Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
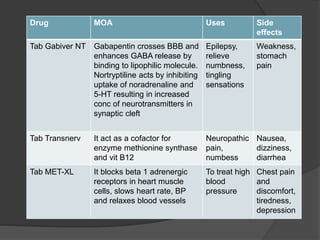 |  |
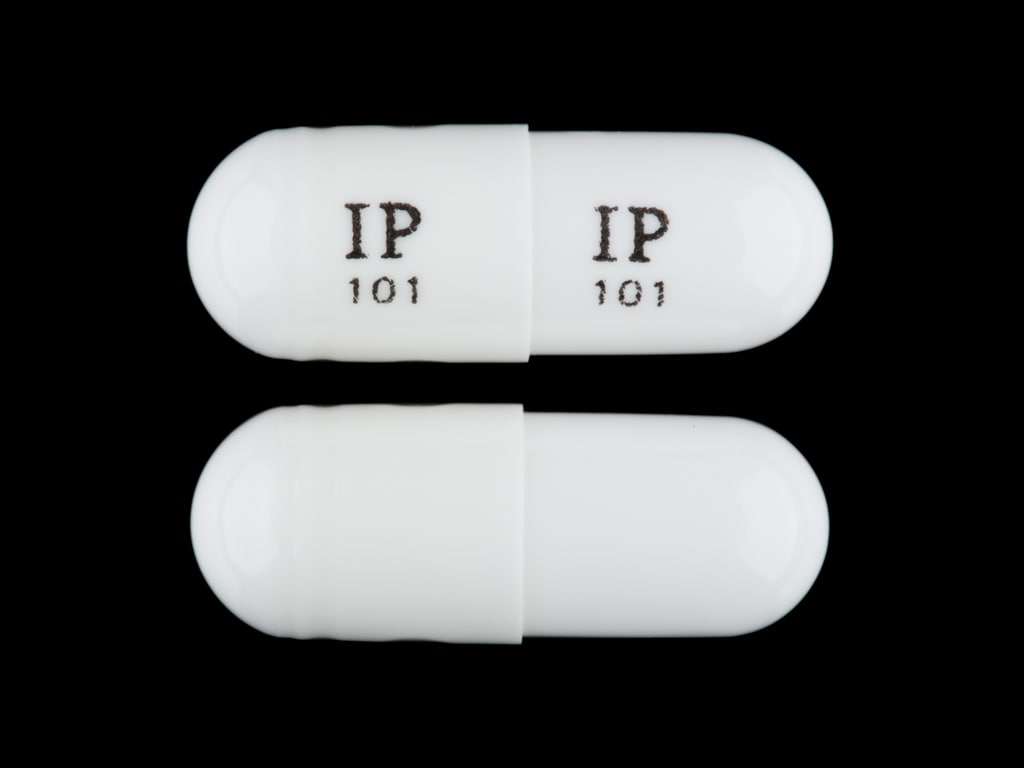
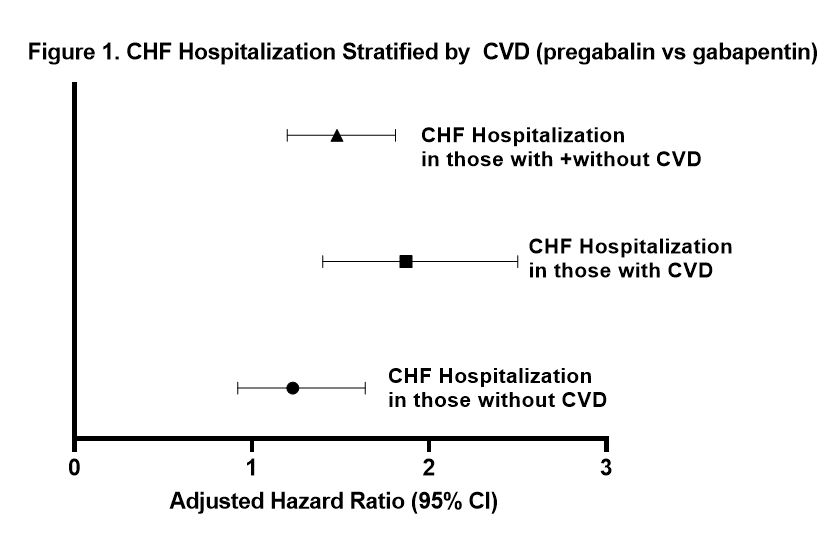
With rapidly increasing usage of gabapentin for approved and off-label indications, it is important to identify unintended adverse effects of this drug as they are considered safe alternatives to opioids. New-onset atrial fibrillation could be induced by gabapentin in young individuals. Moreover, the use of gabapentin and pregabalin have increased in the USA from 1.2% of adults in 2002 to 3.9% in 2015, with the largest increases in older adults, those with diabetes and those with at least 5 comorbidities. In this focused review, we discuss the cardiovascular safety of gabapentin and pregabalin. Heart Failure Gabapentin is available as Gralise, Neurontin, and generic gabapentin in the following dosage forms that are taken by mouth. 100 mg, 300 mg, 400 mg oral capsules 250 mg/5 mL oral solution For healthcare professionals. Applies to gabapentin: compounding powder, oral capsule, oral solution, oral tablet, oral tablet extended release. General adverse events. The most common adverse reactions associated with the use of this drug were dizziness, somnolence, and peripheral edema. GD-Gabapentin: Gabapentin belongs to the class of medications called anti-epileptics. It is used in combination with other seizure control medications to manage and prevent seizures associated with epilepsy. Gabapentin does not cure epilepsy and only works to control seizures as long as the medication is taken. Gabapentin works by affecting the transmission of nerve signals in the brain. Gabapentin and pregabalin are widely prescribed to elderly people, but data on their pharmacokinetics, safety, and efficacy in this population are scarce. Neurological adverse effects are common. Atrial fibrillation (AF) associated with their use AFib also increases your chances for heart failure, a condition in which the heart muscle fails to pump enough blood to meet your body’s needs. Taking NSAIDs can lead to heart failure or make The evidence suggests that gabapentin can lower heart rate, particularly in acute settings such as anesthesia induction and in hypertensive models. Chronic administration also appears to suppress cardiovascular function, leading to bradycardia. Rapid and irregular heartbeat is usually caused by suddenly stopping gabapentin usage or from misusing the drug for recreational use. Generally, gabapentin is safe for use by adults and children over the age of 6 years old. Oral and intravenous gabapentin can markedly attenuate blood pressure (BP) in hypertensive rats. The nucleus tractus solitarii (NTS) is the primary integrative center for cardiovascular control and other autonomic functions in the central nervous system. duced heart failure. J Amer Coll Cardiol Mar,79 (9_Supplement). 2231; 2022. 5. Tellor KB, Ngo-Lam R, Badran D, Armbruster AL, Schwarze MW. A rare case of a gabapentin-induced cardiomyopathy. J Clin Pharm Ther. 2019; 44: 644-646. 6. Wynn E, Biskupiak J, K Kibum, Munger MA. Pregabalin use in-creases the risk of acute heart failure in patients The goal was to determine whether the prescription of gabapentin and pregabalin in patients with fibromyalgia increases the risk of adverse cardiovascular events, including peripheral vascular disease, strokes, myocardial infarcts, heart failure, deep venous thrombosis, and pulmonary embolism. In patients with diabetic neuropathy who were prescribed gabapentin and pregabalin, there is an increased risk for heart failure, myocardial infarction, peripheral vascular disease, stroke, deep venous thrombosis, and pulmonary embolism with long-term use. Our findings suggest that increased risk fo Yes, gabapentin can cause heart palpitations. Some people have experienced their heart beating too hard and fast after taking gabapentin. This side effect is most commonly experienced after an increase or decrease in dose, or when you start on a dose which is too high for you. It is also experienced while tapering off gabapentin. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Gabapentin and the Heart 1. Can Gabapentin cause heart palpitations? While not commonly reported, some individuals may experience palpitations (a feeling of a rapid or irregular heartbeat) while taking gabapentin. This may be linked to anxiety or other side effects and is not necessarily a direct Learn the differences and similarities between gabapentin and an opioid medication. 1. Dizziness is the No. 1 side effect of gabapentin. In studies, almost 30% of people taking gabapentin for postherpetic neuralgia, and over 15% of people taking it for seizures, experienced dizziness. Dizziness is similarly common with Horizant. Gabapentin is a commonly used medication used as an anti-convulsant or analgesic. The well-known side-effects of gabapentin are dizziness, drowsiness and fatigue. In rare cases, it can lead to development of new onset congestive heart failure (CHF) or decompensation of pre-existing CHF. Heart palpitations is reported as a side effect among people who take Gabapentin (gabapentin), especially for people who are female, 60+ old, have been taking the drug for < 1 month also take Humira, and have Multiple sclerosis. Can gabapentin cause heart palpitations? Yes, abnormal heartbeats or heart palpitations are a possible side effect of gabapentin. If you experience these, consult your doctor immediately. Case reports and observational studies have showed that gabapentin can be associated with increased risk of atrial fibrillation. However, all the evidence is concentrated in patients older than 65 years old with comorbidities that predispose them to the development of arrhythmias.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |