Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | :max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/VWH-GettyImages-1348724431-3f5c216541064d2a85f13ddc273fb650.jpg) |
 |  |
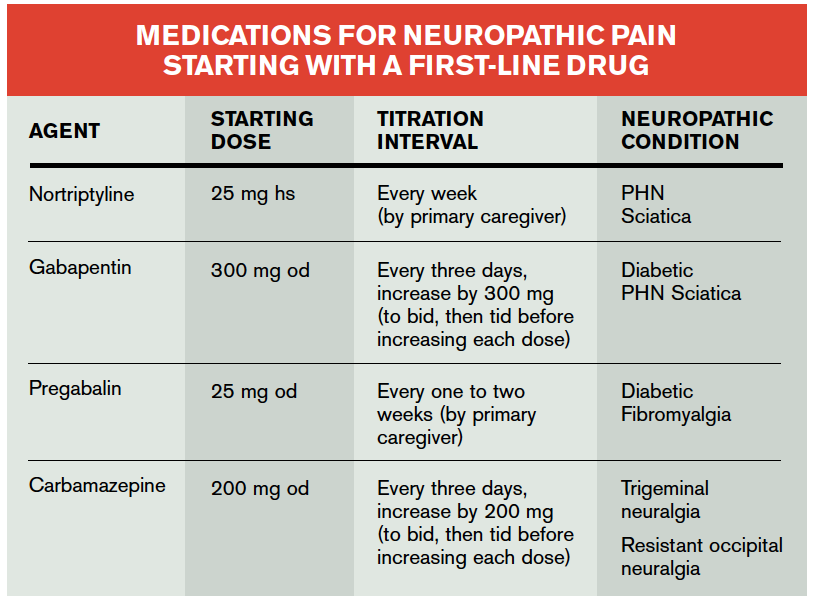
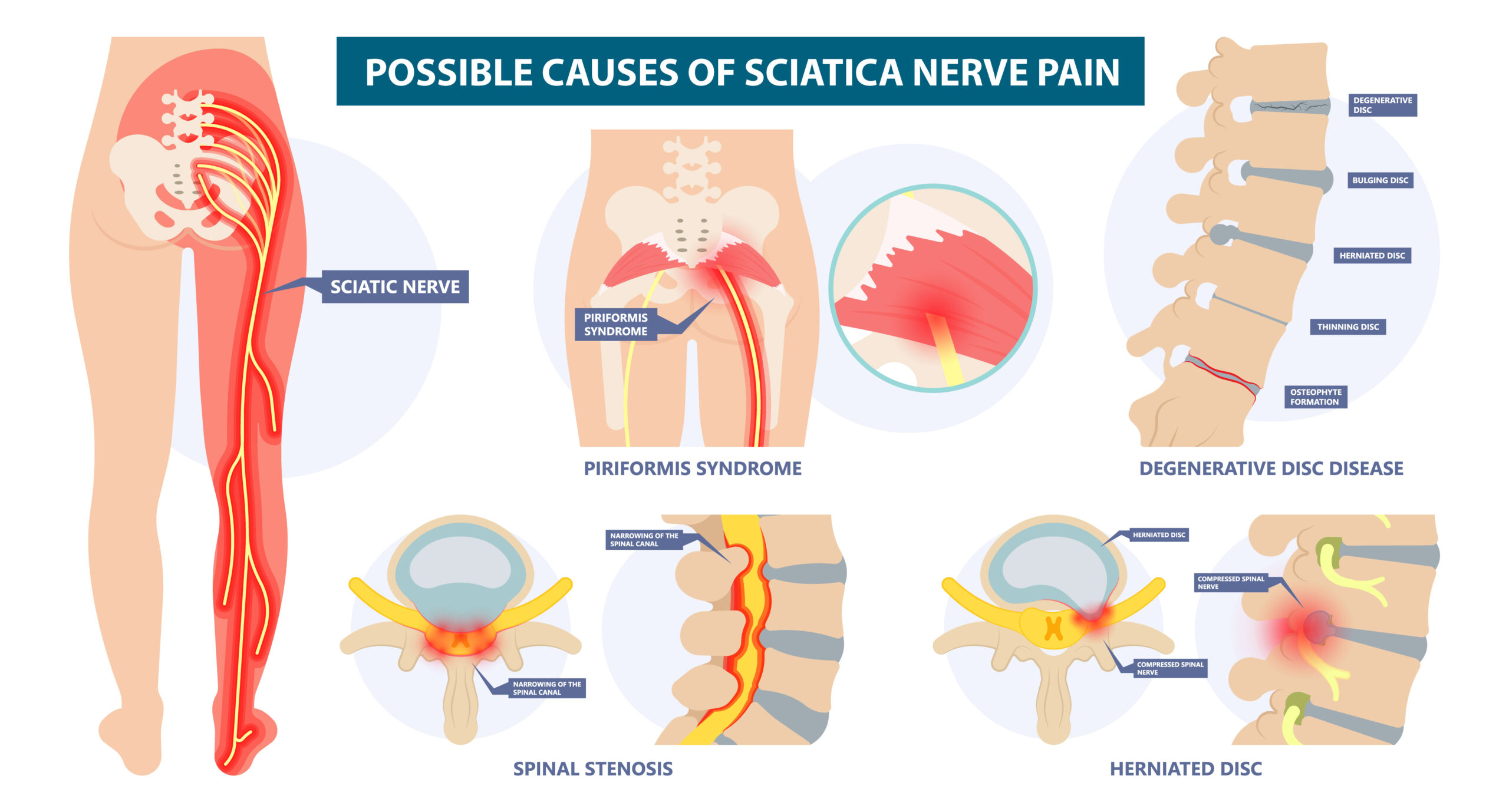
Gabapentin is approved to treat seizures and postherpetic neuralgia, a type of nerve pain from shingles. It is thought to work by changing how nerves send messages to your brain. It is also used off-label to treat other neuropathic pain conditions. How does gabapentin work to relieve sciatic nerve pain? In general, gabapentin calms down neurons (nerve cells) to relieve nerve pain. It does this by lowering the amounts of excitatory chemicals, like norepinephrine and glutamate, in the nervous system. How Gabapentin Helps with Sciatica Pain. Gabapentin’s ability to alleviate sciatica pain lies in its mechanism of action. By modulating the release of certain neurotransmitters involved in pain perception, Gabapentin can reduce the intensity and frequency of pain signals traveling from the sciatic nerve to the brain. Nerve pain medication: Gabapentin (Neurontin) and pregabalin (Lyrica) may help reduce neck and back nerve pain, especially sciatica. Begin with low doses to avoid daytime drowsiness and fall risk. Muscle relaxants. Tizanidine (Zanaflex) and baclofen (Lioresal) may reduce pain from muscle spasms. Sciatica is commonly seen in primary care. Its prevalence in the general population varies between 3% and 14%, depending on the definition used. 1 The prognosis of acute sciatica is generally favourable: data from a prospective study of 183 patients with a median disease duration of 16 days show that in approximately one third of patients, symptoms improve greatly (ie, measured on a 4 point The term sciatica is used by clinicians in different ways: Some refer to any leg pain referred from the back as sciatica; others prefer to restrict the term to pain originating from the lumbar nerve root. Others believe sciatica is a form of ‘neuropathic’ pain caused by compression or irritation of the roots or nerves that comprise the Gabapentin helps manage sciatica by calming overactive nerve signals, reducing pain without treating the underlying cause, says Dr.Richard Honekar The pooled results of two trials of corticosteroids (mean difference in overall and leg pain −12.2, 95% confidence interval −20.9 to −3.4) and a single trial of the anticonvulsant gabapentin for chronic sciatica (mean difference in overall pain relief −26.6, −38.3 to −14.9) showed some benefits but only in the short term. Gabapentin is widely prescribed for management of peripheral neuropathic pain syndromes. To our knowledge, however, these two case reports are the first to describe sciatica successfully controlled with gabapentin. Treatment. For pain that doesn't improve with self-care measures, some of the following treatments might help. Medications. The types of medicines that might be used to treat sciatica pain include: Sciatica pain is often a dull pain, but it also can be sharp and, at times, you may feel the pain travel or “shoot” down your leg. Symptoms of sciatica may include numbness, tingling or weakness along with the pain. Sciatica develops due to a change in one of the cartilage pads in your spine, called discs. Gabapentin changes the way the brain and body exchange messages. It calms the nerves by blocking pain-causing neurotransmitters, making gabapentin an effective treatment for sciatica and
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | :max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/VWH-GettyImages-1348724431-3f5c216541064d2a85f13ddc273fb650.jpg) |
 |  |