Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
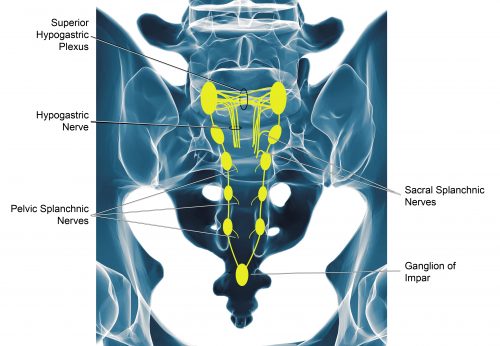 |  |
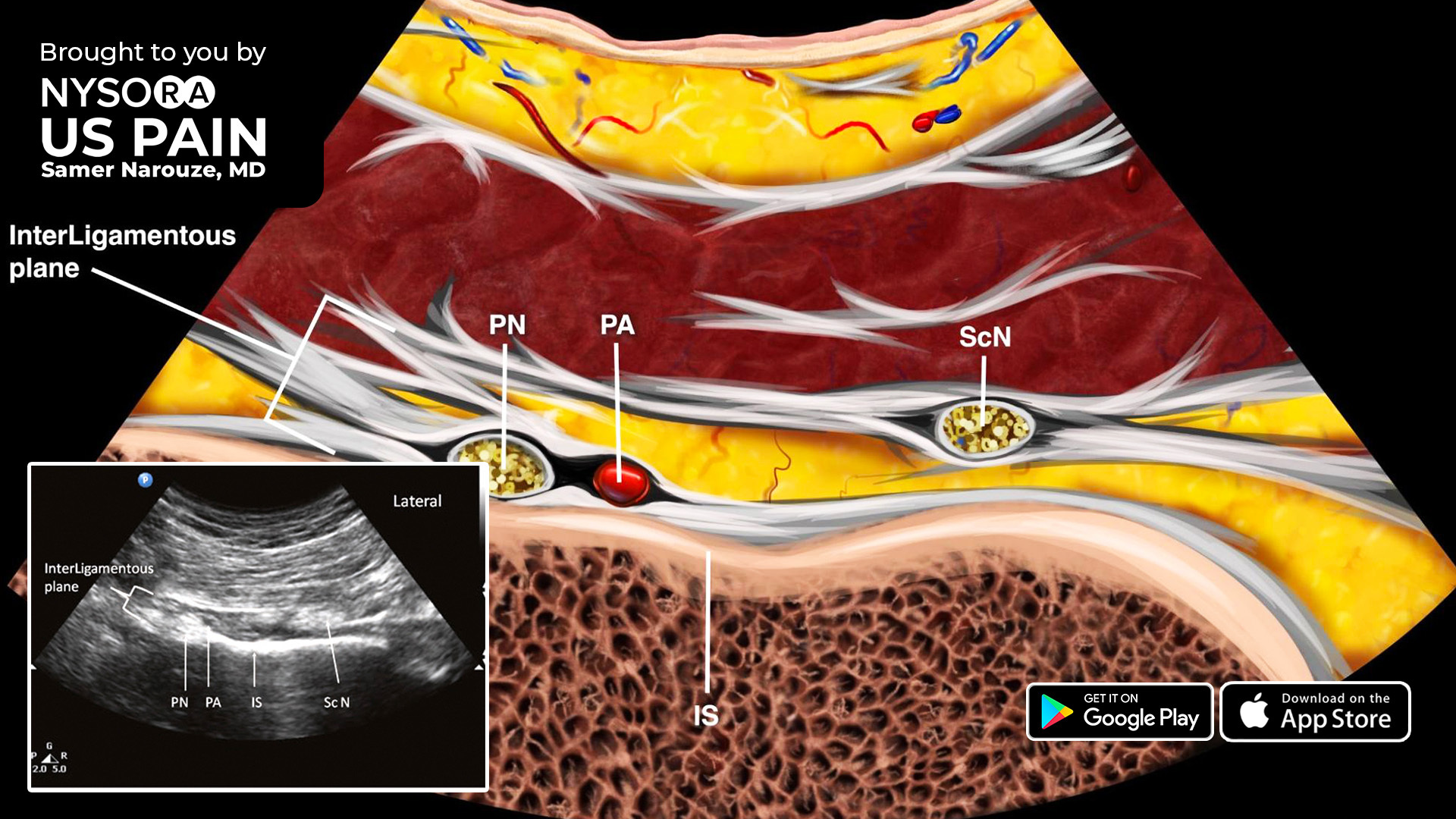
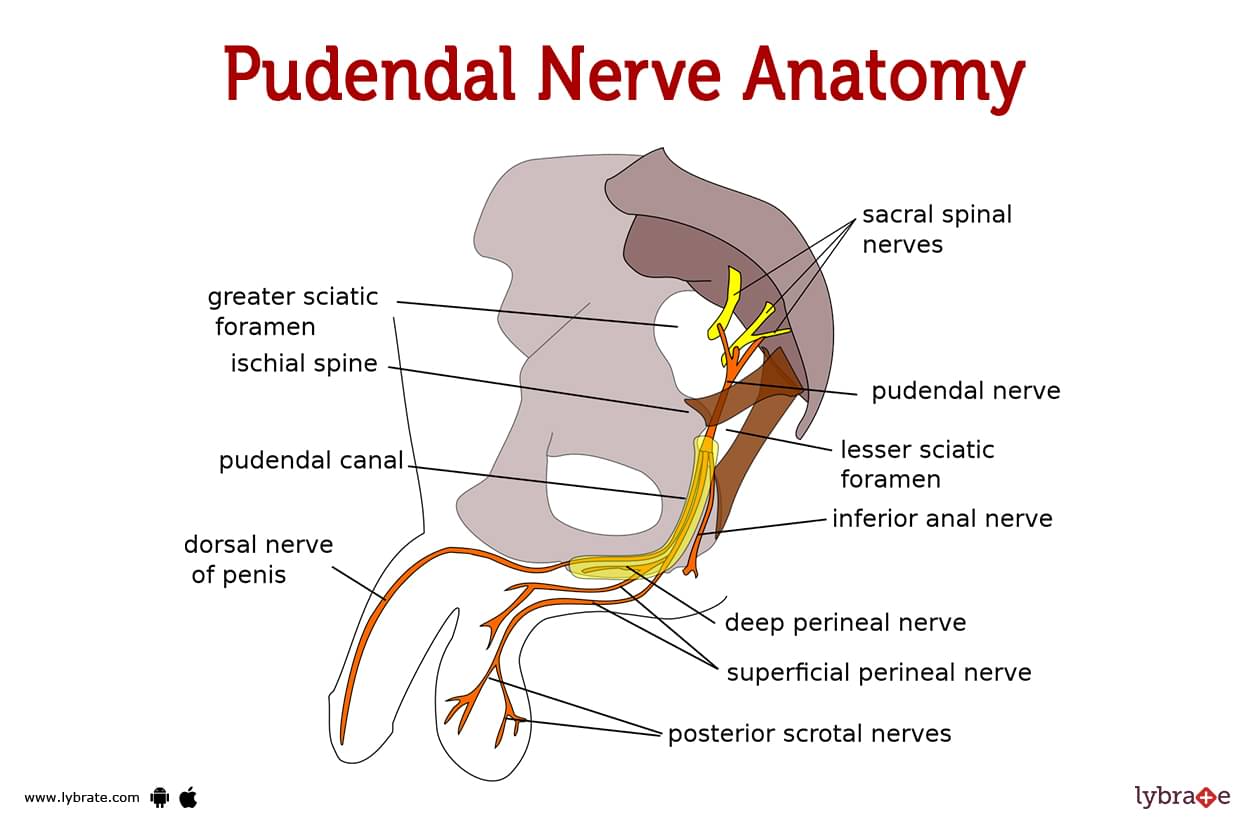
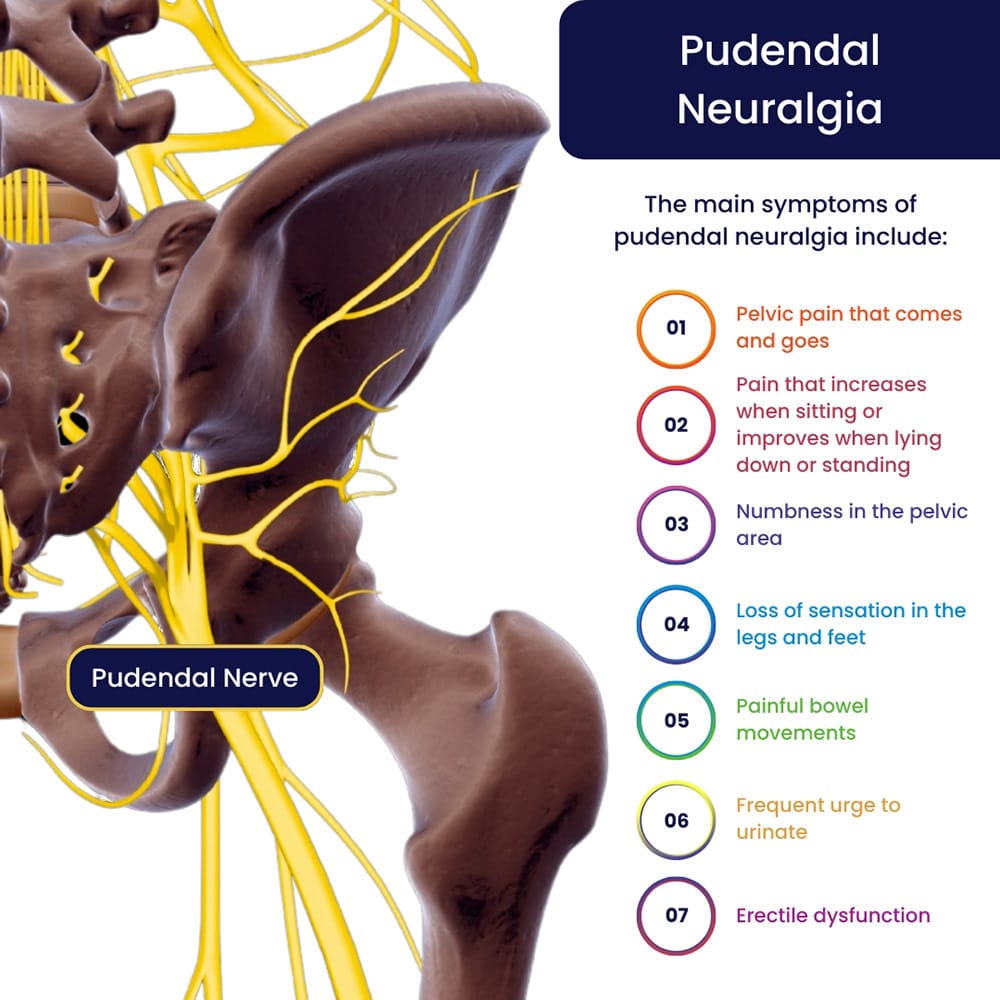
Purpose of Review Clinicians have become increasingly aware of pudendal neuralgia as a cause of persistent genital pain. The purpose of this review is to summarize the current knowledge regarding the presentation, etiology, evaluation, and management of this condition. Recent Findings Pudendal neuralgia can be reliably diagnosed and successfully managed. There are many available treatments The pudendal neuralgia, caused by entrapment and compression of the pudendal nerve, Gabapentin 300 mg daily for 6 months did not yield any success . Context: Although pudendal neuralgia (PN) has received growing interest over the last few years, diagnosis remains difficult, and many different therapeutic approaches can be considered. Objectives: This article aims to provide an overview of the possible treatments of PN and investigate their efficacies. medicines that can help with nerve pain, such as amitriptyline, duloxetine, gabapentin or pregabalin a strong painkiller called tramadol , if other pain relief does not work and you need pain relief for a short time while you're waiting to see a specialist Pudendal Neuralgia in Men is a condition that causes severe and persistent pelvic pain due to irritation, compression, or damage to the pudendal nerve. Gabapentin is more effective than placebo at reducing diabetic neuropathy and postherpetic neuralgia-associated pain. The most common side effects associated with gabapentin are asthenia, headache, dizziness and somnolence. Ironically, gabapentin has been reported to induce polyneuropathy. Gabapentin and Pregabalin are common anticonvulsants prescribed for pudendal neuralgia. In some cases, muscle spasms may exacerbate the pain of pudendal neuralgia. Muscle relaxants can help alleviate these spasms, reducing pain and discomfort. Use of both gabapentin and pregabalin for treatment of pudendal neuralgia is not FDA approved, although it is clearly beneficial in reducing pain. The usual starting dose for Neurontin is 300–900 mg/day in three divided doses, titrated up to maximum 3600 mg/day. Chronic primary pain (CPP) is defined as pain lasting more than three months, with significant emotional and psychological disability. 1 CPP is frequently encountered in primary care and its management is often a challenge. 2 In addition to the physiological basis of the pain itself, the psychological aspects often complicate matters. 3 Pudendal neuralgia (PN) is a form of pelvic CPP Pudendal neuralgia is chronic pelvic pain caused by an irritated or damaged pudendal nerve. Your pudendal nerve runs from the back of your pelvis to all the muscles and skin in your genital area, including your anus, vagina and penis. Treatment options include medication, physical therapy, lifestyle changes or surgery. What is pudendal neuralgia? Context Although pudendal neuralgia (PN) has received growing interest over the last few years, diagnosis remains difficult, and many different therapeutic approaches can be considered. Objectives This article aims to provide an overview of the possible treatments of PN and investigate their efficacies. Methods Utilizing PubMed and ScienceDirect databases, a systematic review was carried out I am a 23 F who developed pudendal neuralgia after getting married. I am currently being seen at Northwestern Hospital in Chicago for this condition at their speciality vulvar clinic. While waiting to be evaluated for other treatment options, I was prescribed gabapentin 100mg (I have a tapering up schedule ). Pudendal nerve blocks are also diagnostic for pudendal neuralgy- if you feel no pain immediately after they inject it the diagnosis is confirmed, but I would not recommend them for treatment Symptoms- pain with sitting, sex, bowel movements; later on radiating pain in sacrum and legs; pain can feel like burning, shutting, neuralgy, itching Medications like gabapentin or amitriptyline help manage nerve pain, while more advanced options, such as pudendal nerve decompression surgery, are considered for those with severe or persistent symptoms. Use of both gabapentin and pregabalin for treatment of pudendal neuralgia is not FDA approved, although it is clearly beneficial in reducing pain. The usual starting dose for Neurontin is 300–900 mg/day in three divided doses, titrated up to maximum 3600 mg/day. Pudendal Neuralgia (PN) refers to pain along the distribution of the nerve – the pudendal nerve has 3 primary branches that go toward the anus, the perineum, and the clitoris or penis. Pudendal neuralgia does not mean that the nerve is damaged or trapped. Pudendal neuralgia is the neuropathic pain component of the syndrome caused by pudendal nerve entrapment and neuropathy. The pudendal nerve is a mixed nerve having sensory, motor, and autonomic functions. As a result, inflammation or injury to the nerve can cause bladder, bowel, sexual and autonomic Pudendal nerve blocks not only are used in the diagnosis of pudendal neuralgia, but also can provide some relief of the nerve pain. Medication Pain relief can be achieved with painkillers or nerve stabilizing medications like gabapentin, duloxetine, amitriptyline. Compare risks and benefits of common medications used for Pudendal Neuralgia. Find the most popular drugs, view ratings and user reviews. Gabapentin has an average rating of 8.0 out of 10 from a total of 3 reviews for the off-label treatment of Pudendal Neuralgia. 67% of reviewers reported a positive experience, while 0% reported a negative experience.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |