Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
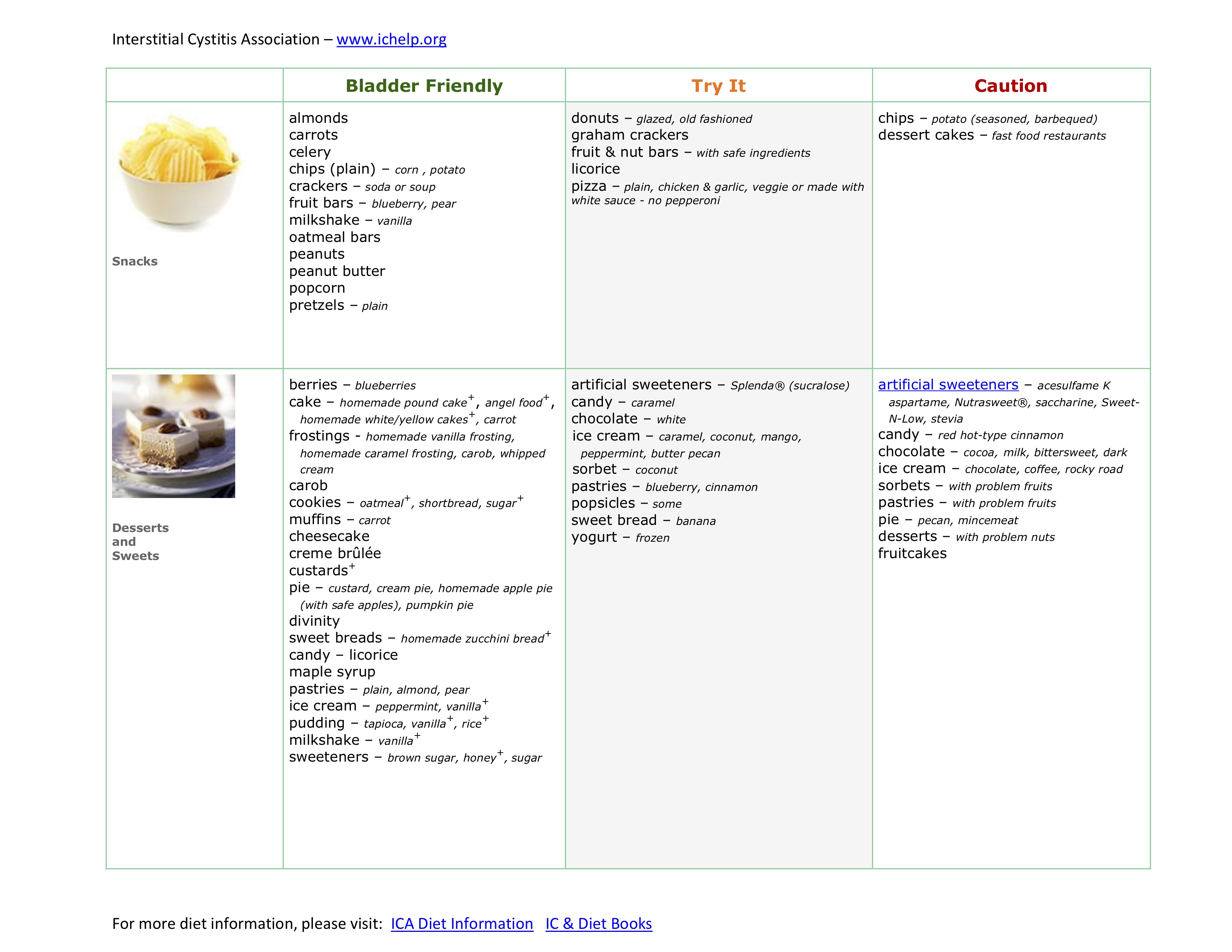
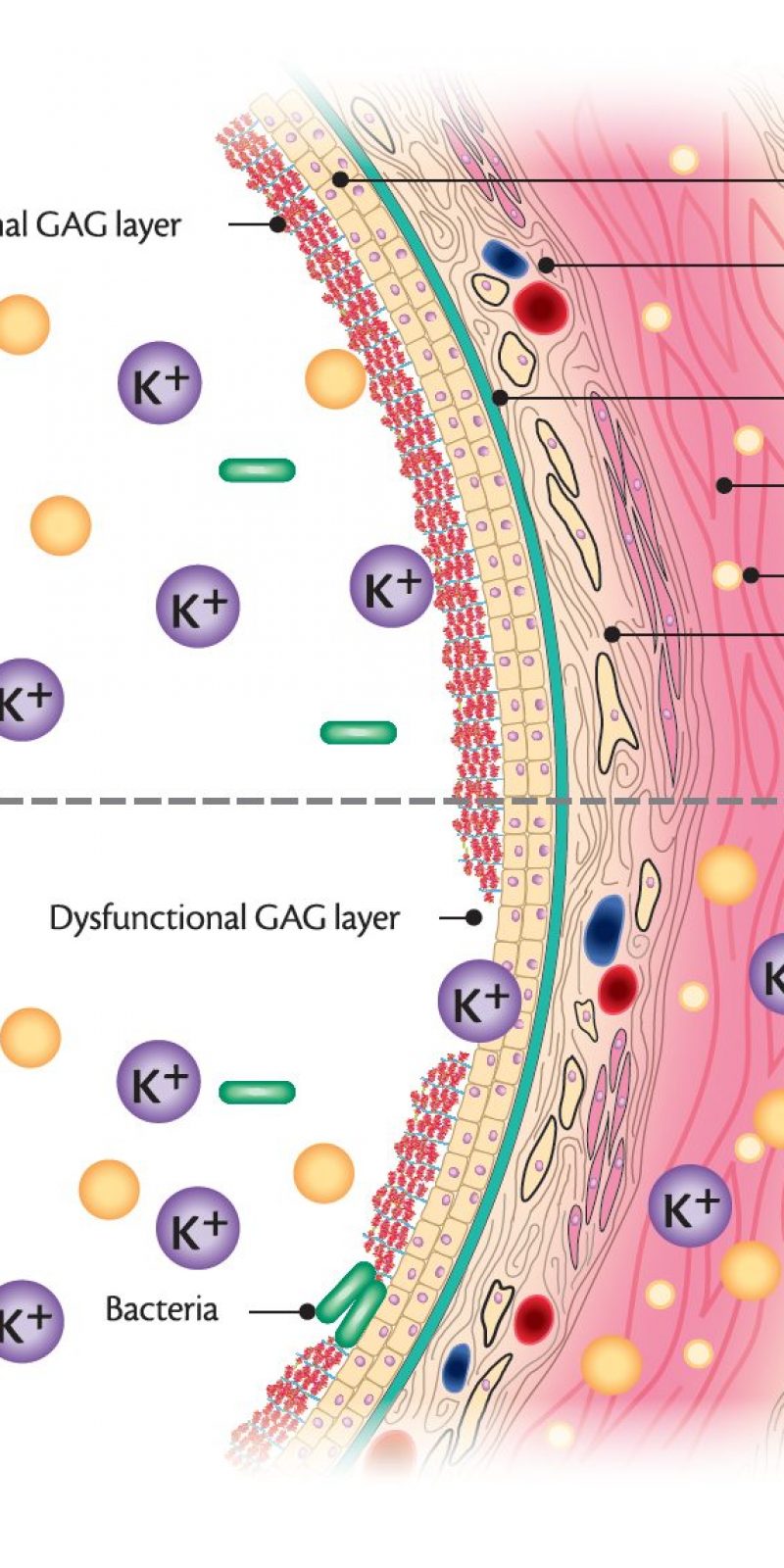
Bladder pain syndrome/interstitial cystitis (BPS/IC) is defined as no infection or other clinically identified causes with lower urinary tract symptoms and unpleasant bladder-related sensations such as pain, pressure, and discomfort for ≥6 weeks [1,2]. Bladder pain syndrome is a poorly understood condition where you have pelvic pain and problems peeing. It's sometimes called interstitial cystitis (IC) or painful bladder syndrome (PBS). It's difficult to diagnose BPS (interstitial cystitis) as there is no single test that confirms the condition. Symptoms of BPS (interstitial cystitis) Purpose: Bladder pain syndrome is a chronic disease that manifests as bladder pain, frequency, nocturia, and urgency. Gabapentin, amitriptyline, and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are efficacious treatments for bladder pain syndrome. Here, we assessed the effect of triple therapy with these drugs in women with bladder pain syndrome. Histopathology totally differs between Hunner-type interstitial cystitis and bladder pain syndrome; Hunner-type interstitial cystitis is associated with severe inflammation of the urinary bladder accompanied by lymphoplasmacytic infiltration and urothelial denudation, whereas bladder pain syndrome shows little pathological changes in the bladder. Efficacy outcomes included individual symptoms such as pain, frequency, urgency, and nocturia, as well as structured questionnaires measuring IC/BPS symptoms. A comprehensive literature search was conducted which identified 70 RCTs with 3,651 patients. Oral medications. Certain medicines that you take by mouth (oral medications) may improve signs and symptoms of interstitial cystitis: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, such as ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin IB, others) or naproxen sodium (Aleve), to relieve pain. Interstitial cystitis (in-tur-STISH-ul sis-TIE-tis) is a chronic condition causing bladder pressure, bladder pain and sometimes pelvic pain. The pain ranges from mild discomfort to severe pain. The condition is a part of a spectrum of diseases known as painful bladder syndrome. Treatment options for people with bladder pain syndrome and either glomerulations or Hunner's lesions include (7): oral treatments (such as amitriptyline, gabapentin, pregabalin, paracetamol, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, hydroxyzine, cimetidine and ranitidine) Gabapentin is available as a compound suppository to help never pain for IC/PFD. Oral gabapentin does nothing for the bladder. I have found gabapentin 300mg helps calm nerves in bladder and pelvic area. I know everyone is different and yes, it has caused few side effects in beginning. As your body adjusts, lightheadedness goes away and increased appetite slows down. Urology (SUFU) defined interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome (IC/BPS) as “an unpleasant sensation (pain, pressure, discomfort) perceived to be related to the uri-nary bladder, associated with lower urinary tract symp-toms for more than six weeks duration, in the absence of infection or other identifiable causes.” [1]Thisisthe Interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome (IC/BPS) is a clinical diagnosis based primarily on chronic symptoms of pain perceived to be related to the bladder or urethra, often associated with urinary urgency or frequency, in the absence of another identifiable cause. It is a diagnosis of exclusion. Effect of low-dose triple therapy using gabapentin, amitriptyline, and a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug for overactive bladder symptoms in patients with bladder pain syndrome. Int Neurourol J [Internet]. 2013 Jun;17(2):78–82. Gabapentin, amitriptyline, and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are efficacious treatments for bladder pain syndrome. Here, we assessed the effect of triple therapy with these drugs in women with bladder pain syndrome. Studies with one of these H2 blockers, cimetidine, showed it reduced bladder pain as well, maybe because of the histamine-blocking action. But why it works in IC really isn’t so clear. In two small studies (one with 9 and one with 14 patients), Tagamet reduced bladder pain for 40 to 60 percent of the IC patients. 2 Answers - Posted in: anxiety, bladder infection, pain - Answer: I've had very good experience controlling my blabber pain using a tens Gabapentin was significantly more effective in controlling pain compared to pregabalin. Three fourth of patients on gabapentin alone (47/62) reported at least 50% improvement in pain compared to only 40% on pregabalin alone (12/30) (P = 0.0012; χ 2 = 9.765. Bladder reconstruction. Part or all of the bladder is removed and then reconstructed from a segment of the bowel. This expands the capacity of the bladder but pain may persist. Bladder removal (cystectomy). Very occasionally, when pain persists despite urinary diversion, the bladder may be removed. Even still pain can persist. Effect of low‐dose triple therapy using gabapentin, amitriptyline, and a nonsteroidal anti‐inflammatory drug for overactive bladder symptoms in patients with bladder pain syndrome. Int Neurourol J . 2013; 17 :78‐82.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |