Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
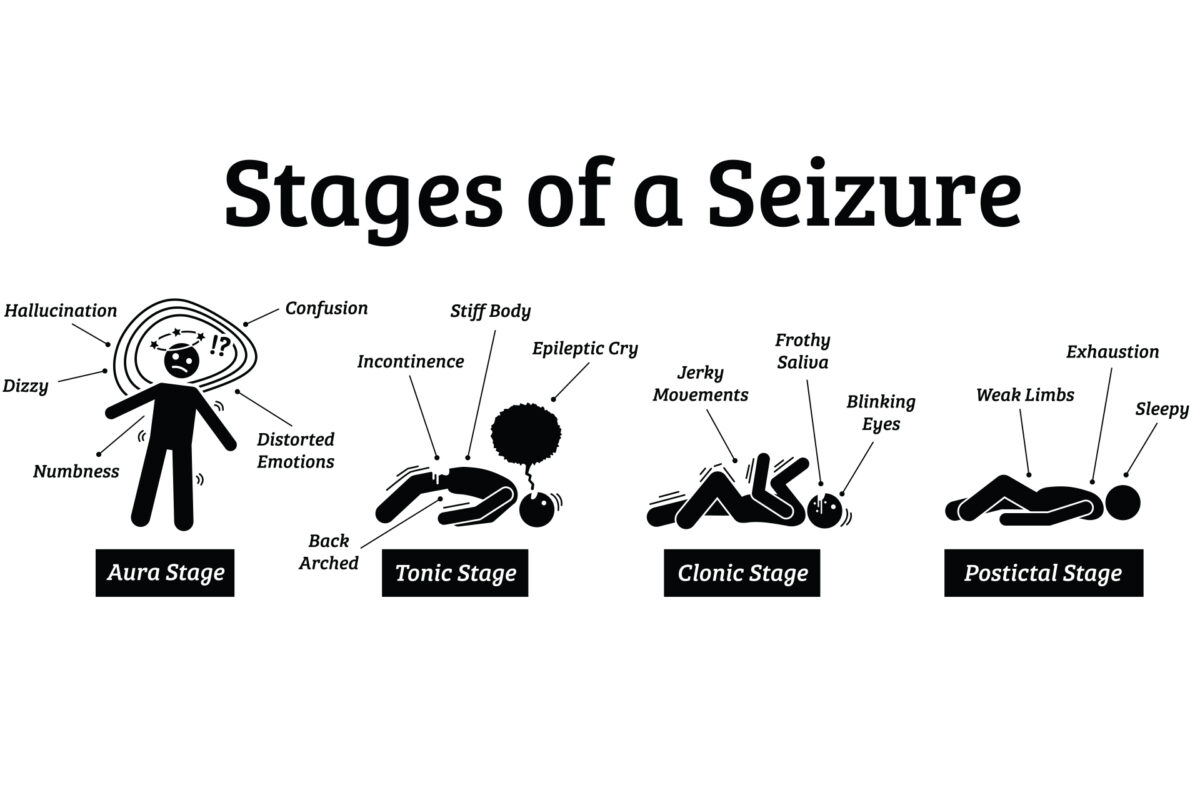
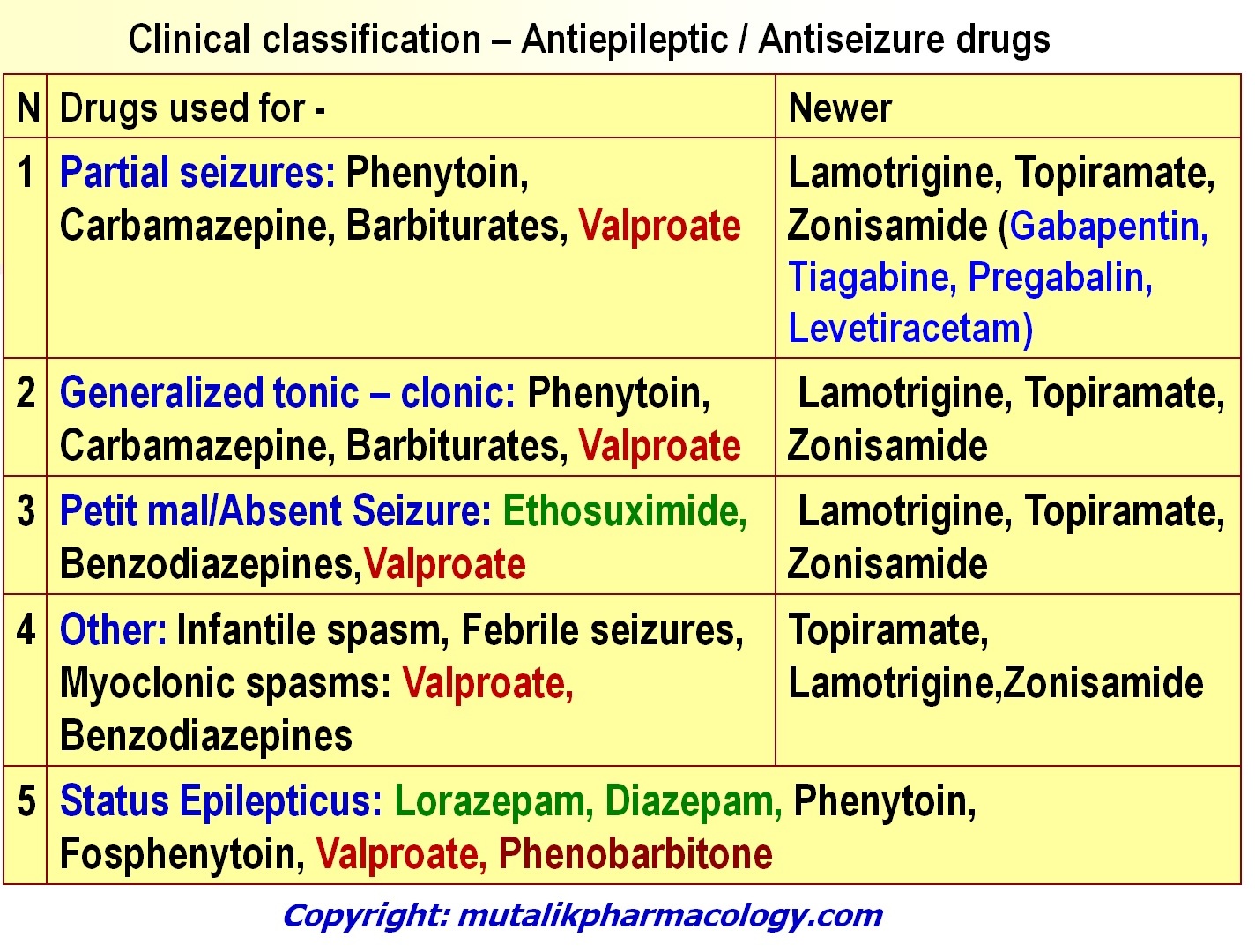
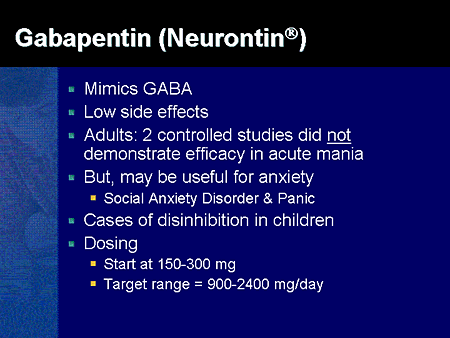
Gabapentin for Epilepsy User Reviews Brand names: Neurontin, Gralise, Gabarone, Fanatrex. Gabapentin has an average rating of 7.3 out of 10 from a total of 16 reviews for the treatment of Epilepsy. 69% of reviewers reported a positive experience, while 19% reported a negative experience. Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant used to treat epilepsy and can also treat pain from shingles. Get a detailed overview of gabapentin, including possible side effects of gabapentin, recommended dosages for gabapentin, potential gabapentin interactions, and what gabapentin is used for. Gabapentin for partial seizures: According to the guidelines from the American Epilepsy Society, clinicians might consider gabapentin as a potential option for patients aged 60 and older with new-onset focal epilepsy, as it could be similarly effective and better tolerated compared to carbamazepine. Gabapentin is used to control seizures, to treat nerve pain that can happen after having had shingles, and to treat a condition called restless legs syndrome. In addition to these FDA-approved uses, doctors sometimes prescribe gabapentin off-label. Research supports the use of the anticonvulsants gabapentin (Gralise, Neurontin, Horizant) and pregabalin (Lyrica) to help relieve pain caused by damaged nerves. Both gabapentin and pregabalin are particularly effective in the treatment of postherpetic neuralgia, diabetic neuropathy and pain caused by a spinal cord injury. Only 25.3% presented with GTCs alone, a lesser amount than described in epidemiologic studies that principally comprise younger adults. 40 GilNagel A 41 in a study of assessment of gabapentin in the treatment of epilepsy in the elderly showed that gabapentin has advantageous pharmacokinetic characteristics such as lack of hepatic metabolism, no Gabapentin is used to help control partial seizures (convulsions) in the treatment of epilepsy. This medicine cannot cure epilepsy and will only work to control seizures for as long as you continue to take it. Gabapentin is also used to manage a condition called postherpetic neuralgia, which is pain that occurs after shingles. According to the Australian Medicines Handbook (AMH), Gabapentin is indicated to treat focal (partial) seizures not controlled adequately by other antiepileptic drugs. Gabapentin is an antiepileptic, or drug that prevents seizures. It is believed that Gabapentin works by inhibiting nerve signals. How do I take it? Focal (partial) epilepsy: Focal epilepsy, also known as partial epilepsy, originates from a specific region of the brain. Seizures in focal epilepsy are characterized by abnormal electrical discharges localized in a specific area, which may result in motor, sensory, autonomic, or cognitive symptoms. Focal seizures can be Currently, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) recommends gabapentin use for postherpetic neuralgia in adults, and as an adjunctive therapy in the treatment of partial onset seizures with and without secondary generalisation in adults and paediatric patients three years of age or older with epilepsy (U.S. Food and Drug Administration 201 Background: Epilepsy is one of the most common chronic neurological disorders, affecting more than 50 million people globally. In this review we summarised the evidence from randomised controlled trials of gabapentin used as monotherapy for the treatment of focal epilepsy, both newly diagnosed and drug-resistant, with or without secondary generalisation. Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant primarily used to treat epileptic seizures, but it can also be prescribed off-label to treat a range of mental disorders. Gabapentin has efficacy as an add-on treatment in people with drug-resistant focal epilepsy, and seems to be fairly well-tolerated. However, the trials reviewed were of relatively short duration and provide no evidence for the long-term efficacy of gabapentin beyond a three-month period. The results Gabapentin - Brand name: Neurontin. Read about how gabapentin treats epilepsy and nerve pain and how to take it. Gabapentin (GA ba PEN tin) has been approved by the FDA as adjunctive therapy in the treatment of focal onset seizures, with and without secondary generalization, in pediatric patients 3 years and older with epilepsy. Gabapentin is a Pfizer-made medication for focal aware and impaired seizures. For more information, visit the Epilepsy Foundation online. However, a MEDLINE search using the search terms gabapentin and epilepsy, spanning back to the year 1986, produced numerous published reports from randomized, placebo-controlled and open-label trials, as well as case reports. These were reviewed to assess the range of dosing and titration schedules reported. Currently, the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) recommends gabapentin for use in postherpetic neuralgia in adults, and as an adjunctive therapy in the treatment of focal onset seizures with and without secondary generalisation in adults and paediatric patients three years of age or older with epilepsy , whilst the European Medicines Agency Gabapentin has efficacy as an add‐on treatment in people with drug‐resistant focal epilepsy, and seems to be fairly well‐tolerated. However, the trials reviewed were of relatively short duration and provide no evidence for the long‐term efficacy of gabapentin beyond a three‐month period. To help determine the potential place in therapy for gabapentin in the treatment of epilepsy in adults, we sought to identify and summarize studies of the clinical- and cost-effectiveness of gabapentin as well as recommendations from evidence-based guidelines.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |