Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | 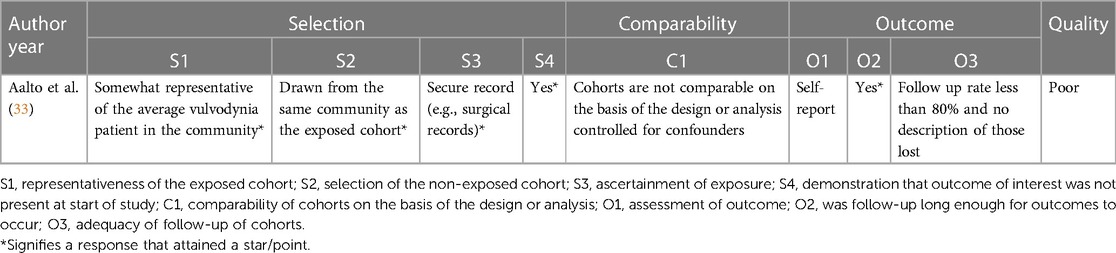 |
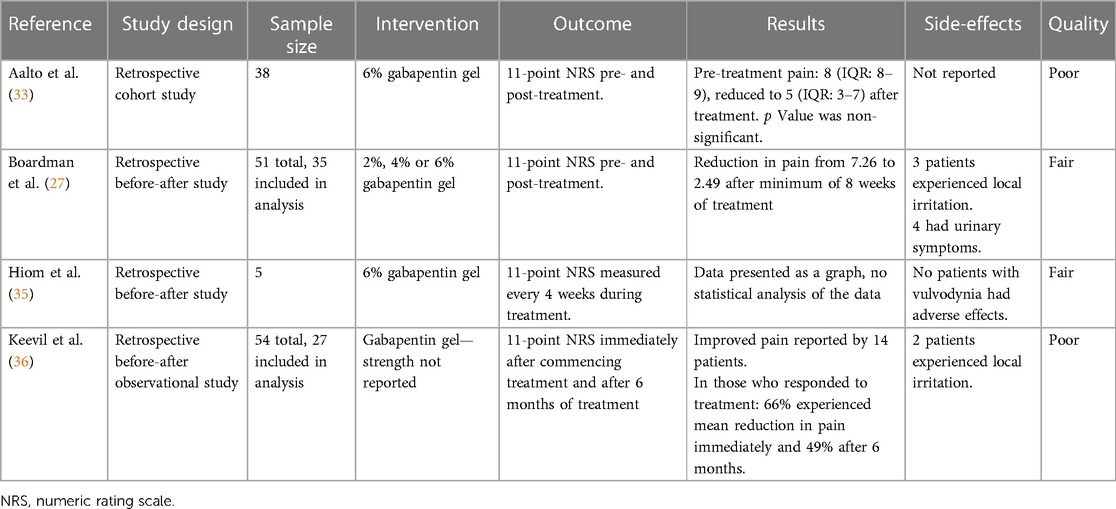
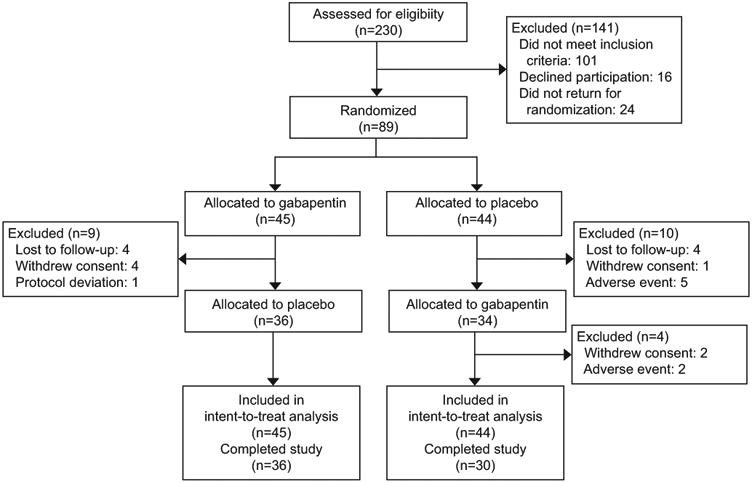
Application of topical gabapentin (10% gel) significantly reduced allodynia and vulvodynia in a streptozotocin-induced diabetic neuropathic rat model . An analgesic effect was also observed in a rabbit model in which ocular pain was ameliorated following application of gabapentin eye drops ( 40 ). Vulvodynia means ongoing pain in the vulva (the female genital area) when there is Lidocaine cream and ointment can be bought without a Gabapentin. This is an We evaluated the efficacy of gabapentin, in an extended release formulation, in women diagnosed with localized provoked vulvodynia, defined as superficial vulvar vestibular pain that is provoked by touch, in a demographically diverse sample. Topical 0.05% cream, decreasing dose from twice per day to twice per week for 4 months: Anti-convulsant agents: 2–6% topical cream, 8 weeks: Gabapentin: Highest tolerable oral dose between 1200 and 3000 mg per day for 8 weeks: Oral gabapentin, 1200–3000 mg per day for 8 weeks: Anti-inflammatory agents In a retrospective chart review, 28 gabapentin cream reduced vulvar pain in PV and generalized vulvodynia pre‐ to post‐treatment. Gabapentin cream must be obtained through a compounding pharmacy. Efficacy of gabapentin cream needs to be tested in future RCTs. Tricyclic antidepressants should be considered for the treatment of vulvodynia. Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors and gabapentin (Neurontin) should be considered for symptomatic relief of Application of topical gabapentin (10% gel) significantly reduced allodynia and vulvodynia in a streptozotocin-induced diabetic neuropathic rat model . An analgesic effect was also observed in a rabbit model in which ocular pain was ameliorated following application of gabapentin eye drops ( 40 ). The diagnosis of vulvodynia is clinical A team approach may be necessary to address the different com-ponents of vulvodynia. A lead clinician should triage patients and consider referral to other health professionals who have a role in vulvodynia management, e.g. psychosexual medicine, physiotherapy, pain management teams We begin by adding Neurontin and Elavil for sleep in those with Vulvodynia, but these sometimes cause unacceptable side effects. This new study showed that putting the Neurontin (Gabapentin) in a topical cream decreased pain by an average of 2/3, and decreased pain by over 50% in 80% of the women. Focal points • Some patients cannot tolerate oral gabapentin for neuropathic pain due to significant central side effects • Topical gabapentin, an NHS Pharmaceutical unlicensed 'special', has been used as a treatment alternative • Significant reduction in pain scores after treatment were demonstrated (n = 23) with no reported side effects • Topical gabapentin is an alternative Gabapentin. There is a lot of good research out there on the topical use of gabapentin 2-6%. In a study that appeared in Obstetrics & gynecology in 2008, women with vulvodynia were treated with 2% to 6% gabapentin. Vulvodynia is defined by the International Society for the Study of Vulvovaginal Disease (ISSVD) as ‘chronic vulvar discomfort, most often described as burning pain, occurring in the absence of relevant findings or a specific, clinically identifiable, neurologic disorder’. 4 It is diagnosed when other causes of vulvar pain have been excluded (Table 1) or when pain persists despite adequate Results: Between January 2001 and December 2006, 51 women with vulvodynia (19 or 37% with generalized vulvodynia, 32 or 63% with localized) were treated with 2% to 6% gabapentin. After a minimum of 8 weeks of therapy, the mean pain score among the 35 evaluable women was significantly reduced from 7.26 to 2.49 (mean change -4.77, 95% confidence For treating vulvodynia, gabapentin works by inhibiting pain signals that are sent from damaged neurons. The retrospective study that was published in Obstetrics and Gynecology showed that gabapentin cream was well tolerated and effective for women experiencing vulvodynia. Although gabapentin is recommended and commonly prescribed for vulvodynia, its value in such cases is usually associated with complaints that have neuropathic components, such as dynamic allodynia. Multiple treatments have been used for vulvodynia, in-cluding vulvar care measures; topical, oral, and injectable medications; biofeedback; physical therapy; low-oxalate diet and calcium citrate supplementation; and surgery (Figure 2). Newer treatments being used include acupunc-ture, hypnotherapy, nitroglycerin, and botulinum toxin. Twenty-five trials explored the use of oral and topical medications in the treatment of vulvodynia. Data Synthesis: Vulvodynia is a poorly understood disease with an unknown etiology. Oral tricyclic antidepressants and gabapentin continue to be the most commonly used treatments for vulvodynia pain. Vulvodynia - 4 - o Vulvodynia pain is often described as burning, but it may also feel sharp, pressure, aching, or something else. • Where is it located? o Your pain may include the entire vulva (generalized vulvodynia) or it may only be in a smaller specific area (localized vulvodynia). • What seems to cause your pain or make it worse? Gabapentin 6% Vaginal Gel is a gel-like semisolid formulation, specifically designed for easy and controlled application in the vaginal area. This topical medication is primarily used to treat vulvodynia, a chronic pain condition of the vulva. Pelvic floor hypertonicity and vulvodynia are frequently present concomitantly. 31,32 Baclofen’s muscle relaxation actions and decreased adverse effect profile make it a feasible treatment option. 33,34 One study found baclofen an effective treatment when combined in a cream with amitriptyline. 27 Additionally, a case report used a compounded
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |