast surgeries, and is often a component of ERAS protocols. 35, 36 In their randomized control trial, Fassoulaki et al found that combining perioperative gabapentin and local anesthesia led to a significant decrease in chronic pain 3 months
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |