Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |
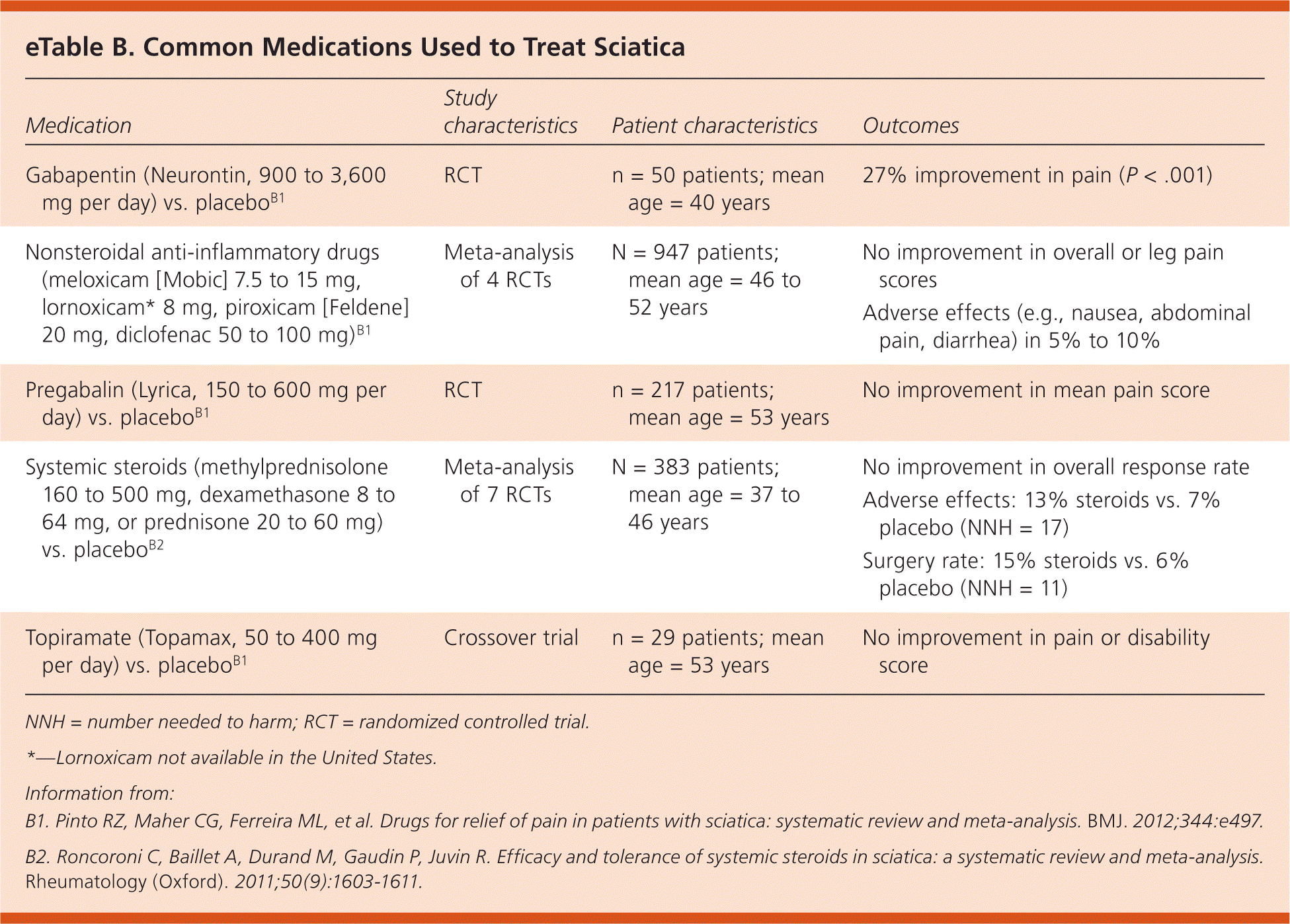
How Gabapentin Helps with Sciatica Pain. Gabapentin’s ability to alleviate sciatica pain lies in its mechanism of action. By modulating the release of certain neurotransmitters involved in pain perception, Gabapentin can reduce the intensity and frequency of pain signals traveling from the sciatic nerve to the brain. Previous trials of pregabalin and gabapentin in patients with chronic low back pain or sciatica did not show a beneficial effect over placebo. 10,11 Our trial extends this finding by the inclusion Gabapentin can help relieve sciatica, intense pain that runs along the sciatic nerve from the lower back through the hips and buttocks (12). Sciatica affects one side of the body and is usually caused by disk herniation or spinal stenosis (12). Keywords: Gabapentin, Pregabalin, Sciatica, Pain, Clinical trial, Protocol. Background. Sciatica or sciatic neuralgia, a common form of lumbosacral radiculopathy, is characterised by low back pain which radiates to the leg and which may be accompanied by sensory loss, motor weakness and/or reflex abnormalities. Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant that can help treat nerve pain and numbness caused by sciatica. Learn how to use it, what to expect, and what precautions to take. Evaluating the Efficacy, Dosage, and Impact of Gabapentin on Sciatic Nerve Pain. Sciatica can be an extremely painful and debilitating condition, shooting sharp pains from the lower back all the way down the leg. For many suffering from this nerve pain, finding relief seems impossible. Nerve pain medication: Gabapentin (Neurontin) and pregabalin (Lyrica) may help reduce neck and back nerve pain, especially sciatica. Begin with low doses to avoid daytime drowsiness and fall risk. Muscle relaxants. Tizanidine (Zanaflex) and baclofen (Lioresal) may reduce pain from muscle spasms. Question Is gabapentin or pregabalin the more optimal pharmacological treatment for chronic sciatica? Findings This randomized clinical trial of pregabalin vs gabapentin in 18 patients with chronic sciatica found that gabapentin was superior to pregabalin with greater reduction of leg pain intensity and fewer adverse events. Surgical diskectomy can be offered to patients with refractory sciatica, but there is only modest, short-term improvement in leg pain and disability scores. Epidural steroid injections may be Gabapentin is a common prescription for sciatica, but the evidence supporting its use is weak. Learn about other medications that may help sciatica, such as diclofenac, prednisone, pregabalin, and amitriptyline. Gabapentin for sciatica The cause of sciatica back pain is compression of the sciatic nerve. This type of back pain typically starts in the lower back and travels down the back of one or both legs. Exercise, physical therapy, and NSAIDs work well to treat this kind of back pain. Physical therapy can be an excellent treatment option for sciatica. It often involves learning stretches to improve your flexibility, techniques for pain control and exercises to strengthen and condition the muscles that support your back. This type of physical therapy helps reduce sciatica pain and lowers your risk for future injuries. Gabapentin for sciatica pain can take 1-2 weeks to start showing any noticeable effects. Although, depending on the patient’s condition, dosage and response to the treatment, it may take longer to register relief. Gabapentin is widely prescribed for management of peripheral neuropathic pain syndromes. To our knowledge, however, these two case reports are the first to describe sciatica successfully controlled with gabapentin. My MD then prescribed gabapentin 300mg 3x a day. It took a day or so to really kick in, but once it did WOW, the pain in my R buttocks and down the front of my right leg were almost gone. I took it faithfully for 2 months, then the pain went away. So I stopped. Other causes of impingement include spondylolisthesis and spinal tumours or cysts.4 For this reason, symptoms of sciatica often co-exist with low back pain, but disturbances along the course of the sciatic nerve can also arise from locations other than the lower back (ie, due to piriformis syndrome, diabetic radiculopathy, and hip fracture or One study assessed the effect of gabapentin vs pregabalin in a crossover head-to-head trial. A statistically significant improvement on leg pain at 2 weeks and leg pain with movement at 3 and 4 months was found in a RCT comparing gabapentin with placebo. The types of medicines that might be used to treat sciatica pain include: Anti-inflammatories. Corticosteroids. Antidepressants. Anti-seizure medications. Opioids. Physical therapy. Once the pain improves, a healthcare professional can design a program to help prevent future injuries. Sciatica pain originates from the compression, irritation, or damage of the sciatic nerve, resulting in aching in the lower back that extends through the leg. This condition is often accompanied by limitations in physical functionality and sensory symptoms like numbness or a prickling feeling.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |