Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
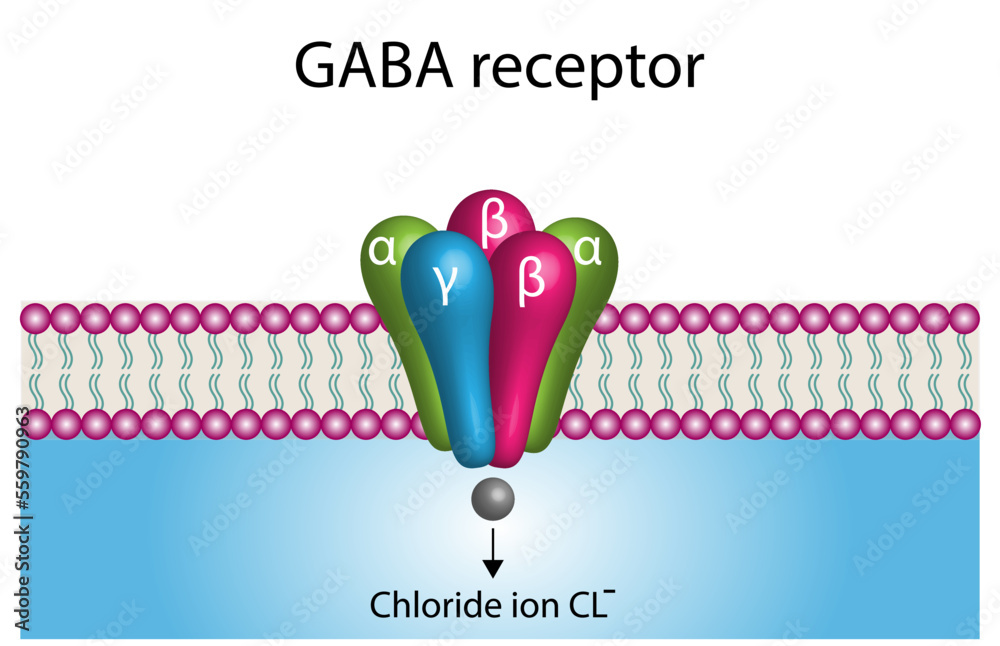 |  |
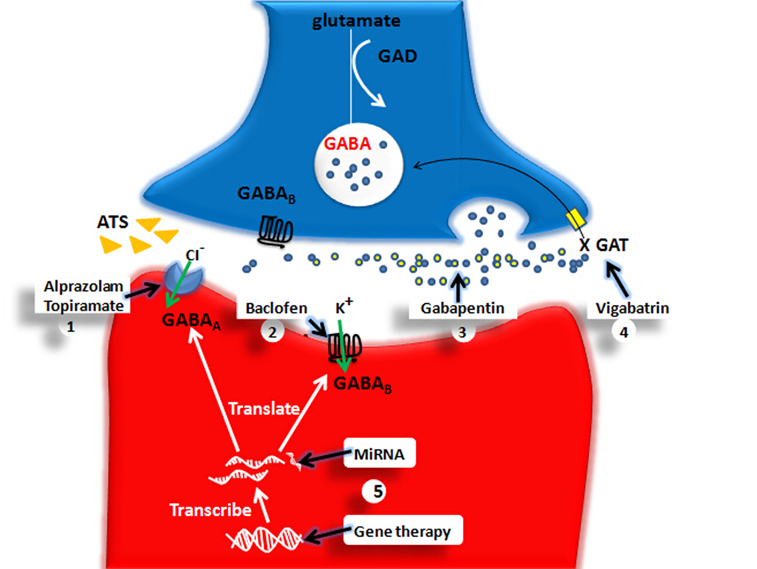
GABA is a naturally occurring neurotransmitter, while gabapentin is a synthetic medication designed to mimic GABA’s effects. GABA is available as a supplement, whereas gabapentin requires a prescription and is used for specific medical conditions like epilepsy and neuropathic pain. Gabapentin is used to control seizures, to treat nerve pain that can happen after having had shingles, and to treat a condition called restless legs syndrome. In addition to these FDA-approved uses, doctors sometimes prescribe gabapentin off-label. Gabapentin (3-cyclohexyl-GABA) is designed as a lipophilic analogue of GABA for blood-brain barrier penetration and closely resembles pregabalin. Although gabapentin does not directly modify GABA-A receptor function, it may indirectly increase tonic inhibition via enhanced expression of extrasynaptic receptors in specific brain regions Gabapentin (Neurontin, Gralise, Horizant) is a medicine used to treat partial seizures, nerve pain from shingles and restless leg syndrome. It works on the chemical messengers in your brain and nerves. The chemical structure of gabapentin (Neurontin) is derived by addition of a cyclohexyl group to the backbone of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA). Gabapentin prevents seizures in a wide variety of models in animals, including generalized tonic-clonic and partial seizures. Gabapentin has no activity at Type: Anticonvulsants; GABA analog; Dosage Forms: capsule, tablet, oral solution 250mg/5mL; Common Trade Names: Neurontin, Gralise; Adult Dosing Partial Seizures. Adjunctive therapy for partial seizures with or without secondary generalization; Initial: 300mg PO q8hr; May increase up to 600mg PO q8hr; Post herpetic neuralgia. Day 1: 300mg PO qDay Gabapentin是美国Warner-Lanbert公司首先开发的抗癫痫药,于1993年首次在英国上市。加巴喷丁是一种新颖的抗癫痫药,它是 γ -氨基丁酸(GABA)的衍生物,其药理作用与现有的抗癫痫药不同,最近研究表明加巴喷丁的作用是改变GABA代谢的。加巴喷丁在各种动物模型中 GABA is a naturally occurring neurotransmitter in the brain that inhibits or slows down nerve activity, helping to reduce anxiety and promote relaxation. On the other hand, Gabapentin is a medication that is structurally similar to GABA but does not directly bind to GABA receptors. Gabapentin is approved to prevent and control partial seizures, relieve postherpetic neuralgia after shingles and moderate-to-severe restless legs syndrome. Learn what side effects to watch for, drugs to avoid while taking gabapentin, how to take gabapentin and other important questions and answers. The differences between GABA and gabapentin lie in their mechanisms of action in the brain – GABA targets GABA receptors whereas gabapentin interacts with voltage-gated calcium channels. Structure of GABA: gabapentin and pregabalin. 10. Pharmacokinetics. The actions of gabapentinoids are mainly at an intracellular site and require active uptake. They undergo facilitated transport across cell membranes through system l-amino acid transporters (LAT) as both drugs are structurally similar to the amino acid leucine. Research regarding gabapentin's effects on GABA and glutamate synthetic and metabolizing enzymes reveals a complex pattern of activity and provides an incomplete explanation for its anticonvulsant effects. Gabapentin is structurally related to GABA. However, it does not bind to GABA A or GABA B receptors, and it does not appear to influence synthesis or uptake of GABA. High affinity gabapentin binding sites have been located throughout the brain; these sites correspond to the presence of voltage-gated calcium channels specifically possessing the Gabapentin, sold under the brand name Neurontin among others, is an anticonvulsant medication primarily used to treat neuropathic pain and also for partial seizures [10][7] of epilepsy. It is a commonly used medication for the treatment of neuropathic pain caused by diabetic neuropathy, postherpetic neuralgia, and central pain. [11] . GABA and gabapentin are often mistakenly used interchangeably, but they are not the same. GABA is an amino acid supplement and neurotransmitter, while gabapentin is a prescription medication. While practitioners may confuse the two, it’s important to understand their differences. We would like to show you a description here but the site won’t allow us. Both GABA and gabapentin are similar to each other but they have their differences. The first point of difference is their structural make-up. Gabapentin is a GABA analog, meaning that it looks very similar structurally but it is not completely the same. 2. Was ist GABA 3. Was ist Gabapentin 4. GABA gegen Gabapentin in tabellarischer Form 5. Zusammenfassung - Gaba gegen Gabapentin . Was ist GABA? Der Begriff GABA ist kurz für Gamma-Aminobuttersäure. Es ist ein Haupt inhibitorischer Neurotransmitter, der bei der Entwicklung und Reifung des Zentralnervensystems des Säugetiers nützlich ist. Gabapentin, a novel anticonvulsant and analgesic, is a gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) analogue but was shown initially to have little affinity at GABA(A) or GABA(B) receptors. It was recently reported to be a selective agonist at GABA(B) receptors containing GABA(B1a)-GABA(B2) heterodimers, although Gabapentin (Neurontin) Carisoprodol (Soma) Diazepam (Valium) Alprazolam (Xanax) Lorazepam (Ativan) There are also herbs and amino acids available without a prescription that can be used as GABA surrogates: Valerian root. Ashwagandha. Taurine. Brahmi. Bacopa. Glutamine: GABA’s Precursor
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |