Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
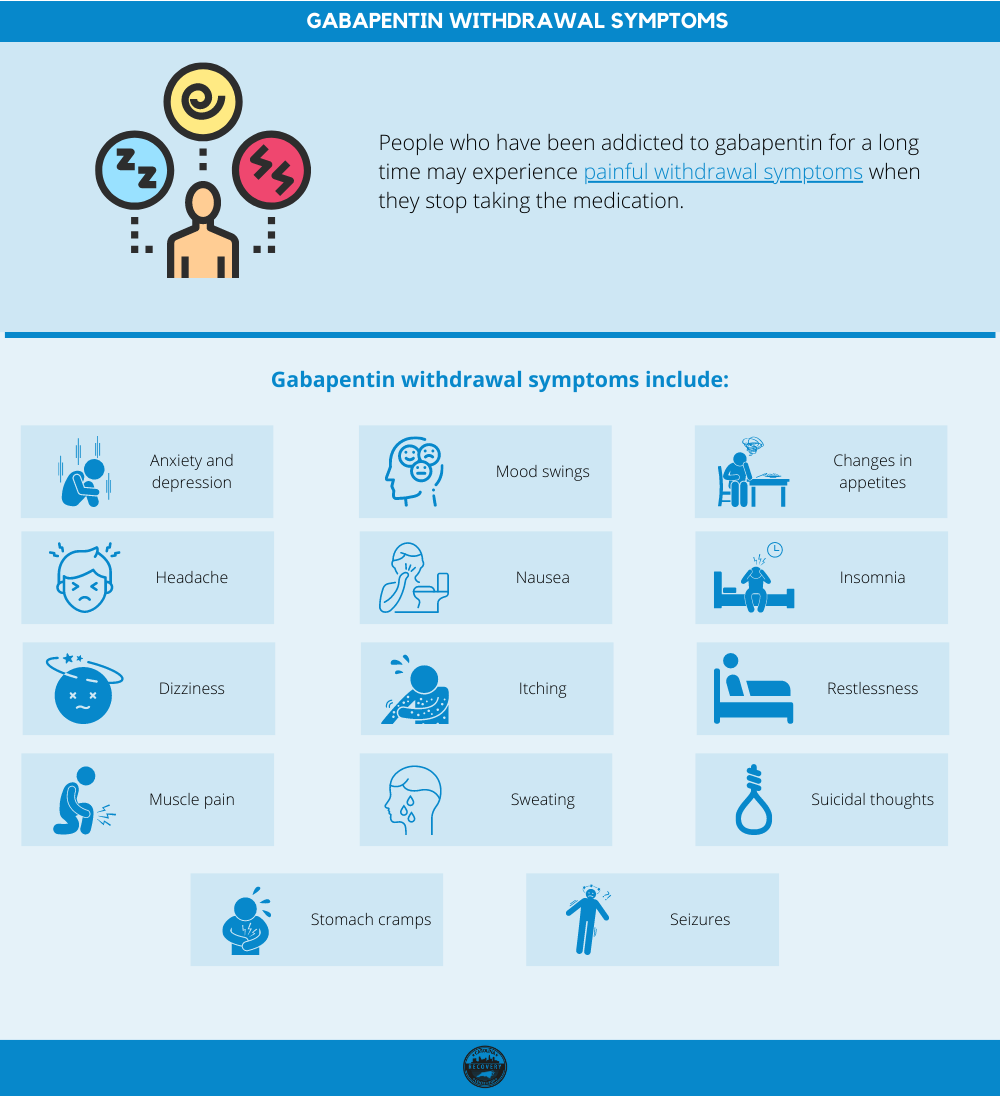
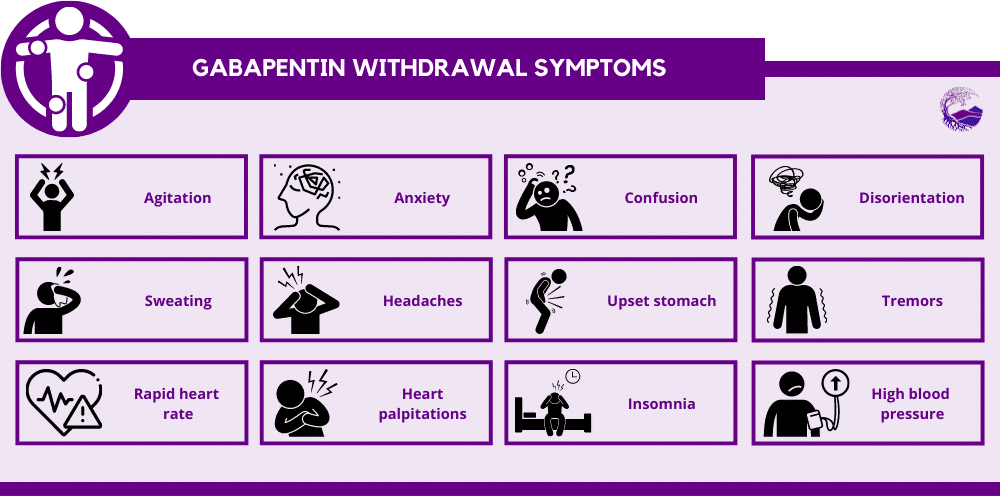
Gabapentin primarily functions as an anticonvulsant medication employed in the treatment of epilepsy. However, recent studies have shown its effectiveness as an adjunct treatment for opiate withdrawal. A study published in the Journal of Clinical Psychopharmacology evaluated the use of gabapentin. Add-on gabapentin with a dose of 1600 mg/d is effective in reducing some of the withdrawal symptoms in patients addicted to opiate undergoing methadone-assisted detoxification. Yes, Neurontin works wonders for withdrawal of all sorts- including opes, benzos, and alcohol withdrawal. But you need to take it safely and responsibly or you will damage your body. Also, just FYI, I have taken Neurontin for 3 or 4 days consecutively before to help me get over both alcohol and benzo withdrawals only to have withdrawal from Opioid addicts may take gabapentin to hold off withdrawal symptoms when a drug of choice isn’t available, or to attempt at-home detox from opioid drugs. Oral use of the medication in pill form is most common, but the medications can also be crushed or snorted, chewed, or injected. Despite the effect of pregabalin and gabapentin on controlling some of the withdrawal symptoms, no significant differences were reported among the 3 groups. Conclusions: Dosages of 450 mg/d of pregabalin and 1600 mg/d of gabapentin are not significantly superior to placebo in controlling opiate withdrawal symptoms. I too have experience with taking gabapentin for my opiate withdrawals. Yes, indeed it does work by helping alleviate most of the horrid withdrawals that come from opiate discontinuation. But, you must be careful when using Gabapentin for you can become addicted or dependent on Gabapentin itself. 4g of gabapentin and 12mg of imodium takes away 90% of physical opiate withdrawal and 90% of mental opiate withdrawal for me personally. Also, Gabapentin is a very safe drug. I've taken upwards of 12 grams a day and never have any adverse effects except for a little bloating and a lot of appetite increase. Gabapentin, at a dose of 600 mg three times a day, was evaluated as an add-on medication to a standard detoxification regime in seven heroin dependent individuals undergoing outpatient opiate withdrawal treatment. Benefits of Gabapentin for Opiate Withdrawal. Gabapentin has been found to be effective in relieving opiate withdrawal symptoms. When individuals stop using opiates, they often experience a range of physical and psychological symptoms as their body adjusts to the absence of the drug. If you are finding it difficult to stop using opiates or manage the gabapentin for opiate withdrawal process, reach out to Resurgence Behavioral Health at 877-855-3470 to discover more about our detox programs or to begin your treatment right away. Make small dose changes, which are less likely to cause withdrawal symptoms and will build confidence in the tapering process. Where possible engage the person in deciding which dose they would like to reduce initially, i.e. morning / evening dose. Dose reductions can be made weekly (except in the instance of transdermal fentanyl), two weekly or Using a withdrawal easing medicine such as Gabapentin accelerates the process of getting the opiate drug out. It makes all the uncomfortable effects vanish. Gabapentin is a gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) analogue that was created for the treatment of epilepsy, pain relief, and neuropathic pain. Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant medication that may help ease opioid withdrawal and, as a result, help treat OUD. But is it the best option for you? Let’s break it down. Studies show mixed results regarding gabapentin’s effectiveness in combating opioid withdrawal. • Gabapentin start at 100 to 300 mg and titrate to 1800 to 2100 mg divided in2 to 3 daily doses* – Can help reduce withdrawal symptoms and help with pain, anxiety, and sleep Opioid withdrawal is an important clinical syndrome that can cause considerable discomfort, perpetuate drug-seeking behaviour, and preclude engagement in appropriate treatment in patients with opioid use disorder and chronic, non-cancer pain (CNCP). 2 Although conventionally considered non-life threatening, the clinical manifestations of opioid Yes, Gabapentin can help with opiate withdrawal symptoms. It is a medication that is commonly used to treat seizures, nerve pain, and hot flashes. Gabapentin helps to reduce the cravings for opiates, as well as reducing the severity of the withdrawal symptoms. Preliminary evidence indicates that gabapentin might effectively attenuate opiate withdrawal symptoms such as: body aches and pain, restlessness, and restless leg syndrome. For this reason, a subset of patients undergoing opiate detoxification may receive an off-label prescription for gabapentin to help manage discontinuation symptoms. Gabapentin is an antiepileptic drug shown to be effective in the treatment of pain disorders and appears to be useful as well for several psychiatric disorders, including bipolar disorder, anxiety disorders, alcohol withdrawal and cocaine dependence. Gabapentin, at a dose of 600 mg three times a day, was evaluated as an add-on medication to a Opiates and synthetic opioids are some of the most addictive drugs in the world. Opiate withdrawal refers to the physical and mental symptoms a former user experiences when they stop taking opiates, typically after their body has become adjusted to taking a certain amount of the drug on a regular schedule. Chronic opiate misuse can Data from early clinical trials showed that gabapentin could reduce withdrawal symptoms and, when compared with placebo, was associated with reductions in opioid use. 1 However, more recent studies and research has demonstrated that gabapentin did not produce better results than a placebo when used for withdrawal symptoms. 1
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |